What Is Creatine And How Does It Work?

Table of Contents
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring organic acid primarily found in skeletal muscle. Its chemical structure is a methylated guanidinoacetic acid, acting as a high-energy phosphate molecule crucial for energy production within muscle cells. Your body naturally produces creatine from the amino acids glycine, arginine, and methionine, primarily in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. However, dietary intake, especially from meat and fish, also contributes to your overall creatine levels. Supplementing with creatine monohydrate increases these stores within your muscles, leading to enhanced performance. Creatine monohydrate is the most researched and popular form due to its proven efficacy and safety.
Key characteristics of creatine include:
- Naturally occurring in the body
- Supports ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production, the primary energy source for muscle contractions.
- Improves muscle strength and power
- Increases muscle mass (hypertrophy)
- Enhances athletic performance across various disciplines.
How Does Creatine Work?
Creatine's primary mechanism of action revolves around the creatine-phosphate energy system. This system is crucial for short bursts of high-intensity activity, such as weightlifting, sprinting, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Creatine is phosphorylated to form phosphocreatine (PCr), a high-energy molecule that acts as a reservoir for phosphate groups. When ATP is broken down during intense exercise, PCr rapidly donates its phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), regenerating ATP and providing immediate energy for muscle contractions.
[Insert Diagram of Creatine-Phosphate Cycle Here]
The creatine-phosphate cycle ensures a rapid replenishment of ATP, delaying muscle fatigue and allowing for greater power output and endurance during high-intensity activities. Beyond ATP regeneration, creatine supplementation also contributes to:
- Increased ATP regeneration
- Enhanced muscle cell hydration, leading to increased muscle size and strength.
- Improved muscle protein synthesis, promoting muscle growth.
- Reduced muscle fatigue, allowing for more intense and longer workouts.
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
Decades of research support the efficacy of creatine supplementation for enhancing athletic performance and muscle growth. Studies consistently demonstrate significant improvements in:
- Muscle strength and power: Creatine supplementation leads to noticeable gains in both maximal strength and power output, particularly in short-duration, high-intensity activities.
- High-intensity exercise performance: Athletes across various disciplines, including weightlifters, sprinters, and HIIT enthusiasts, experience improved performance metrics with creatine supplementation.
- Muscle growth (hypertrophy): Creatine promotes muscle protein synthesis, contributing to increased muscle mass and size.
- Possible cognitive benefits: While more research is needed, some studies suggest potential benefits for cognitive function, such as improved memory and learning. These benefits might be related to creatine's role in brain energy metabolism.
- Faster recovery from exercise: Creatine may aid in faster muscle recovery post-workout, reducing muscle soreness and allowing for more frequent training sessions.
Creatine Safety and Side Effects
Creatine supplementation is generally considered safe for healthy individuals when used as directed. However, like any supplement, potential side effects exist. The most common side effects are usually mild and include:
- Water retention: Creatine attracts water into muscle cells, leading to a temporary increase in body weight. This is generally harmless.
- Stomach cramps: Some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort, such as cramping or bloating.
- Muscle spasms: Rarely, muscle spasms may occur, usually due to dehydration.
It's crucial to maintain adequate hydration while taking creatine to minimize these potential side effects. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, particularly kidney disease, should consult a doctor before starting creatine supplementation.
Key points regarding creatine safety:
- Generally safe for healthy individuals
- Importance of adequate hydration
- Potential for mild side effects (water retention, stomach upset)
- Consult a doctor if you have pre-existing health conditions
Conclusion: Understanding Creatine for Enhanced Performance
Creatine monohydrate is a naturally occurring compound that plays a vital role in muscle energy production. Supplementation effectively increases muscle creatine stores, leading to significant improvements in muscle strength, power, and growth, while also potentially benefiting cognitive function. While generally safe, it's crucial to use creatine responsibly, maintain adequate hydration, and consult a healthcare professional before incorporating it into your routine, especially if you have pre-existing health concerns. Learn more about incorporating creatine into your fitness routine and unlock your athletic potential. Research creatine supplementation further to see how it can benefit you!

