U.S. Labor Market Update: 177,000 Jobs Added In April, Unemployment Rate 4.2%

Table of Contents
Job Growth Analysis: A Moderate Increase in April's Employment Numbers
The headline figure – 177,000 new jobs – represents a moderate increase in employment numbers. While positive, this falls short of analysts' expectations and raises concerns about the pace of the economic recovery. Analyzing job growth across various sectors offers a more nuanced understanding. Key sectors contributing to job growth include:
-
Professional and Business Services: This sector added approximately 70,000 jobs, reflecting continued growth in consulting, financial services, and other professional fields. This growth is a positive sign, indicating ongoing business expansion and investment. Compared to March's growth in this sector, however, the increase was slightly lower, suggesting some potential slowing.
-
Leisure and Hospitality: This sector added roughly 40,000 jobs, demonstrating a continued, albeit slower, recovery in this area hard-hit by the pandemic. The sector is still significantly below pre-pandemic employment levels, indicating further room for growth. This slower-than-expected growth may be attributed to ongoing labor shortages and persistent inflationary pressures.
-
Manufacturing: Manufacturing added a modest number of jobs, indicating steady, but not explosive, growth in this sector. This relatively flat performance highlights the challenges facing the manufacturing sector, such as supply chain disruptions and global economic uncertainty.
Significant revisions to previous months' job reports were minimal, indicating relative stability in the data, though this does not negate the concerns raised by the slower-than-expected growth in April.
Unemployment Rate Deep Dive: 4.2% – What Does it Mean?
The 4.2% unemployment rate signals a tightening labor market, though it's unclear whether this signifies "full employment." While lower than pre-pandemic levels, further context is needed for complete analysis.
-
Labor Force Participation Rate: The labor force participation rate remains below pre-pandemic levels, indicating that a segment of the population is still not actively seeking employment. This could be due to various factors, such as early retirement, childcare challenges, or continued health concerns related to COVID-19. Understanding this factor is vital to properly assessing the true employment picture.
-
Employment-Population Ratio: Examining the employment-population ratio provides a broader perspective. This ratio, while improving, still lags behind pre-pandemic levels, further highlighting the incomplete recovery in the labor market.
-
Key Findings:
- Comparison to pre-pandemic levels: The unemployment rate is lower than before the pandemic, but the participation rate and employment-population ratio remain below pre-pandemic highs.
- Potential factors influencing the unemployment rate: These include ongoing labor shortages, particularly in certain sectors, and shifts in worker preferences post-pandemic.
- Regional variations: Regional unemployment rates vary significantly across the U.S., with some areas experiencing tighter labor markets than others.
Wage Growth and Inflation: The Impact on Workers' Purchasing Power
Average hourly earnings saw a modest increase, but when considering the current inflation rate, the impact on workers' purchasing power is critical to evaluate.
-
Real Wages: While nominal wage growth is present, inflation is eroding real wages. This means workers' purchasing power may be decreasing, limiting consumer spending and potentially impacting overall economic growth.
-
Sector-Specific Wage Growth: Certain sectors are experiencing higher wage growth than others due to intensified competition for talent. These are typically sectors with persistent labor shortages.
-
Key Considerations:
- Percentage change in average hourly earnings: The actual percentage increase in average hourly earnings should be compared to the inflation rate to determine the change in real wages.
- Comparison to inflation rate: If inflation outpaces wage growth, real wages are declining, which negatively impacts consumer spending.
- Potential effects on consumer spending: Decreasing real wages could lead to reduced consumer spending, potentially hindering economic growth.
Future Outlook: Projections for the U.S. Labor Market
Predicting the future of the U.S. labor market involves assessing various economic indicators and potential risks.
-
Expert Predictions: Economists offer varied projections for job growth and unemployment rates, reflecting the inherent uncertainty in the current economic climate. Many predictions point to continued, albeit slower, job growth.
-
Potential Risks: Key risks include persistent inflation, potential recessionary pressures, and ongoing supply chain disruptions. These factors could impact business investment and hiring decisions.
-
Policy Implications: Government policies, such as monetary policy adjustments by the Federal Reserve, will play a significant role in shaping the future labor market.
-
Key Predictions and Risks:
- Continued job growth, albeit at a slower pace than previously anticipated.
- Potential for a slowdown in economic growth, increasing the risk of recession.
- Continued upward pressure on wages, potentially exacerbating inflationary pressures.
Conclusion: Interpreting the April U.S. Labor Market Update and What to Expect Next
The April U.S. Labor Market Update reveals a complex picture. While job growth remains positive, it is slower than expected, and inflation continues to erode workers' purchasing power. The unemployment rate is falling, but other indicators suggest a less complete recovery than the headline numbers suggest. Monitoring the U.S. labor market closely is vital for gauging the overall health of the economy. Future U.S. labor market updates will be critical in assessing the trajectory of the economic recovery and understanding the implications for businesses, investors, and policymakers. Stay updated on crucial U.S. labor market updates by subscribing to our newsletter and following our blog for further analysis.

