The Student Loan Crisis: Economic Ripple Effects And Consequences
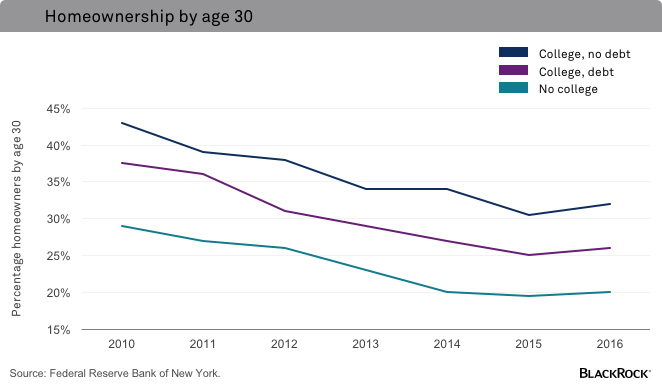
Table of Contents
Individual Financial Hardship and the Student Loan Crisis
The weight of student loan debt significantly impacts the financial well-being of individuals, delaying life milestones and creating long-term financial instability.
Delayed Life Milestones
The crushing burden of student loan repayments often forces borrowers to postpone major life decisions:
- Difficulty in saving for a down payment on a house: High monthly loan payments leave little room for saving, making homeownership a distant dream for many. This contributes to a decreased homeownership rate among younger generations.
- Postponement of marriage and starting a family: Financial constraints due to student loan debt often lead couples to delay marriage and family planning, impacting demographic trends and societal structures.
- Inability to pursue higher education or professional development opportunities: The need to repay loans can prevent individuals from pursuing further education or professional development, limiting career advancement and earning potential. This perpetuates a cycle of financial hardship.
- Increased stress and mental health issues related to overwhelming debt: The constant pressure of student loan debt contributes significantly to stress, anxiety, and depression, impacting overall mental and physical health.
Impact on Credit Scores and Future Borrowing
Defaulting on student loans, even partially, can have catastrophic consequences:
- Defaulting on student loans severely damages credit scores: This makes it difficult to secure loans for essential purchases or investments in the future.
- Difficulty securing loans for cars, mortgages, or business ventures: A damaged credit score severely limits access to credit, hindering major life purchases and entrepreneurial pursuits.
- Higher interest rates on future borrowing opportunities: Even when credit is available, individuals with damaged credit scores face significantly higher interest rates, exacerbating their financial burden.
- Limited access to financial products and services: Many financial institutions will refuse service to those with poor credit, further limiting opportunities for financial stability.
Reduced Consumer Spending Power
Student loan debt significantly reduces disposable income:
- Significant portion of income allocated to loan repayments: A large chunk of monthly income is diverted towards loan repayment, leaving little for other expenses.
- Reduced disposable income impacting overall consumer spending: This decrease in consumer spending can lead to slower economic growth across various sectors.
- Slowed economic growth due to decreased consumer demand: Reduced consumer spending creates a ripple effect, impacting businesses and potentially slowing overall economic expansion.
- Potential for a long-term negative impact on economic activity: This cycle of reduced spending and economic slowdown can have long-lasting and detrimental effects on the economy.
Macroeconomic Effects of the Student Loan Crisis
The student loan crisis isn't just a personal problem; it has significant macroeconomic consequences:
Impact on the Housing Market
The student loan crisis significantly affects the housing market:
- Reduced homeownership rates due to student loan debt: Many young adults are unable to afford a down payment or manage monthly mortgage payments alongside student loan repayments.
- Lower demand for housing impacting construction and related industries: Decreased demand leads to slower growth in the construction sector and related industries.
- Stagnation in the real estate market: Reduced demand can create a stagnant real estate market, impacting property values and investment opportunities.
- Potential for a decrease in property values: A prolonged period of low demand could potentially lead to a decline in property values, affecting homeowners and the overall economy.
Effect on Small Business Growth
Student loan debt hampers entrepreneurial activity:
- Reduced entrepreneurial activity as individuals prioritize debt repayment: The burden of loan repayments discourages individuals from starting their own businesses, reducing job creation and economic innovation.
- Limited access to capital for small business expansion: Existing business owners burdened with student loan debt may struggle to secure additional funding for expansion.
- Slower economic growth due to reduced business formation: The decrease in new business formation slows economic growth and limits job creation.
- Potential for job creation stagnation: A lack of entrepreneurial activity can result in stagnation in job creation and limit economic dynamism.
Strain on the National Budget
The student loan crisis puts a strain on government resources:
- Increased government spending on student loan programs: Government expenditure on student loan programs continues to rise, creating a significant financial burden on taxpayers.
- Potential for rising tax burdens to cover loan defaults: Rising loan defaults require increased government spending to cover losses, potentially leading to higher taxes for citizens.
