Wildfires Drive Record-Breaking Global Forest Loss
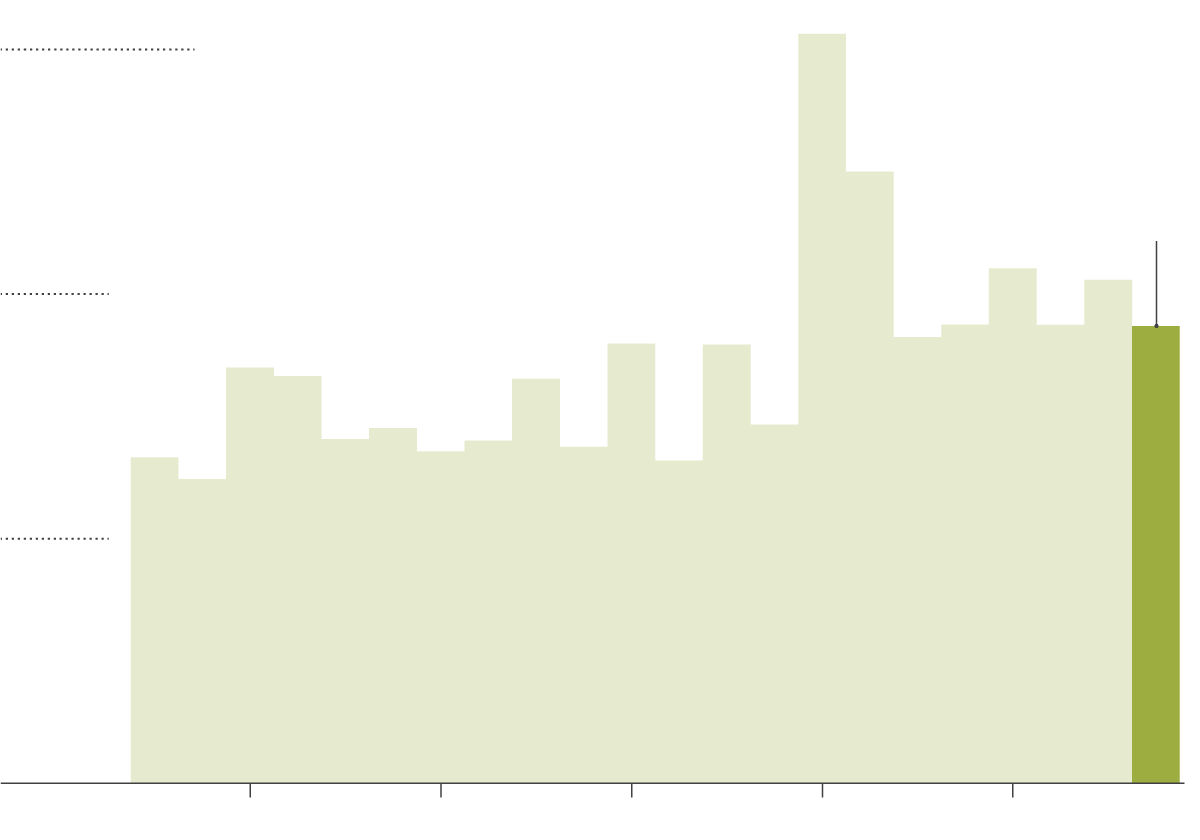
Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires on Global Forests
Wildfires are causing unprecedented destruction to the world's forests, resulting in severe ecological consequences. The scale of forest loss is staggering, with millions of hectares consumed annually. Major wildfire events, such as those witnessed in Australia, the Amazon, and California in recent years, have profoundly impacted specific ecosystems, leaving behind landscapes scarred by fire and loss.
- Quantifiable Loss: Data from organizations like Global Forest Watch show a significant increase in forest area lost to wildfires in the past decade, with specific regions experiencing particularly devastating losses. For example, [Insert statistic on area lost in a specific region and source]. This represents an alarming increase compared to previous years.
- Biodiversity Devastation: Wildfires decimate biodiversity, wiping out habitats and leading to the extinction or endangerment of countless plant and animal species. Endangered species, already vulnerable, are particularly hard hit by the loss of their critical habitats. [Insert example of endangered species affected by wildfires and source].
- Carbon Emissions Surge: The burning of forests releases massive quantities of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, significantly contributing to global warming and climate change. Wildfires are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, accelerating the pace of climate change. [Insert statistic on CO2 emissions from wildfires and source].
