Tracking The Spread: A New COVID-19 Variant And Rising Case Numbers
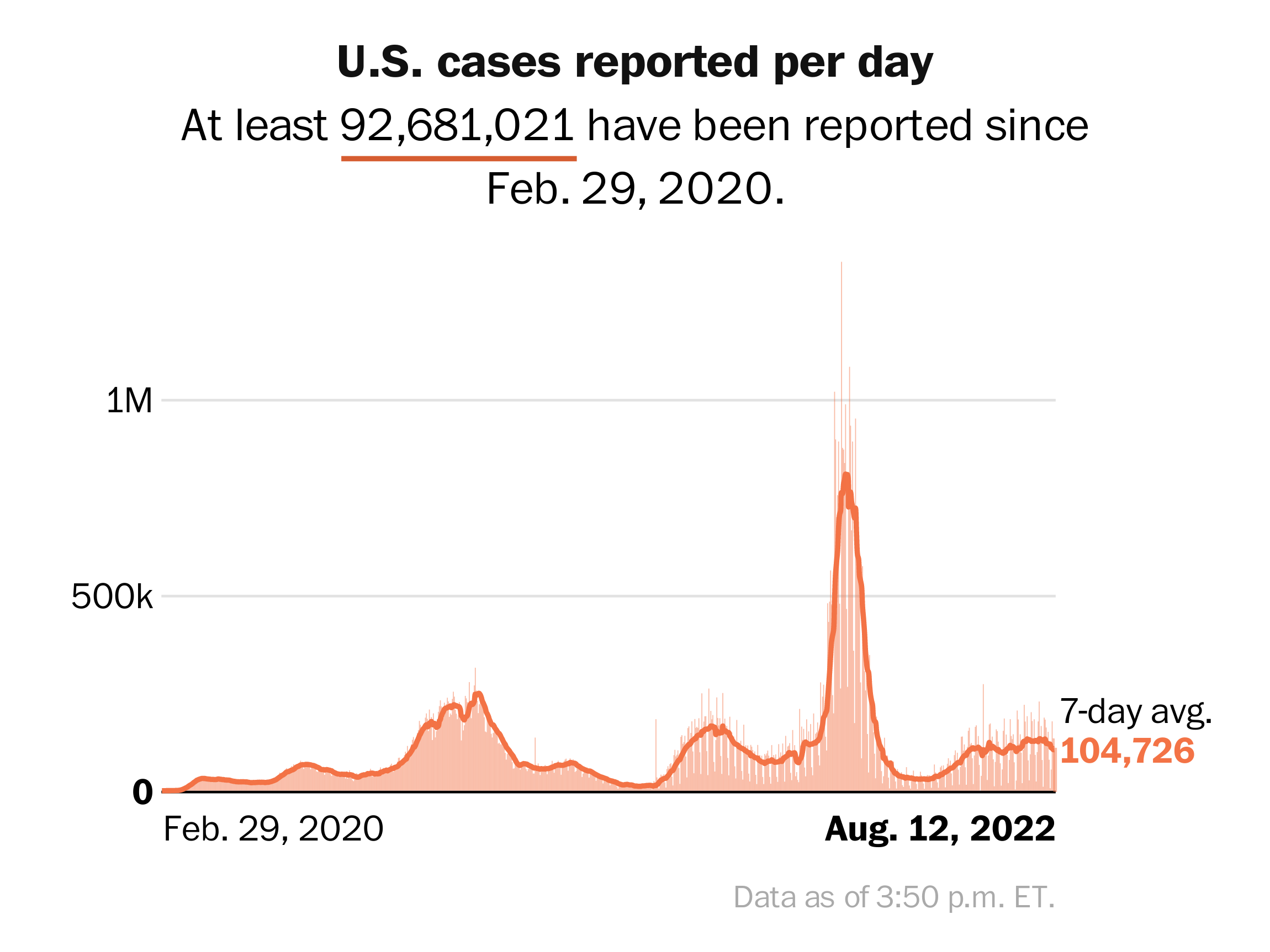
Table of Contents
Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant
Increased Transmissibility
The novel COVID-19 variant demonstrates significantly higher contagiousness compared to previous strains like Delta and Omicron. This increased transmissibility is a key factor driving the current surge in case numbers.
- Evidence of faster transmission rates: Studies show a substantially shorter incubation period and a higher secondary attack rate compared to previous variants.
- Potential mutations affecting infectivity: Specific mutations in the spike protein are believed to enhance the virus's ability to bind to and infect human cells. Research is ongoing to pinpoint the exact mutations responsible.
- R0 value comparisons: The basic reproduction number (R0) – the average number of people infected by a single person – is significantly higher for the novel variant, indicating its greater potential for spread within a population. Preliminary data suggests an R0 value approximately [Insert data if available, otherwise state "significantly higher than previous variants"].
Severity of Infection
While the increased transmissibility is alarming, the severity of illness associated with the novel variant remains a crucial area of investigation. Initial data suggests a [Insert data on severity – e.g., "similar" or "slightly lower" or "higher"] level of severity compared to previous variants.
- Hospitalization rates: Current hospitalization rates are [Insert data if available, otherwise describe trend – e.g., "rising," "relatively stable," "declining"]. Further analysis is needed to determine if this is directly attributable to the variant itself or other factors.
