U.S. Federal Reserve Holds Steady: Inflation And Economic Pressures
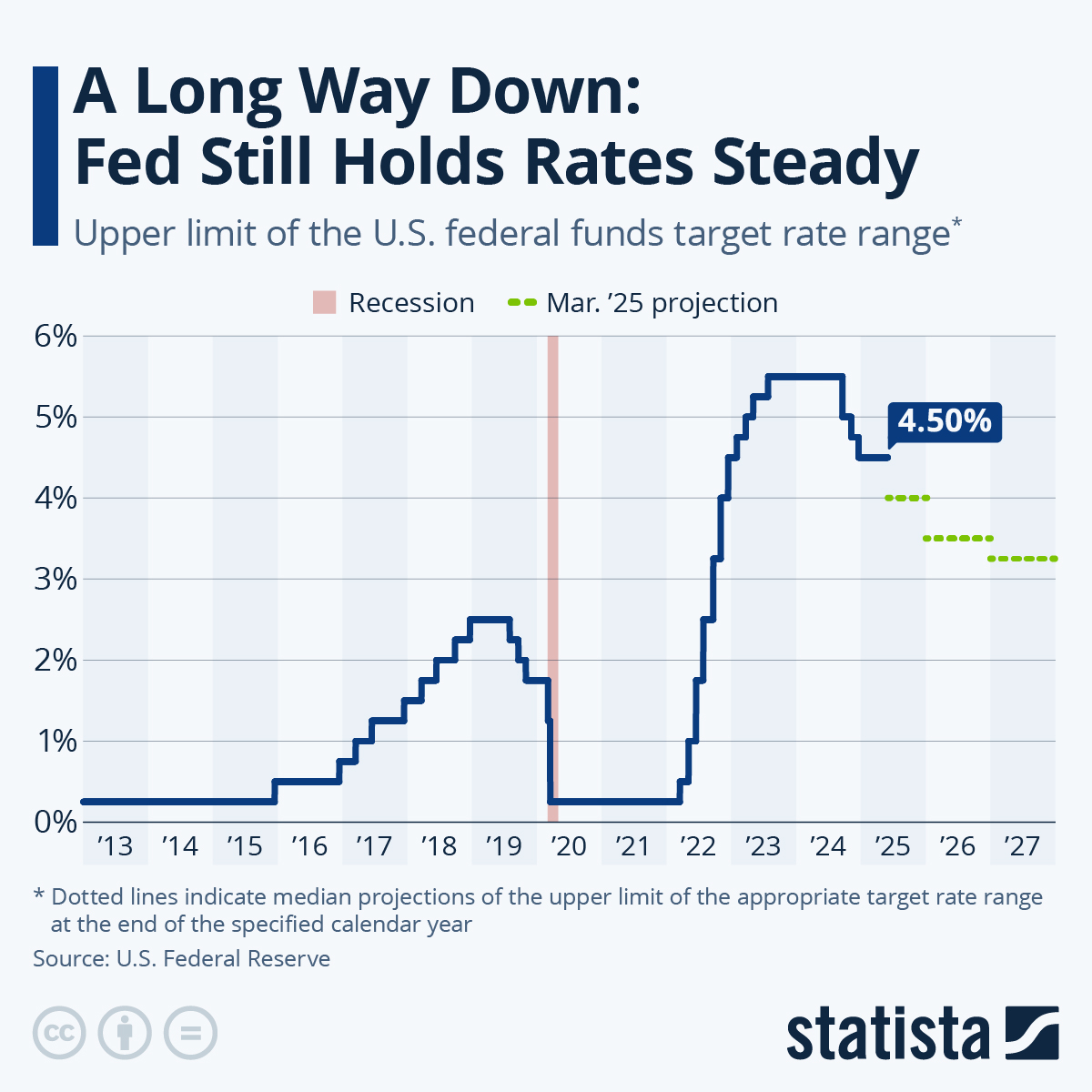
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures Remain a Concern
Persistent Inflation
The current inflation rate remains a significant concern for the Federal Reserve. Despite previous interest rate hikes aimed at cooling the economy and curbing price increases, persistent inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), continues to exceed the Fed's target. Core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, also shows stubborn resistance to decline. Achieving price stability remains a primary challenge.
- Examples of persistent price increases: Shelter costs, healthcare services, and certain durable goods continue to show significant price increases.
- Comparison to previous inflation cycles: The current inflation cycle is unique in its combination of supply chain disruptions, geopolitical instability, and robust consumer demand. Comparing it to historical inflation cycles helps illuminate the current situation and potential future trajectories.
- Role of supply chain issues and geopolitical factors: The war in Ukraine, ongoing supply chain bottlenecks, and energy price volatility all contribute to inflationary pressures, making the Fed's task more complex.
