Unprecedented Global Forest Loss: The Impact Of Wildfires
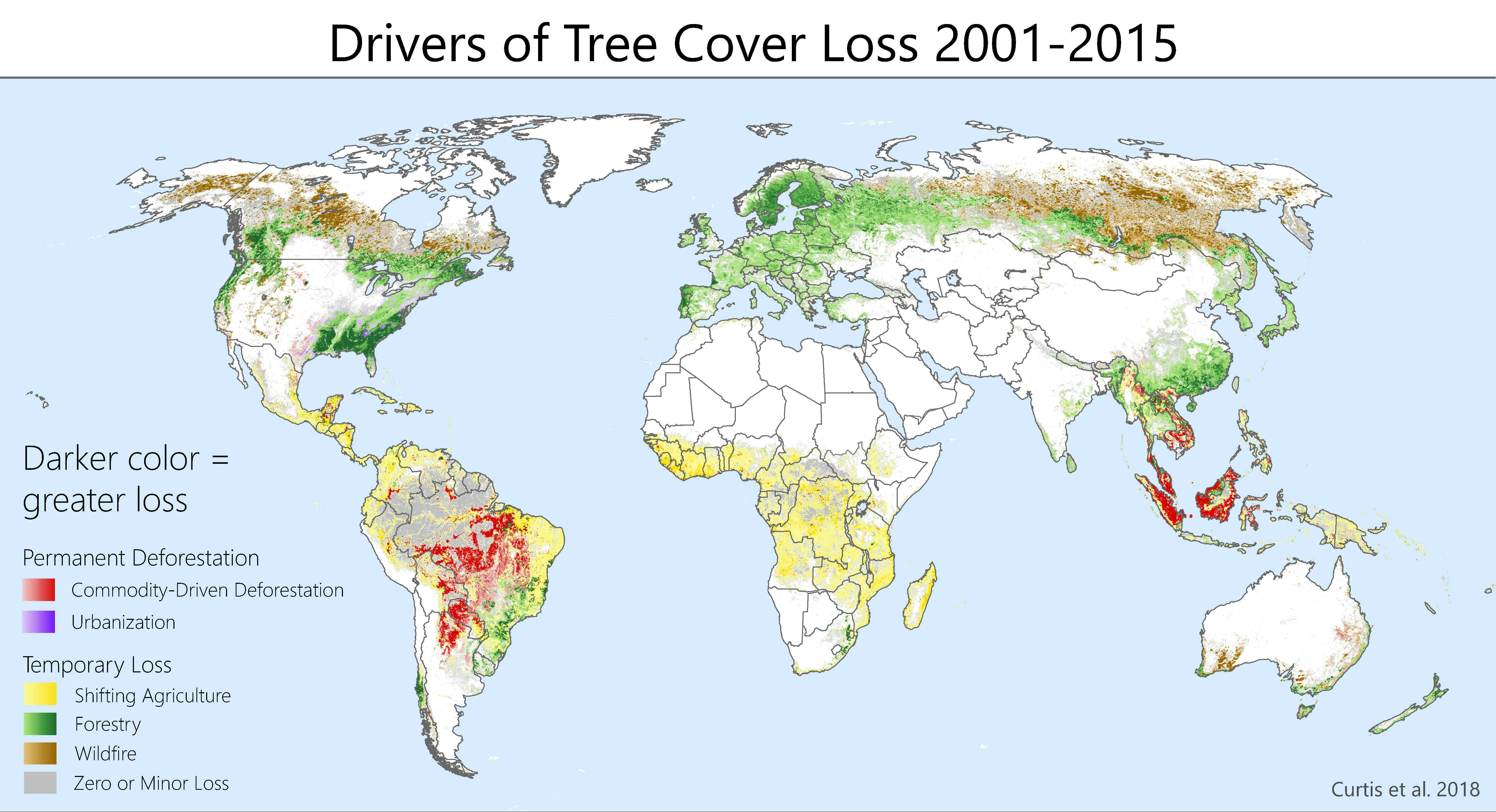
Table of Contents
The Rising Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
The dramatic increase in global forest fire occurrences is undeniable. Longer, hotter summers and drier conditions are creating a perfect storm for unprecedented global forest loss.