- Mortality rates: Mortality data associated with the novel variant is still being collected and analyzed. [Insert data or trend, e.g., "Early indications suggest mortality rates are comparable to previous variants."]
- Severity compared to previous variants (Delta, Omicron, etc.): Ongoing studies are comparing the clinical outcomes of patients infected with the novel variant to those infected with previous strains. This will help determine if specific populations are at higher risk of severe illness.
Immune Evasion
A concerning aspect of the novel variant is its potential ability to evade existing immunity, both from vaccination and prior infection.
- Reduced vaccine effectiveness: Preliminary evidence suggests that the novel variant may partially evade the protection provided by existing COVID-19 vaccines. This may result in breakthrough infections, although vaccines still offer substantial protection against severe disease.
- Increased reinfection rates: The variant's ability to evade immunity might lead to increased reinfection rates, even in individuals who have previously been infected with other COVID-19 variants.
- Impact on antibody response: Studies are underway to assess the impact of the novel variant on the antibody response generated by vaccination or prior infection. This will inform the development of updated vaccines or booster shots if necessary.
Factors Contributing to the Spread
Global Travel and Mobility
International travel plays a significant role in facilitating the rapid spread of the novel variant.
- Increased travel during holiday seasons: Increased international travel during peak seasons creates opportunities for the virus to spread across borders.
- Ease of international air travel: The ease and speed of international air travel allow the virus to reach new regions quickly.
- Challenges in border control and testing: Inconsistencies in border control measures and testing protocols across different countries can hinder efforts to contain the spread.
Vaccination Rates and Immunity Levels
Low vaccination rates and waning immunity in certain populations contribute significantly to the spread of the novel variant.
- Population vaccination rates: Areas with lower vaccination rates experience higher rates of transmission.
- Effectiveness of current vaccines: While vaccines remain effective in preventing severe illness, their effectiveness against infection may be reduced against the novel variant.
- Impact of waning immunity: The waning of immunity over time, especially in individuals who received their initial vaccination doses several months ago, increases susceptibility to infection.
Public Health Measures
The effectiveness of various public health measures in controlling the spread of the novel variant is being constantly evaluated.
- Mask mandates: The impact of mask mandates on transmission rates varies depending on adherence and other factors.
- Social distancing measures: Maintaining social distance remains crucial in limiting person-to-person transmission.
- Testing availability: Widespread and readily accessible testing is vital for early detection and isolation of infected individuals.
- Contact tracing effectiveness: Contact tracing plays a role, but its effectiveness is challenged by the variant's high transmissibility.
Implications and Recommendations
Impact on Healthcare Systems
The surge in COVID-19 cases driven by the novel variant places significant strain on healthcare systems globally.
- Hospital bed capacity: Hospitals are facing increased pressure due to a rise in hospitalizations.
- Staffing shortages: Healthcare workers are facing burnout and exhaustion, further impacting the healthcare system's capacity.
- Impact on other healthcare services: The surge in COVID-19 cases may impact the delivery of other essential healthcare services.
Individual Precautions
Individuals can take several precautions to protect themselves from infection with the novel variant:
- Vaccination and boosters: Stay up-to-date with COVID-19 vaccinations and booster shots.
- Mask-wearing: Wear a high-quality mask in crowded indoor settings.
- Social distancing: Maintain physical distance from others whenever possible.
- Hygiene practices: Practice good hand hygiene, including frequent handwashing.
- Testing and self-isolation: Get tested if you experience symptoms and isolate yourself if you are positive.
Future Research and Monitoring
Continued research and robust surveillance are critical in managing the pandemic.
- Variant monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the novel variant's evolution and spread is essential.
- Vaccine development: Research is underway to develop updated vaccines that provide better protection against the novel variant.
- Improved diagnostic tools: Development of more sensitive and rapid diagnostic tests is crucial.
- Public health data analysis: Analyzing public health data helps in understanding the variant's behavior and guiding interventions.
Conclusion
Tracking the spread of this novel COVID-19 variant is crucial for effective public health interventions. Understanding its characteristics, analyzing factors contributing to its spread, and implementing appropriate measures are vital to controlling the pandemic. Continued vigilance, adherence to recommended precautions, and ongoing research are paramount. Stay informed about the latest updates on this evolving situation and take proactive steps to protect yourself and your community from the spread of new COVID-19 variants. Remember, your actions matter in combating this virus. Staying informed about new COVID-19 variants and their spread is essential for protecting yourself and your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Munguias Doping Allegations A Denial Following Adverse Test
May 31, 2025
Munguias Doping Allegations A Denial Following Adverse Test
May 31, 2025 -
 Former Nyc Police Commissioner Bernard Kerik Passes Away At 69
May 31, 2025
Former Nyc Police Commissioner Bernard Kerik Passes Away At 69
May 31, 2025 -
 New Padel Court Proposal For Bannatyne Health Club In Essex
May 31, 2025
New Padel Court Proposal For Bannatyne Health Club In Essex
May 31, 2025 -
 Tigers Drop First Home Series Bats Silenced By Rangers
May 31, 2025
Tigers Drop First Home Series Bats Silenced By Rangers
May 31, 2025 -
 Cyberpunk 2 What We Know About Cd Projekt Reds Sequel
May 31, 2025
Cyberpunk 2 What We Know About Cd Projekt Reds Sequel
May 31, 2025