Featured Posts
-
 7 12
May 17, 2025
7 12
May 17, 2025 -
 Is Josh Hart The Knicks Version Of Draymond Green Analyzing His Contributions
May 17, 2025
Is Josh Hart The Knicks Version Of Draymond Green Analyzing His Contributions
May 17, 2025 -
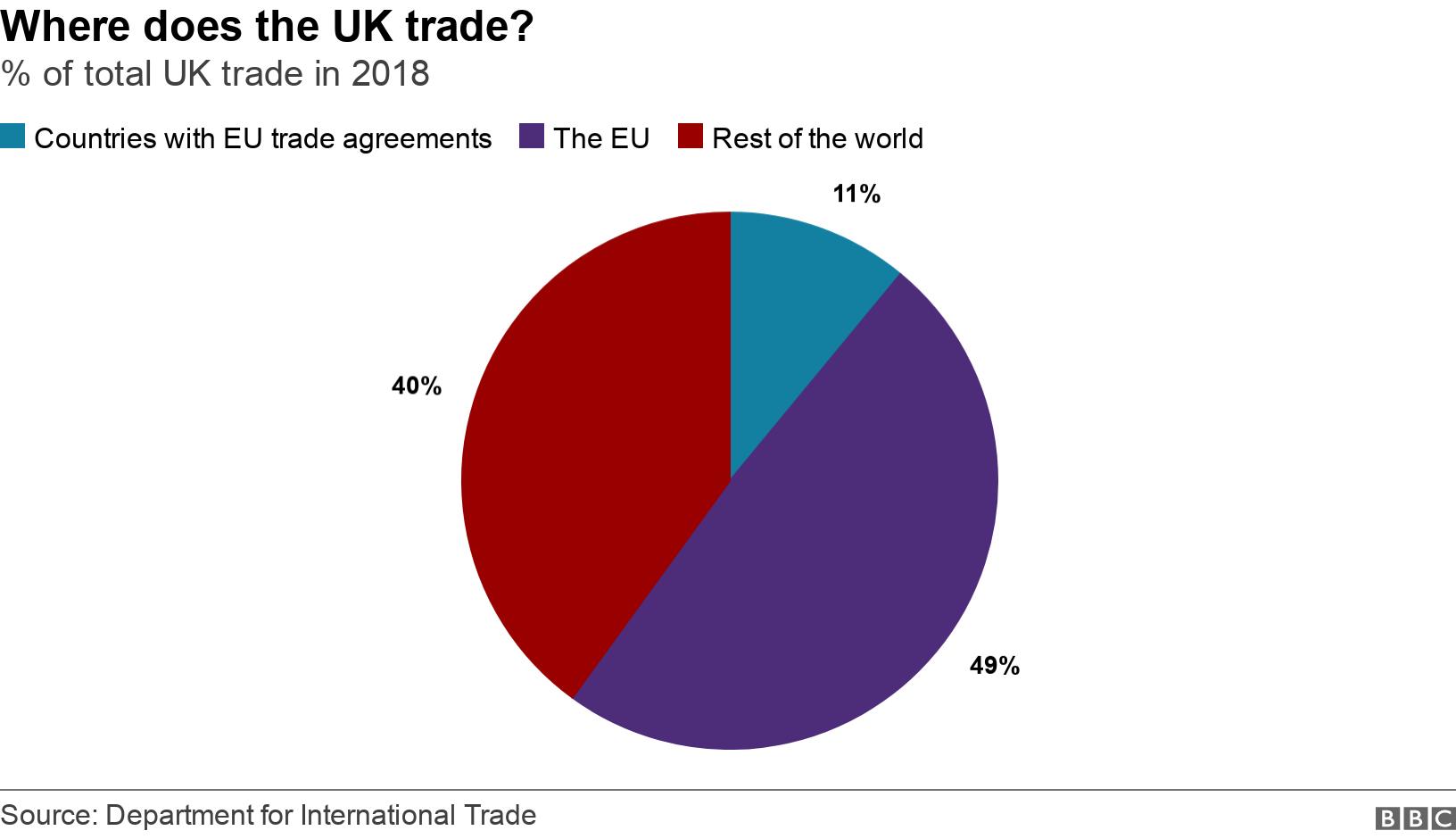 China Open To Formal Trade Deal With Canada Ambassadors Statement
May 17, 2025
China Open To Formal Trade Deal With Canada Ambassadors Statement
May 17, 2025 -
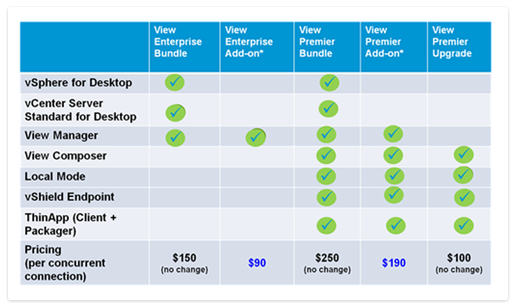 1 050 V Mware Price Increase At And T Sounds Alarm On Broadcoms Proposal
May 17, 2025
1 050 V Mware Price Increase At And T Sounds Alarm On Broadcoms Proposal
May 17, 2025 -
 Lynas The First Heavy Rare Earths Producer Outside Of China
May 17, 2025
Lynas The First Heavy Rare Earths Producer Outside Of China
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Brunson Under Fire Perkins Advice To End Podcast
May 17, 2025
Brunson Under Fire Perkins Advice To End Podcast
May 17, 2025 -
 Nba Analyst Perkins Critiques Brunsons Podcast
May 17, 2025
Nba Analyst Perkins Critiques Brunsons Podcast
May 17, 2025 -
 Detroit Pistons Loss Crew Chief Admits Final Second Non Call Error
May 17, 2025
Detroit Pistons Loss Crew Chief Admits Final Second Non Call Error
May 17, 2025 -
 Week In Review Turning Failures Into Success
May 17, 2025
Week In Review Turning Failures Into Success
May 17, 2025 -
 Crew Chief Admits Wrong Call Cost Detroit Pistons Game
May 17, 2025
Crew Chief Admits Wrong Call Cost Detroit Pistons Game
May 17, 2025
