Understanding Stock Market Valuations: BofA's Argument For Calm
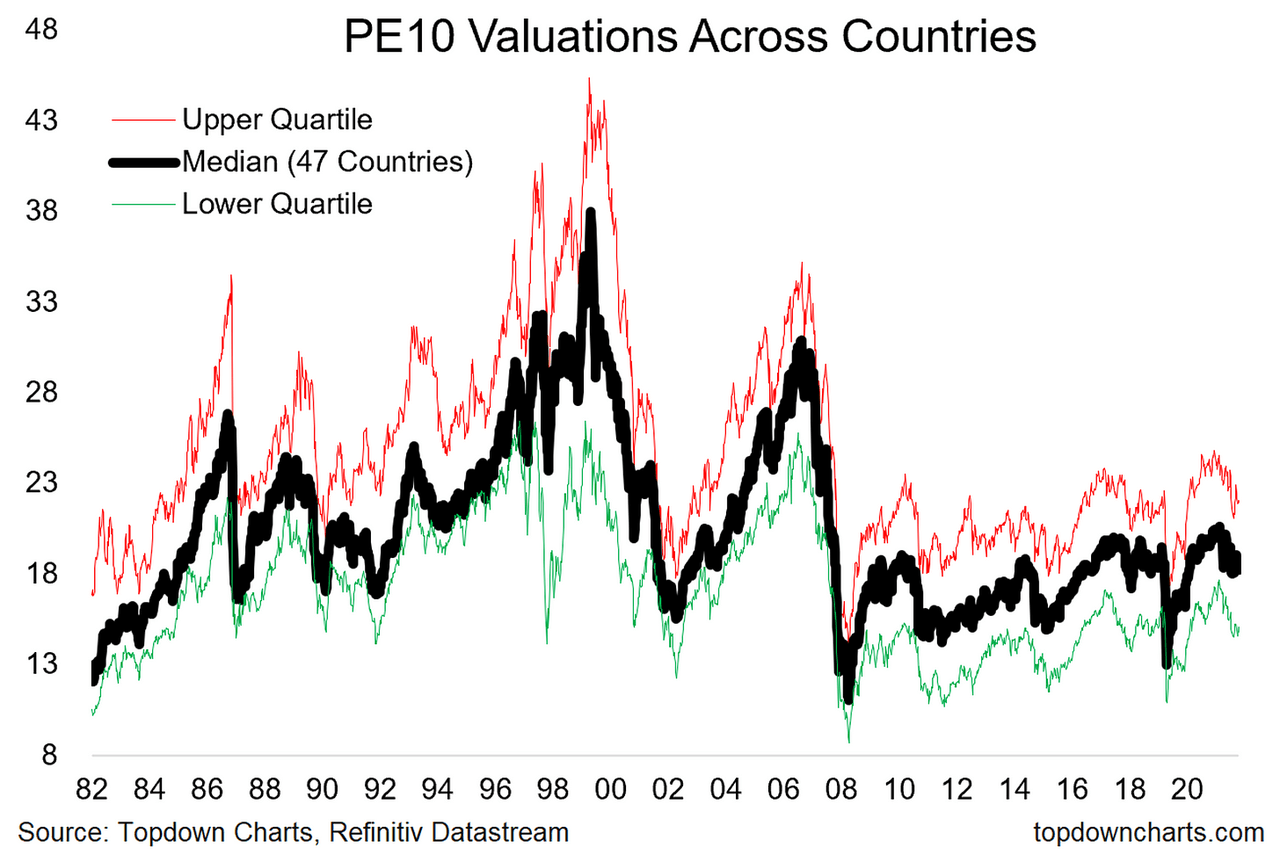
Table of Contents
BofA's Key Arguments for a Relatively Calm Market
BofA's less-alarmed outlook on the current market isn't based on blind optimism; it stems from a careful analysis of various valuation metrics and market trends. Their argument rests on several key pillars:
-
Favorable Valuation Metrics: BofA utilizes a range of valuation metrics, including Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratios, Price-to-Sales (P/S) ratios, and Price-to-Book (P/B) ratios, to assess market valuation. Their analysis suggests that while certain sectors might appear expensive based on historical averages, many indices and sectors show relatively undervalued characteristics compared to current economic expectations.
-
Specific Sector Analysis: BofA's research highlights specific sectors, potentially including undervalued segments in technology, energy, or financials (depending on the specifics of their most recent report), that offer compelling entry points for investors. This targeted approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of the market's overall health.
-
Interest Rate Hike Considerations: BofA acknowledges the impact of interest rate hikes on valuations. However, their analysis suggests that current valuations already reflect much of the anticipated impact of these hikes, tempering concerns about further significant market declines. They may argue that the market has already priced in a degree of future rate increases.
-
Addressing Counterarguments: BofA likely addresses counterarguments, such as persistent inflation or geopolitical risks, by acknowledging their potential negative impact but emphasizing that these factors are already priced into the market to some extent, making drastic corrections less probable. They might point to resilience in certain sectors as evidence supporting their viewpoint.
