U.S. Federal Reserve Maintains Rates: Inflation And Unemployment Outlook
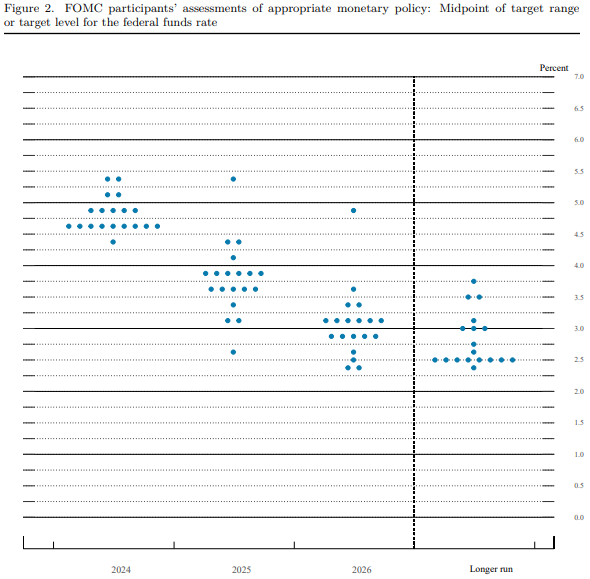
Table of Contents
The Fed's Rationale for Maintaining Rates
The Federal Reserve's decision to hold interest rates steady is a complex one, influenced by several key economic indicators and external factors. Let's examine the primary considerations.
Persistent Inflation Concerns
Inflation remains a persistent concern for the Federal Reserve. The Fed's target inflation rate is around 2%, but current figures are still above this level.
- CPI Data: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) continues to show elevated inflation, although the rate of increase may be slowing.
- Core Inflation: Core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, remains stubbornly high, indicating broader inflationary pressures.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Lingering supply chain bottlenecks continue to contribute to higher prices for many goods.
- Wage Growth: Strong wage growth, while positive for workers, can also fuel inflation if it outpaces productivity gains.
- Energy Prices: Fluctuations in energy prices, particularly oil and gas, significantly impact overall inflation.
The current inflation figures necessitate a cautious approach from the Fed. Determining whether the current inflation is transitory or a more persistent phenomenon is key to their future policy decisions. The Fed is carefully monitoring these indicators to assess the true trajectory of inflation.
Unemployment Rate and Labor Market Dynamics
The unemployment rate and the overall health of the labor market are equally important factors in the Fed's decision-making process.
- Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate remains relatively low, indicating a strong labor market.
- Labor Force Participation Rate: The labor force participation rate is also being closely watched, as it indicates the percentage of the working-age population actively seeking employment.
- Job Creation Numbers: Consistent job creation numbers suggest a healthy economy, but also potentially contribute to upward pressure on wages and inflation.
- Wage Growth: As mentioned earlier, strong wage growth is a double-edged sword. While beneficial for workers, it can contribute to inflationary pressures.
The Fed aims to achieve a "soft landing"—lowering inflation without triggering a significant rise in unemployment. Balancing these competing goals is a critical challenge. The strength of the current labor market is a factor in the Fed's decision to remain cautious before making further adjustments to interest rates.
Geopolitical and Global Economic Factors
External factors also play a significant role in the Fed's deliberations.
- Global Supply Chain Issues: Ongoing global supply chain disruptions continue to impact the availability and pricing of goods in the U.S.
- The War in Ukraine: The war in Ukraine has exacerbated global energy prices and created uncertainty in international markets.
- Energy Prices: As previously noted, energy prices are a key driver of inflation and significantly impact the overall economic outlook.
- International Trade: Global trade tensions and disruptions can affect the U.S. economy and the Fed's policy choices.
These global factors add complexity to the Fed's already challenging task of managing the U.S. economy. The interconnectedness of the global economy means that events outside the U.S. can significantly influence domestic economic conditions.
Potential Economic Impacts of the Rate Decision
The decision to maintain interest rates has various potential impacts across the economy.
Impact on Inflation
Maintaining rates at the current level could have both short-term and long-term effects on inflation.
- Consumer Spending: Stable rates might support consumer spending in the short term, potentially contributing to inflationary pressures.
- Business Investment: Low interest rates can encourage business investment, potentially boosting economic growth but also potentially contributing to inflation.
- Asset Prices: Maintaining low rates can support asset prices (stocks, real estate), but this might also contribute to asset bubbles.
- Imported Goods Prices: Changes in exchange rates, influenced by interest rate decisions, affect the prices of imported goods.
The effectiveness of maintaining rates to curb inflation is a subject of ongoing debate among economists.
Impact on Unemployment
The decision's impact on unemployment is also uncertain.
- Potential for Increased Unemployment: While unlikely in the immediate term, a tightening of monetary policy later could lead to higher unemployment.
- Impact on Wage Growth: Maintaining rates might continue to support wage growth, but also potentially contribute to inflationary pressure.
- Effect on Different Sectors of the Economy: The impact on unemployment may vary across different sectors of the economy, with some sectors potentially more vulnerable to economic slowdowns than others.
The Fed's careful consideration of the employment situation underscores the need to balance inflation control with maintaining employment levels.
Impact on the Stock Market and Bond Yields
The Fed's decision has immediate implications for financial markets.
- Stock Market Volatility: Maintaining rates might lead to increased stock market volatility as investors react to the announcement and assess its implications.
- Changes in Bond Yields: Bond yields are influenced by interest rate decisions and expectations of future rate changes.
- Investor Sentiment: Investor confidence and market behavior are significantly affected by the Federal Reserve's pronouncements on monetary policy.
The uncertainty surrounding future interest rate decisions contributes to the market volatility.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve's decision to maintain interest rates reflects a delicate balancing act between addressing persistent inflation concerns and supporting robust employment growth. While the current economic outlook presents both opportunities and challenges, the Fed’s continued monitoring of inflation and unemployment indicators is crucial. Understanding the implications of the Federal Reserve's monetary policy is vital for navigating the current economic landscape. Stay informed about future announcements from the Federal Reserve regarding interest rates and their impact on the U.S. economy. Regularly check for updates on the Federal Reserve's decisions concerning interest rates and their effect on the overall economic outlook. Understanding the Federal Reserve's actions is key to making informed financial decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Nottingham Attacks Survivors Break Silence Detailing The Events
May 10, 2025
Nottingham Attacks Survivors Break Silence Detailing The Events
May 10, 2025 -
 7 Year Reunion Two Actors Reunite In High Potential Finale
May 10, 2025
7 Year Reunion Two Actors Reunite In High Potential Finale
May 10, 2025 -
 Gpb Capital Founder Sentenced 7 Years For Ponzi Scheme Fraud
May 10, 2025
Gpb Capital Founder Sentenced 7 Years For Ponzi Scheme Fraud
May 10, 2025 -
 Understanding Elon Musks Wealth A Comprehensive Look At His Investments And Ventures
May 10, 2025
Understanding Elon Musks Wealth A Comprehensive Look At His Investments And Ventures
May 10, 2025 -
 Uk Government Considering Visa Restrictions Impact On Specific Nationalities
May 10, 2025
Uk Government Considering Visa Restrictions Impact On Specific Nationalities
May 10, 2025