Climate Change as a Key Driver
Climate change is supercharging wildfires, creating a perfect storm of conditions that lead to larger, more intense, and longer-lasting blazes. The escalating effects are clear:
- Increased ignition potential: Higher temperatures and dry conditions increase the likelihood of wildfires starting, both naturally (lightning strikes) and through human activity.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer temperatures extend the periods of the year when conditions are favorable for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
- Faster fire spread: Drier vegetation and stronger winds caused by climate change accelerate the rate at which wildfires spread, making them harder to contain.
- More extreme fire behavior: Climate change contributes to more unpredictable and intense fire behavior, including larger crown fires and increased spotting (the spread of embers to start new fires).
Human Activities and Deforestation
Human activities significantly contribute to the increased risk of global forest fire. Deforestation, land-use change, and improper forest management practices create landscapes highly susceptible to wildfire.
- Increased fuel loads: The accumulation of dry underbrush and dead trees in forests creates massive fuel loads that readily ignite and burn intensely.
- Proximity of settlements to forests: Expansion of human settlements into forested areas increases the risk of accidental or intentional ignitions.
- Accidental and intentional ignitions: Human negligence (e.g., discarded cigarettes, unattended campfires) and arson are major causes of wildfires.
- Deforestation creates a domino effect: Removing trees leaves behind dry, easily combustible landscapes that are highly susceptible to wildfire, contributing to unprecedented global forest loss.
Devastating Ecological Consequences of Wildfires
The ecological consequences of wildfires, especially at the scale we are currently witnessing, are far-reaching and devastating. Unprecedented global forest loss directly translates into significant biodiversity loss.
Loss of Biodiversity and Habitat Destruction
Wildfires cause widespread habitat destruction, threatening countless plant and animal species. The impact includes:
- Loss of keystone species: The disappearance of keystone species can trigger a cascade of negative effects throughout the entire ecosystem.
- Disruption of ecological processes: Wildfires disrupt essential ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and seed dispersal.
- Reduced carbon sequestration: The loss of forest cover significantly reduces the planet's capacity to absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- Habitat fragmentation: Wildfires can fragment habitats, isolating populations and increasing their vulnerability to extinction.
Soil Degradation and Water Cycle Disruption
The impact of wildfires extends beyond the immediate loss of vegetation. Wildfires severely damage soil health and disrupt the water cycle:
- Increased runoff: The loss of vegetation increases soil erosion and runoff, leading to sedimentation of waterways and water pollution.
- Soil erosion: The loss of vegetation leaves soil exposed to the elements, making it vulnerable to erosion and degradation.
- Reduced water infiltration: Burned soil has reduced water infiltration capacity, leading to increased runoff and decreased groundwater recharge.
- Changes in water availability: Wildfires can drastically alter water availability, impacting both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
The Global Impact on Climate Change
Wildfires exacerbate climate change through a dangerous feedback loop, contributing to unprecedented global forest loss and further warming the planet.
Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Burning forests release massive amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, accelerating climate change.
- Contribution to climate change: Wildfires are a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global warming.
- Feedback loops: Wildfires create a dangerous feedback loop, as warmer temperatures increase the risk of more frequent and intense wildfires, releasing more greenhouse gases.
- Exacerbation of global warming: The release of greenhouse gases from wildfires contributes to the acceleration of global warming, creating a vicious cycle.
Reduced Carbon Sequestration Capacity
Forests play a vital role in absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide. The loss of forest cover due to wildfires significantly reduces this capacity.
- Long-term impact on climate mitigation efforts: Reduced carbon sequestration makes it harder to achieve climate mitigation goals.
