The Student Loan Crisis: How It Affects The Economy And What To Expect

Table of Contents
The Economic Ripple Effects of Mounting Student Loan Debt
The sheer volume of student loan debt has created a significant drag on the US economy, rippling through various sectors. The financial burden placed on borrowers significantly impacts their ability to participate fully in the economy.
Reduced Consumer Spending
Massive student loan payments drastically reduce disposable income, leading to a decline in consumer spending. This has a cascading effect on economic growth.
- Fewer major purchases: Borrowers often delay or forgo significant purchases like homes, cars, and even appliances, impacting various industries.
- Reduced retail sales: Lower consumer spending directly translates to reduced retail sales, affecting businesses and potentially leading to job losses.
- Negative impact on GDP: Decreased consumer spending contributes to a lower Gross Domestic Product (GDP), a key indicator of economic health. Studies have shown a direct correlation between high student loan debt and reduced GDP growth. For example, a recent study by [insert credible source and citation here] estimated that [insert statistic about GDP reduction].
Impact on the Housing Market
Student loan debt significantly affects homeownership rates and the broader housing market.
- Mortgage difficulties: High student loan payments can make it challenging for borrowers to qualify for mortgages, delaying or preventing homeownership.
- Delayed home buying: Many young adults postpone buying a home due to the burden of student loan repayments, impacting the demand side of the housing market.
- Potential impact on property values: Reduced demand can potentially affect property values in certain areas, though this effect is complex and depends on other market factors. The National Association of Realtors [insert citation here] has noted [insert relevant statistic or observation].
Delayed Major Life Decisions
The financial strain of student loan debt often leads to delays in major life milestones.
- Delayed marriage and family formation: The financial burden can deter individuals from getting married or starting a family, impacting birth rates and demographic trends.
- Decreased savings rates: The need to prioritize loan repayments often limits the ability to save for retirement or other long-term goals. Data from the Federal Reserve [insert citation here] indicates [insert relevant statistic on savings rates among borrowers].
- Limited investment opportunities: The limited disposable income restricts investment opportunities, hindering wealth accumulation and future economic participation.
The Role of Government Policies in the Student Loan Crisis
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the student loan landscape. While intended to increase access to higher education, these policies have also contributed to the current crisis.
Government Loan Programs and their Effectiveness
Government student loan programs, while aiming to provide access to education, have faced criticism regarding their effectiveness.
- Loan forgiveness programs: While offering relief, these programs have faced questions about their cost-effectiveness and overall impact.
- Interest rates and repayment plans: The interest rates on student loans and the availability of various repayment plans significantly impact the overall debt burden. Income-driven repayment (IDR) plans, for example, offer varying degrees of relief.
- Effectiveness of existing programs: Data on the success of these programs in reducing default rates and improving borrower outcomes is crucial for assessing their effectiveness. [Insert data and citation here].
Political and Economic Implications of Government Intervention
The student loan crisis is not only an economic issue but also a significant political one. Government intervention has broad implications.
- Budgetary impact: Government loan forgiveness programs, for instance, place a significant burden on the federal budget.
- Potential for inflation: Significant increases in government spending to address the crisis could potentially contribute to inflation.
- Political ramifications: The student loan crisis has become a central issue in political debates, influencing election outcomes and shaping policy agendas. Recent legislative efforts such as [mention specific legislative acts] reflect this.
What to Expect in the Future of the Student Loan Crisis
Predicting the future of the student loan crisis requires considering various potential solutions and long-term economic projections.
Potential Solutions and Policy Changes
Several potential solutions are being debated to address the crisis.
- Loan forgiveness programs: These programs, while politically charged, offer debt relief to borrowers.
- Interest rate reforms: Lowering interest rates on student loans could reduce the overall debt burden.
- Changes in higher education funding: Increased funding for higher education could reduce the reliance on student loans. Each of these solutions has its pros and cons, and their economic impacts need careful evaluation. [Insert expert opinions and citations here].
Long-Term Economic Projections
The long-term economic effects of the student loan crisis are uncertain, but several scenarios are possible.
- Continued economic drag: If the crisis remains unresolved, it could continue to negatively impact economic growth for years to come.
- Increased inequality: The burden of student loan debt disproportionately affects lower-income individuals, potentially exacerbating income inequality.
- Impact on future generations: The crisis could have lasting consequences for future generations, limiting their economic opportunities. Economic modeling and forecasting by [insert reputable source and citation here] suggest [insert prediction and explanation].
Conclusion: Navigating the Student Loan Crisis and Looking Ahead
The student loan crisis presents a significant challenge to the US economy. Its effects on consumer spending, the housing market, and future economic prospects are undeniable. Understanding the student loan crisis and its implications is crucial for policymakers, individuals, and businesses alike. Staying informed about policy changes, exploring available repayment options like income-driven repayment plans, and engaging in informed discussions about solutions are vital steps in navigating this complex issue. To effectively manage your student loan debt and stay updated on the latest developments, visit resources like the Federal Student Aid website ([insert link here]) and the National Foundation for Credit Counseling ([insert link here]). Let's work together to find effective solutions to this persistent economic challenge and create a more equitable and sustainable future by addressing the student loan crisis head-on.