Understanding Current Market Valuations
Understanding stock market valuations requires familiarity with several key metrics and concepts:
-
P/E Ratio: This ratio (Price per share / Earnings per share) indicates how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company's earnings. A high P/E ratio can suggest overvaluation, while a low P/E ratio might indicate undervaluation.
-
PEG Ratio: This ratio (P/E Ratio / Earnings Growth Rate) adjusts the P/E ratio for the company's expected earnings growth.
-
Dividend Yield: This metric (Annual Dividend per Share / Stock Price) represents the annual dividend income relative to the stock price. It's particularly relevant for income-focused investors.
-
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B): This ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its book value (assets minus liabilities). A low P/B ratio might suggest undervaluation.
-
Market Capitalization: The total market value of a company's outstanding shares.
-
Earnings Per Share (EPS): A company's net profit divided by the number of outstanding shares.
How these metrics are used: By comparing these metrics across different companies and industries, and by analyzing trends over time, investors can attempt to assess whether a stock or the overall market is overvalued or undervalued. For example, a consistently high P/E ratio for an industry might suggest that sector is overvalued. However, relying solely on these metrics is risky as other critical factors, discussed below, play a significant role.
Limitations: These valuation metrics are not foolproof. They are backward-looking, failing to fully account for future growth prospects or unforeseen events.
Factors Influencing Stock Market Valuations Beyond Traditional Metrics
While quantitative metrics are crucial, qualitative factors significantly impact stock prices:
-
Economic Growth Forecasts: Strong economic growth projections typically boost market valuations, while recessionary fears can trigger declines.
-
Geopolitical Events: International conflicts, political instability, and trade wars create uncertainty and can negatively impact market sentiment.
-
Technological Advancements: Breakthroughs in technology can create new opportunities and drive market growth, but disruptive technologies can also displace existing industries.
-
Consumer Confidence: Consumer spending is a major driver of economic growth, and strong consumer confidence usually supports higher market valuations.
Impact on Investor Sentiment: These qualitative factors profoundly influence investor sentiment, which, in turn, drives market valuations. Positive news generally leads to increased buying and higher prices, while negative news can trigger selling pressure and price declines. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic initially caused a sharp market downturn due to uncertainty and economic disruption.
Comparing BofA's Analysis with Other Market Perspectives
It's crucial to remember that BofA's perspective is just one among many. Other financial institutions and analysts may hold contrasting views. Some might argue that current valuations are still elevated, reflecting excessive optimism and ignoring potential downside risks.
-
Differing Perspectives: These differing opinions might stem from differing interpretations of economic data, different weighting of various valuation metrics, or varying assessments of qualitative factors. Some analysts might be more sensitive to inflation risks, while others might focus on long-term growth prospects.
-
Areas of Agreement and Disagreement: While there might be consensus on certain trends, substantial disagreement could exist regarding the likelihood and severity of potential market corrections. This disparity underlines the importance of conducting thorough independent research.
-
Implications for Investors: The range of perspectives highlights the need for a diversified and carefully considered investment strategy. Investors shouldn't solely rely on a single opinion but should conduct their research, weighing different perspectives to form their own informed conclusions.
Maintaining Calm in the Face of Stock Market Valuation Uncertainty
BofA's core argument centers on a relatively calm market outlook, supported by a detailed assessment of valuation metrics and a consideration of market trends. They likely emphasize the current valuations already reflecting potential risks, making drastic corrections less likely. However, it's essential to remember that understanding stock market valuations involves a comprehensive approach. Investors should not only focus on quantitative data but also consider the influence of qualitative factors such as economic forecasts and geopolitical events.
To navigate the complexities of stock market valuations successfully, conduct thorough research, considering BofA's perspective alongside other analyses. Avoid panic-driven decisions based on short-term market fluctuations. Develop a well-informed investment strategy that incorporates diversification and a long-term outlook. For a deeper understanding of stock market valuations, explore resources like financial news websites, investment textbooks, and reputable financial analysis reports. Remember that responsible investing relies on a thorough understanding of stock market valuations.

Featured Posts
-
 Colgate Cl Tariff Increases Result In Significant Drop In Sales And Earnings
Apr 26, 2025
Colgate Cl Tariff Increases Result In Significant Drop In Sales And Earnings
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Nintendo Switch 2 Preorder My Game Stop Store Visit
Apr 26, 2025
Nintendo Switch 2 Preorder My Game Stop Store Visit
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Car Found Inside Sunken World War Ii Warship A Cnn Report
Apr 26, 2025
Car Found Inside Sunken World War Ii Warship A Cnn Report
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Jennifer Anistons Split With Chelsea Handler An Inside Look
Apr 26, 2025
Jennifer Anistons Split With Chelsea Handler An Inside Look
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Activision Blizzard Deal Faces Ftc Appeal
Apr 26, 2025
Activision Blizzard Deal Faces Ftc Appeal
Apr 26, 2025