- Long-Term Ecological Damage: The consequences of wildfires extend far beyond immediate destruction. Soil health is severely compromised, leading to erosion and reduced fertility. Water cycles are disrupted, causing changes in water availability and quality. The long-term recovery of affected ecosystems can take decades, if not centuries.
Climate Change: A Key Driver of Increased Wildfire Activity
The relationship between climate change and increased wildfire activity is undeniable. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered wind patterns are all contributing to more frequent and intense wildfires. This creates a dangerous feedback loop, where wildfires release more carbon, further accelerating climate change.
- Warmer Temperatures: Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, creating ideal conditions for ignition and rapid fire spread. Even small sparks can ignite dry fuels, leading to large and uncontrolled fires.
- Prolonged Droughts: Extended periods of drought leave forests parched and vulnerable, increasing the flammability of vegetation and creating an environment ripe for wildfires.
- Changing Wind Patterns: Shifts in wind patterns can dramatically influence the spread and intensity of wildfires, causing them to burn faster and cover larger areas.
- Positive Feedback Loop: Wildfires release vast amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect and contributing to higher temperatures, creating a cycle that perpetuates the problem.
Human Activities Contributing to Wildfire Risk
While climate change is a primary driver, human activities significantly exacerbate wildfire risk. Deforestation, poor land management practices, and urban sprawl all contribute to creating more flammable landscapes and increasing the likelihood of devastating fires.
- Deforestation's Role: Clearing forests for agriculture, logging, or urbanization removes natural barriers to fire spread, creating continuous fuel sources.
- Poor Forest Management: The accumulation of dry underbrush and dead trees due to inadequate forest management practices increases the risk of large-scale wildfires.
- Urban Encroachment: Expanding urban areas into forested regions increases the risk of human-caused wildfires and complicates firefighting efforts.
- Agricultural Practices: While controlled burns can be a part of land management, uncontrolled or improperly managed burns can easily escape and escalate into major wildfires.
Combating Wildfires and Protecting Our Forests: Solutions and Strategies
Addressing the crisis of global forest loss due to wildfires requires a multifaceted approach encompassing improved forest management, sustainable forestry practices, climate change mitigation, and international cooperation.
- Improved Forest Management: Implementing techniques like controlled burns and fuel reduction measures helps to reduce the amount of flammable material available for wildfires.
- Sustainable Forestry: Promoting sustainable forestry practices ensures forest health and resilience, making them less susceptible to the impacts of wildfires.
- Climate Action: Addressing climate change is paramount to reducing the frequency and intensity of wildfires. This requires global cooperation to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- International Collaboration: Wildfires are a global problem that requires international collaboration to share best practices, resources, and research.
Conclusion
The record-breaking global forest loss driven by wildfires is a devastating trend with far-reaching consequences. Climate change and human activities are inextricably linked to this crisis, creating a dangerous feedback loop. To protect our forests and mitigate future devastation, we need immediate and concerted action. This includes implementing effective forest management strategies, promoting sustainable forestry practices, aggressively addressing climate change, and fostering international cooperation. Learn more about wildfire prevention, support organizations dedicated to forest conservation and climate action, and advocate for policies that tackle the root causes of this devastating problem. Reduce your carbon footprint and embrace sustainable practices – the future of our forests depends on it.