- Reduced government spending in other crucial areas: Increased spending on student loans might force cuts in other essential public services.
- Long-term fiscal sustainability concerns: The growing cost of student loan programs poses a long-term threat to the fiscal sustainability of the nation.
Potential Solutions and Policy Recommendations to Address the Student Loan Crisis
Addressing the student loan crisis requires a multi-faceted approach:
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Making repayment plans more flexible and affordable is crucial:
- Making repayment plans more flexible and affordable: Adjusting repayment plans based on income allows borrowers to manage their debt more effectively.
- Ensuring that loan payments are manageable for borrowers: This helps reduce the risk of default and allows individuals to focus on other financial goals.
- Reducing the risk of default and improving overall economic outcomes: More manageable repayment plans lead to fewer defaults, benefiting both individuals and the economy.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
Targeted loan forgiveness can provide relief, but requires careful consideration:
- Targeted forgiveness for specific professions or demographics: Forgiveness programs could focus on individuals working in public service or those from low-income backgrounds.
- Evaluating the potential economic impact of large-scale forgiveness: A careful analysis of the economic implications is necessary before implementing widespread forgiveness.
- Exploring equitable and effective solutions to alleviate debt burdens: The design of loan forgiveness programs should be equitable and efficient in delivering relief to those most in need.
Addressing the Root Causes of Rising Tuition Costs
Tackling rising tuition costs is essential to prevent future crises:
- Increasing government funding for higher education: Increased government support could help keep tuition costs down and make education more accessible.
- Promoting transparency and accountability in college pricing: Greater transparency in college pricing would help students make informed decisions and potentially incentivize colleges to control costs.
- Encouraging alternative education models and affordability solutions: Exploring alternative models like online education and community colleges can provide more affordable pathways to higher education.
Conclusion
The student loan crisis poses a significant threat to individual financial well-being and the broader economy. The consequences are far-reaching, impacting consumer spending, the housing market, small business growth, and the national budget. Addressing this crisis requires a multi-pronged approach, including improved repayment plans, targeted loan forgiveness programs, and a concerted effort to curb rising tuition costs. We must act decisively to mitigate the damaging effects of the student loan crisis and build a more equitable and sustainable economic future. Understanding the complex web of student loan debt consequences is crucial to developing effective solutions and preventing further economic hardship. Take action today and learn more about resources available to manage your student loan burden.

Featured Posts
-
 Lawsuit Against Ryan Reynolds Justin Baldonis Lawyer Refuses To Back Down
May 28, 2025
Lawsuit Against Ryan Reynolds Justin Baldonis Lawyer Refuses To Back Down
May 28, 2025 -
 Kanye West Amidst Marriage Troubles New Woman Sparks Reconciliation Speculation In La
May 28, 2025
Kanye West Amidst Marriage Troubles New Woman Sparks Reconciliation Speculation In La
May 28, 2025 -
 Six Figure Euro Millions Prizes Claimed Locations Revealed In Ireland
May 28, 2025
Six Figure Euro Millions Prizes Claimed Locations Revealed In Ireland
May 28, 2025 -
 Jadwal Lengkap Km Lambelu Nunukan Makassar Sampai 25 Juni 2025
May 28, 2025
Jadwal Lengkap Km Lambelu Nunukan Makassar Sampai 25 Juni 2025
May 28, 2025 -
 Cok Cirkinsin Dedikten Sonra Adanali Ronaldo Dan Gelen Sasirtici Cevap
May 28, 2025
Cok Cirkinsin Dedikten Sonra Adanali Ronaldo Dan Gelen Sasirtici Cevap
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 48 Sati Krasnici Dpk O Formiranju Vlade Na Kosovu
May 29, 2025
48 Sati Krasnici Dpk O Formiranju Vlade Na Kosovu
May 29, 2025 -
 Formiranje Vlade Kosova Ultimatum Krasnica Dpk Kurtiju
May 29, 2025
Formiranje Vlade Kosova Ultimatum Krasnica Dpk Kurtiju
May 29, 2025 -
 50 Days Of Crypto Diplomacy How Pcc Transformed Pakistans Global Standing
May 29, 2025
50 Days Of Crypto Diplomacy How Pcc Transformed Pakistans Global Standing
May 29, 2025 -
 Rok Od 48 Sati Krasnici Dpk Spreman Za Formiranje Vlade
May 29, 2025
Rok Od 48 Sati Krasnici Dpk Spreman Za Formiranje Vlade
May 29, 2025 -
 Pakistans Rise In Global Crypto A 50 Day Pcc Success Story
May 29, 2025
Pakistans Rise In Global Crypto A 50 Day Pcc Success Story
May 29, 2025