Featured Posts
-
 Uncomfortable Exchanges Analyzing Blake Lively And Anna Kendricks Interactions Through Body Language
May 04, 2025
Uncomfortable Exchanges Analyzing Blake Lively And Anna Kendricks Interactions Through Body Language
May 04, 2025 -
 Effective Middle Management Key To Employee Engagement And Business Growth
May 04, 2025
Effective Middle Management Key To Employee Engagement And Business Growth
May 04, 2025 -
 Alleged Torture Starvation And Assault Lead To Murder Charge Against Stepfather Of 16 Year Old
May 04, 2025
Alleged Torture Starvation And Assault Lead To Murder Charge Against Stepfather Of 16 Year Old
May 04, 2025 -
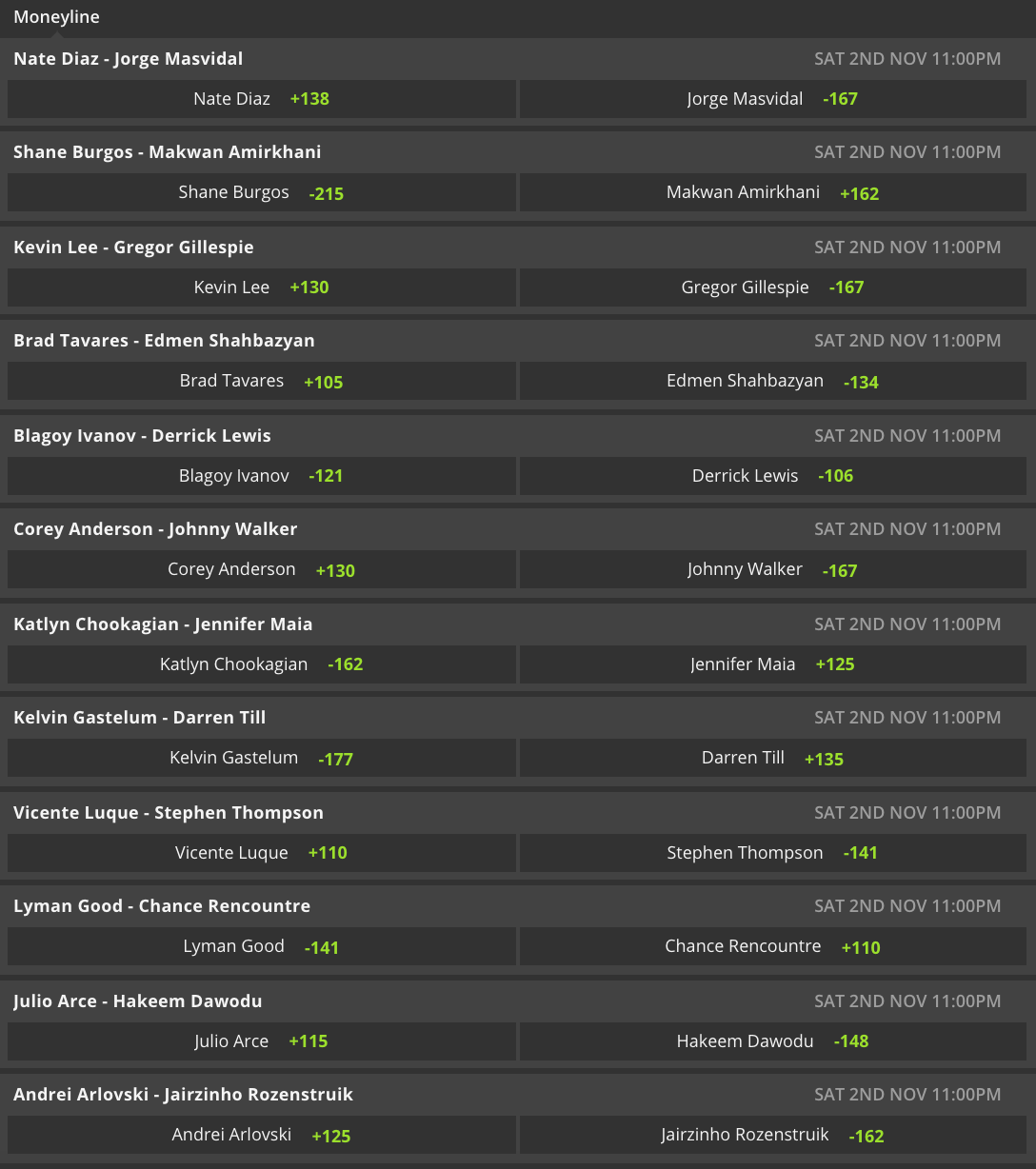 Analyzing Ufc 314s Opening Fight Card Betting Odds
May 04, 2025
Analyzing Ufc 314s Opening Fight Card Betting Odds
May 04, 2025 -
 Fallica Critiques Trumps Actions Towards Putin
May 04, 2025
Fallica Critiques Trumps Actions Towards Putin
May 04, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Alleged Torture Starvation And Assault Lead To Murder Charge Against Stepfather Of 16 Year Old
May 04, 2025
Alleged Torture Starvation And Assault Lead To Murder Charge Against Stepfather Of 16 Year Old
May 04, 2025 -
 Murder Charge Filed Against Stepfather Accused Of Torturing Starving And Beating 16 Year Old Stepson
May 04, 2025
Murder Charge Filed Against Stepfather Accused Of Torturing Starving And Beating 16 Year Old Stepson
May 04, 2025 -
 Stepfather Faces Murder Charges In Stepsons Death Allegations Of Torture Starvation And Assault
May 04, 2025
Stepfather Faces Murder Charges In Stepsons Death Allegations Of Torture Starvation And Assault
May 04, 2025 -
 Hospital Hammer Incident Belfast Mans Violent Past Revealed
May 04, 2025
Hospital Hammer Incident Belfast Mans Violent Past Revealed
May 04, 2025 -
 Emma Stone And Margaret Qualley Oscars Incident Fact Or Fiction
May 04, 2025
Emma Stone And Margaret Qualley Oscars Incident Fact Or Fiction
May 04, 2025