Featured Posts
-
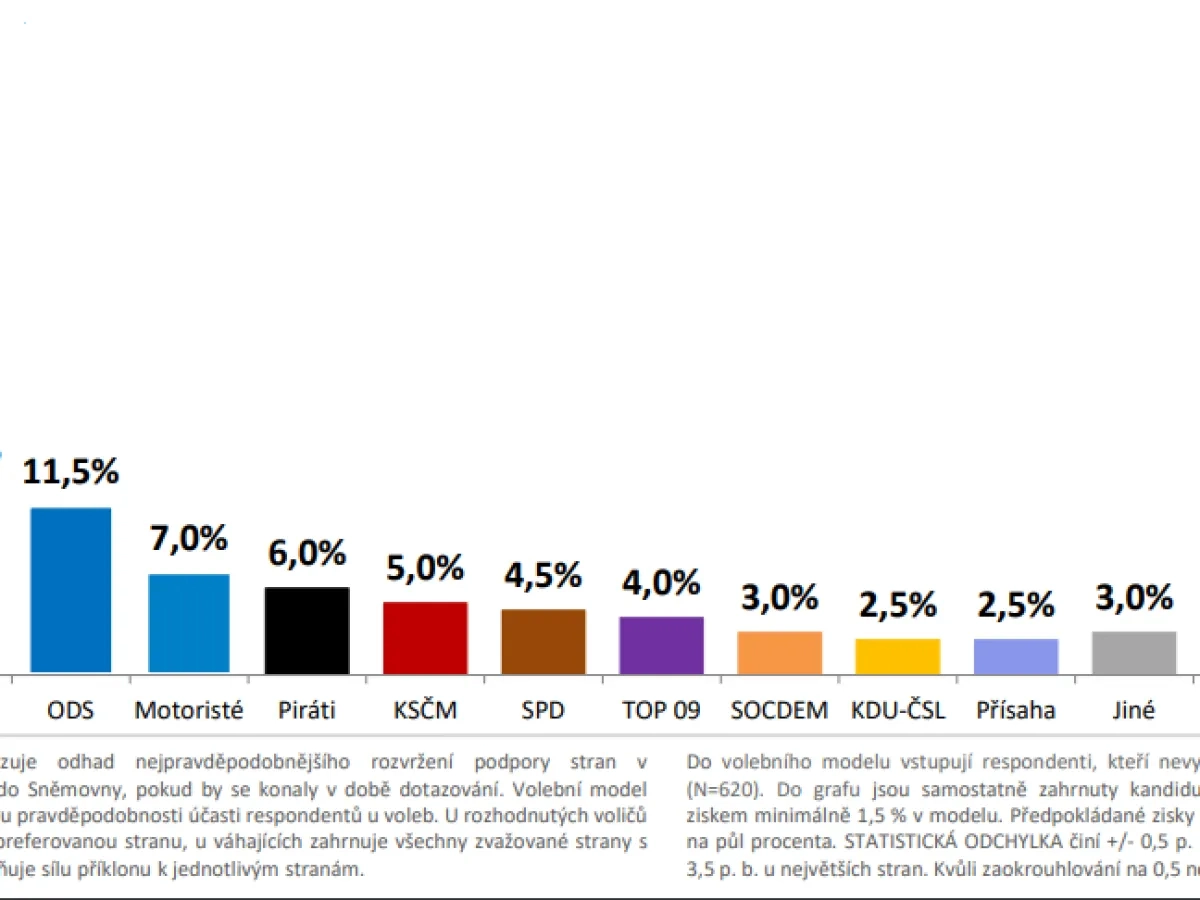 Snemovni Volby Pirati A Zeleni Spojuji Sily
May 28, 2025
Snemovni Volby Pirati A Zeleni Spojuji Sily
May 28, 2025 -
 Padres Pregame Arraez Day Off Sheets Returns To Left Field
May 28, 2025
Padres Pregame Arraez Day Off Sheets Returns To Left Field
May 28, 2025 -
 Test Et Avis Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go Bon Plan A 985 56 E
May 28, 2025
Test Et Avis Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go Bon Plan A 985 56 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Nadal Bids Tearful Adieu To Roland Garros Sabalenka Claims Victory
May 28, 2025
Nadal Bids Tearful Adieu To Roland Garros Sabalenka Claims Victory
May 28, 2025 -
 Braves Defeat Pirates Triolos Highlights And Solid Bullpen Performance
May 28, 2025
Braves Defeat Pirates Triolos Highlights And Solid Bullpen Performance
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Enjoy Four Days Of Sunshine San Diego Weather Forecast
May 30, 2025
Enjoy Four Days Of Sunshine San Diego Weather Forecast
May 30, 2025 -
 Schools Closed Again Winter Weather Impacts Continue
May 30, 2025
Schools Closed Again Winter Weather Impacts Continue
May 30, 2025 -
 San Diego County Four Days Of Sunny Warm Weather Ahead
May 30, 2025
San Diego County Four Days Of Sunny Warm Weather Ahead
May 30, 2025 -
 Second Straight Day Of School Cancellations Due To Winter Storm
May 30, 2025
Second Straight Day Of School Cancellations Due To Winter Storm
May 30, 2025 -
 Otay Mountains Border Patrols Successful Rescue Operation
May 30, 2025
Otay Mountains Border Patrols Successful Rescue Operation
May 30, 2025