The Fed's Inflation Target
The Federal Reserve has a stated inflation target of 2%, aiming for price stability. The current inflation rate significantly exceeds this goal, highlighting the challenge the Fed faces in bringing inflation back to its target. Achieving this target requires careful management of monetary policy.
- Tools used to control inflation: The Fed primarily uses interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing/tightening (QE/QT) to influence inflation. Raising interest rates increases borrowing costs, slowing economic activity and reducing demand-pull inflation. Quantitative tightening involves reducing the Fed's balance sheet, further tightening monetary conditions.
- Lags in monetary policy effects: It's crucial to understand that monetary policy changes don't have an immediate impact on the economy. There are significant lags between policy adjustments and their effects on inflation and economic activity, making precise control challenging.
Economic Growth and the Employment Picture
GDP Growth and Recession Risks
Assessing the current state of GDP growth is vital in understanding the Fed's decision. While the economy has shown resilience, there are growing concerns about the risk of a recession. Several economic indicators provide conflicting signals.
- Indicators suggesting potential recession: The inverted yield curve, where short-term interest rates exceed long-term rates, is often considered a leading indicator of a recession. However, other indicators, like strong consumer spending, present a more optimistic outlook.
- Strength/weakness of the labor market as a counter indicator: The robust labor market, with low unemployment rates and strong job creation, acts as a counterpoint to recessionary fears. This strength has created a complex situation for the Fed, requiring them to balance inflation concerns with potential job losses.
The Employment Report's Influence
The monthly employment report, specifically nonfarm payrolls, unemployment claims, and the labor force participation rate, significantly influences the Fed's decision-making. A strong employment report can signal economic strength but also potentially contribute to wage-push inflation.
- Analysis of the numbers – job creation, unemployment rates, wage growth: Analyzing job creation figures, unemployment rates, and wage growth provides insights into the health of the labor market and its interaction with inflation.
- Implications for inflation: Strong wage growth can fuel inflationary pressures, requiring careful consideration by the Federal Reserve in setting monetary policy.
The Fed's Communication and Future Outlook
Forward Guidance and Market Reactions
Following the decision to hold interest rates steady, the Fed's official statement and press conference provide crucial forward guidance on potential future interest rate adjustments. The market closely scrutinizes these communications.
- Summary of key takeaways from the Fed's communication: The Fed's communication often includes details about its assessment of economic conditions, inflation expectations, and the likely path of monetary policy.
- Market reactions (stock market, bond yields) to the decision: Market participants react to the Fed's decisions and communications. Stock market movements and bond yield changes reflect investor sentiment and expectations regarding future economic conditions and monetary policy.
Uncertainty and Geopolitical Factors
External factors play a significant role in influencing the Fed's decision-making process. Geopolitical risks, global supply chain disruptions, and energy price volatility create uncertainty and significantly impact inflation and economic growth.
- How these factors contribute to inflation and economic uncertainty: These external factors contribute to inflationary pressures through supply chain disruptions, increased energy costs, and uncertainty about future economic conditions.
- How the Fed is accounting for these external factors: The Fed acknowledges these external factors and attempts to incorporate them into its forecasts and decision-making, although their impact is difficult to precisely quantify.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve's decision to hold interest rates steady reflects a careful balancing act between combating persistent inflation and mitigating risks to economic growth. While inflation remains a concern, the strength of the labor market and other economic indicators provide a degree of reassurance. However, significant uncertainties remain, including the potential for a recession and the ongoing impact of geopolitical factors. Monitoring the evolving economic landscape and the Federal Reserve's future actions regarding interest rates and monetary policy will be crucial in the coming months. Stay informed about future U.S. Federal Reserve decisions to effectively manage your investments and navigate the evolving economic climate. Understanding the intricacies of the U.S. Federal Reserve's approach to inflation and economic pressures is vital for both investors and consumers.

Featured Posts
-
 Easing Bond Forward Rules A Key Demand From Indian Insurers
May 09, 2025
Easing Bond Forward Rules A Key Demand From Indian Insurers
May 09, 2025 -
 Bondi Under Fire Senate Democrats Allege Concealment Of Epstein Documents
May 09, 2025
Bondi Under Fire Senate Democrats Allege Concealment Of Epstein Documents
May 09, 2025 -
 The Impact Of The Canada China Dispute On Global Canola Trade
May 09, 2025
The Impact Of The Canada China Dispute On Global Canola Trade
May 09, 2025 -
 Focus On De Escalation A Look At This Weeks U S China Trade Talks
May 09, 2025
Focus On De Escalation A Look At This Weeks U S China Trade Talks
May 09, 2025 -
 Edmonton Federal Riding Changes What Voters Need To Know
May 09, 2025
Edmonton Federal Riding Changes What Voters Need To Know
May 09, 2025
