US Tap Water Contaminated: Millions Exposed To "Forever Chemicals"
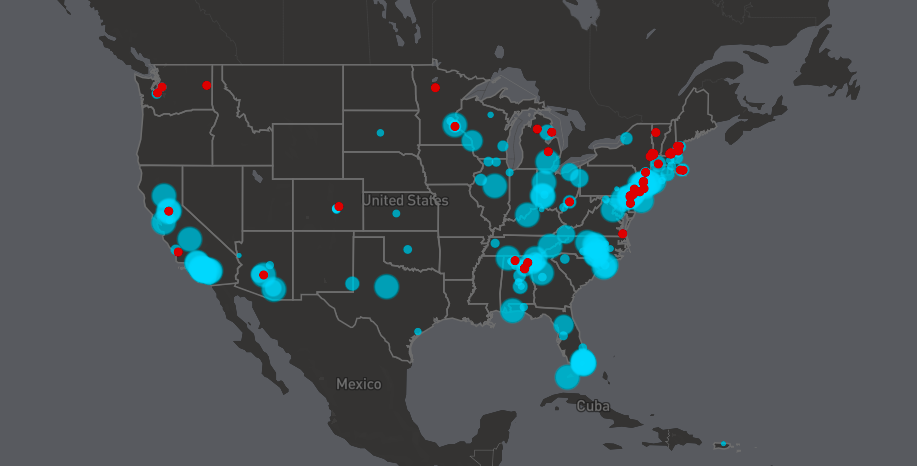
Table of Contents
H2: The Threat of Forever Chemicals (PFAS): What You Need to Know
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of man-made chemicals that have been used in a variety of products for decades, including firefighting foam, non-stick cookware, and food packaging. Their "forever" moniker stems from their remarkable persistence in the environment; they don't break down naturally and can remain in soil and water for many years. This persistence leads to bioaccumulation in the food chain, ultimately affecting human health.
- Bullet Points:
- Types and Effects: Numerous PFAS exist, with PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) and PFOS (perfluorooctanesulfonic acid) being the most studied. Exposure to these chemicals is linked to various health issues, including:
- Kidney and liver cancer
- Thyroid disorders
- Immune deficiency
- Developmental issues in children
- Increased cholesterol levels
- Long-Term Consequences: The long-term effects of PFAS exposure are still being researched, but the current evidence points to a concerning link between chronic exposure and severe health problems. Even low levels of exposure can accumulate over time, leading to significant health risks.
- Vulnerable Populations: Children and pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to the harmful effects of PFAS due to their developing bodies and increased sensitivity.
- Types and Effects: Numerous PFAS exist, with PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) and PFOS (perfluorooctanesulfonic acid) being the most studied. Exposure to these chemicals is linked to various health issues, including:
H2: Extent of US Tap Water Contamination by Forever Chemicals
The prevalence of PFAS contamination in US tap water is alarming. Studies have revealed widespread contamination across numerous states, with some areas showing significantly higher concentrations than others. For example, certain regions in Michigan, New Jersey, and North Carolina have reported alarmingly high levels of PFAS in their drinking water supplies.
- Bullet Points:
- EPA Involvement: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set health advisories for PFAS, but these are non-enforceable. The lack of stringent federal regulations has left many communities struggling to address the contamination. Recent efforts to establish enforceable standards are underway, but progress has been slow.
- Data Sources: Data on PFAS contamination comes from various sources, including state-level water testing programs, independent research studies, and citizen science initiatives. These diverse sources provide valuable information, although inconsistent reporting methods can sometimes make a complete picture difficult to assemble.
- Geographic Distribution: The distribution of PFAS contamination is not uniform. Areas near industrial sites, military bases (due to the use of firefighting foam), and landfills often have higher levels of contamination. This uneven distribution underscores the need for targeted testing and remediation efforts.
H2: Identifying and Reducing Your Exposure to Forever Chemicals in Tap Water
Understanding the potential presence of PFAS in your tap water is the first step towards mitigating your risk.
- Bullet Points:
- Testing: Home testing kits are available to screen your water for PFAS, though they might not detect all types. Professional water testing labs provide more comprehensive analyses.
- Reducing Exposure: Several methods can help reduce your exposure:
- Whole-House Water Filtration: A whole-house system, particularly reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, offers the most comprehensive protection.
- Water Pitcher Filters: These filters can reduce PFAS in drinking water, but their effectiveness varies depending on the type and filter life.
- Boiling Water: Boiling water is not effective in removing PFAS.
- Bottled Water: While a solution, consider the environmental impact of single-use plastic bottles.
- Advocacy: Contacting your elected officials to support stricter regulations and funding for remediation efforts is crucial.
H3: The Role of Government and Industry in Addressing PFAS Contamination
The responsibility for addressing PFAS contamination lies with both government agencies and the industries responsible for producing and releasing these chemicals. The EPA's role is pivotal in setting and enforcing regulations, providing funding for remediation projects, and conducting research. Industries must take accountability for their contribution to PFAS pollution and invest in cleaner production methods. Ongoing debates surrounding PFAS regulation highlight the complexity of the issue and the urgent need for comprehensive legislative action.
3. Conclusion:
PFAS contamination in US tap water is a serious public health concern. The persistence of these "forever chemicals" and their potential for long-term health consequences demand immediate action. Individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their exposure through water testing and filtration. However, lasting solutions necessitate strong government regulations, industry accountability, and increased public awareness. Test your water for PFAS, install a water filter, and contact your representatives to demand stricter regulations. Protecting your family from the dangers of forever chemicals in your tap water is a collective responsibility.

Featured Posts
-
 31
May 15, 2025
31
May 15, 2025 -
 Warriors Loss Jimmy Butler Suffers Pelvic Contusion Future Games In Question
May 15, 2025
Warriors Loss Jimmy Butler Suffers Pelvic Contusion Future Games In Question
May 15, 2025 -
 Nba Play In Warriors Grizzlies Matchup Breakdown
May 15, 2025
Nba Play In Warriors Grizzlies Matchup Breakdown
May 15, 2025 -
 Predicting The Braves Vs Padres Game Atlantas Path To Victory
May 15, 2025
Predicting The Braves Vs Padres Game Atlantas Path To Victory
May 15, 2025 -
 Public Transport Update Bvg Strike Over S Bahn Delays Continue
May 15, 2025
Public Transport Update Bvg Strike Over S Bahn Delays Continue
May 15, 2025