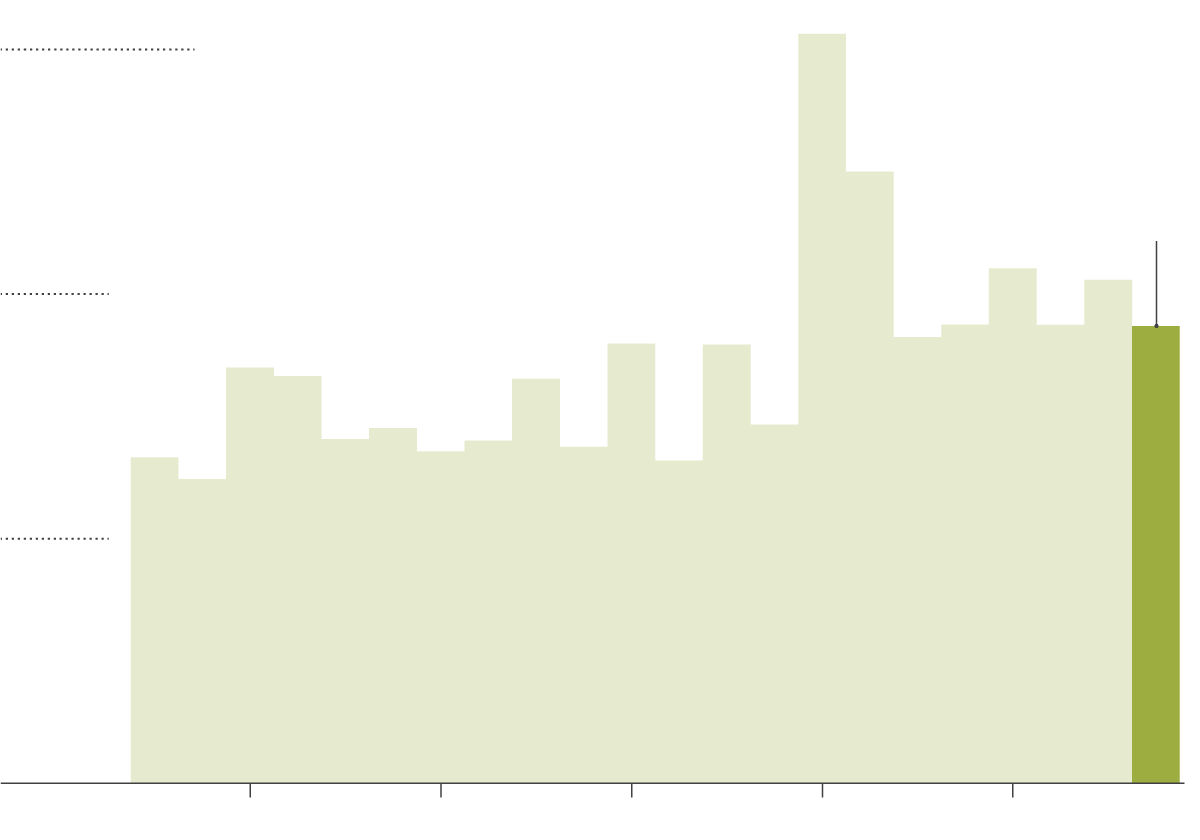
Featured Posts
-
 Boe Rate Cut Probabilities Fall Pound Gains After Uk Inflation Data
May 26, 2025
Boe Rate Cut Probabilities Fall Pound Gains After Uk Inflation Data
May 26, 2025 -
 Jadwal Moto Gp Inggris 2025 Live Streaming Trans7 And Spotv Klasemen Terbaru
May 26, 2025
Jadwal Moto Gp Inggris 2025 Live Streaming Trans7 And Spotv Klasemen Terbaru
May 26, 2025 -
 The Best Office Chairs Of 2025 A Comprehensive Guide
May 26, 2025
The Best Office Chairs Of 2025 A Comprehensive Guide
May 26, 2025 -
 The Painful Truth About Buy And Hold Is The Long Game Worth It
May 26, 2025
The Painful Truth About Buy And Hold Is The Long Game Worth It
May 26, 2025 -
 A Guide To Pride 2024 In The D C Area
May 26, 2025
A Guide To Pride 2024 In The D C Area
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Saeaestae Rahaa Lainan Vertailu Auttaa Loeytaemaeaen Edullisimman Lainan
May 28, 2025
Saeaestae Rahaa Lainan Vertailu Auttaa Loeytaemaeaen Edullisimman Lainan
May 28, 2025 -
 Lainan Vertailu Paras Tapa Loeytaeae Edullisin Laina Korkeiden Korkojen Aikana
May 28, 2025
Lainan Vertailu Paras Tapa Loeytaeae Edullisin Laina Korkeiden Korkojen Aikana
May 28, 2025 -
 Korkeat Korot Ja Edullisempi Laina Vertaile Ja Saeaestae
May 28, 2025
Korkeat Korot Ja Edullisempi Laina Vertaile Ja Saeaestae
May 28, 2025 -
 Kaupallinen Yhteistyoe Lainaa Korkeiden Korkojen Aikaan Loeydae Edullisempi Laina Lainanvertailulla
May 28, 2025
Kaupallinen Yhteistyoe Lainaa Korkeiden Korkojen Aikaan Loeydae Edullisempi Laina Lainanvertailulla
May 28, 2025 -
 Manchester United In 25m Transfer Battle With Liverpool
May 28, 2025
Manchester United In 25m Transfer Battle With Liverpool
May 28, 2025