- Reduced planetary health: The diminished ability of forests to absorb carbon dioxide negatively impacts global efforts to combat climate change and improve planetary health.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Combating unprecedented global forest loss requires a multifaceted approach combining improved forest management and climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Improved Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forest management practices are critical to reducing wildfire risk and promoting forest resilience.
- Reducing fuel loads: Controlled burns and thinning operations help reduce the accumulation of flammable materials in forests.
- Creating firebreaks: Firebreaks act as barriers to slow or stop the spread of wildfires.
- Early detection systems: Advanced technology such as satellite monitoring can help detect wildfires early, allowing for rapid response.
- Community-based fire prevention programs: Engaging local communities in fire prevention and management efforts is crucial.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Addressing climate change is essential to reducing the frequency and intensity of wildfires.
- Transition to renewable energy: Reducing reliance on fossil fuels is crucial to mitigating climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- International cooperation: Global collaboration is necessary to address climate change and protect forests worldwide.
- Climate-resilient forestry: Developing forest management strategies that are resilient to the impacts of climate change is crucial.
Conclusion
The scale of unprecedented global forest loss due to wildfires is alarming. The devastating ecological consequences, coupled with the significant contribution to climate change, highlight the urgent need for action. We must adopt a proactive and comprehensive approach, encompassing improved forest management, climate change mitigation, and international cooperation. The fight to prevent unprecedented global forest loss requires collective action. Learn more about the issue and get involved today. Protecting our forests is protecting our future.

Featured Posts
-
 Reddits Viral Missing Girl Story The Sydney Sweeney Movie
May 22, 2025
Reddits Viral Missing Girl Story The Sydney Sweeney Movie
May 22, 2025 -
 Nouvelle Navette Gratuite En Test Liaison La Haye Fouassiere Haute Goulaine
May 22, 2025
Nouvelle Navette Gratuite En Test Liaison La Haye Fouassiere Haute Goulaine
May 22, 2025 -
 Mothers Tweet After Southport Stabbing Results In Jail Sentence And Housing Issues
May 22, 2025
Mothers Tweet After Southport Stabbing Results In Jail Sentence And Housing Issues
May 22, 2025 -
 Premier League 2024 25 Champions Celebrating The Victory In Pictures
May 22, 2025
Premier League 2024 25 Champions Celebrating The Victory In Pictures
May 22, 2025 -
 Stephane Du Paysage Romand Aux Scenes Parisiennes
May 22, 2025
Stephane Du Paysage Romand Aux Scenes Parisiennes
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Tuerkiye Nin Nato Daki Yuekselen Yildizi Ittifakin Gelecegini Sekillendirecek Rol
May 22, 2025
Tuerkiye Nin Nato Daki Yuekselen Yildizi Ittifakin Gelecegini Sekillendirecek Rol
May 22, 2025 -
 Nato Parlamenter Asamblesi Antalya Toplantisi Teroerizm Ve Deniz Guevenligi Tartismalari
May 22, 2025
Nato Parlamenter Asamblesi Antalya Toplantisi Teroerizm Ve Deniz Guevenligi Tartismalari
May 22, 2025 -
 Antalya Da Nato Parlamenter Asamblesi Teroerizm Ve Deniz Guevenligi Odak Noktasi
May 22, 2025
Antalya Da Nato Parlamenter Asamblesi Teroerizm Ve Deniz Guevenligi Odak Noktasi
May 22, 2025 -
 Ukraina V Nato Analiz Peregovorov I Zayavleniya Evrokomissara
May 22, 2025
Ukraina V Nato Analiz Peregovorov I Zayavleniya Evrokomissara
May 22, 2025 -
 Klyuchevye Momenty Peregovorov O Chlenstve Ukrainy V Nato Mnenie Evrokomissara
May 22, 2025
Klyuchevye Momenty Peregovorov O Chlenstve Ukrainy V Nato Mnenie Evrokomissara
May 22, 2025
