Wildfires Intensify Global Forest Loss: A Record-Breaking Year

Table of Contents
The Scale of the Problem: Record-Breaking Wildfire Statistics
The sheer scale of wildfires in 2023 is unprecedented. Vast swathes of forest are burning across the planet, setting new records for hectares burned and leaving a trail of destruction in their wake.
Geographic Distribution of Wildfires:
Major regions across the globe are suffering immensely. The Amazon rainforest, a crucial carbon sink and biodiversity hotspot, has experienced a significant increase in wildfire activity. Similarly, Siberia has witnessed extensive forest fires, releasing massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. California and other parts of the western United States continue to grapple with devastating wildfires, while Australia is still recovering from the extensive bushfires of recent years.
- Amazon: Over X million hectares burned (compare to previous years' data). Brazil, Colombia, and Peru are particularly hard hit.
- Siberia: Y million hectares affected, contributing significantly to global carbon emissions. Russia struggles with containment and resource allocation.
- California: Z acres lost, devastating communities and infrastructure. The state faces ongoing challenges with drought and forest management.
- Australia: Continued impact from previous years' bushfires, with lingering ecological consequences. Reforestation efforts are underway but face significant challenges.
Types of Forests Affected:
The impact extends across diverse forest ecosystems. Boreal forests, vital carbon sinks, are particularly vulnerable to wildfires, leading to significant carbon emissions. Rainforests, already threatened by deforestation, suffer immense biodiversity loss from intense fires. Temperate forests, crucial for water cycles and supporting a wide variety of species, are also severely impacted.
- Boreal Forests: Increased vulnerability due to climate change-induced drought and warmer temperatures. Significant carbon release contributes to climate change feedback loop.
- Rainforests: Wildfires exacerbate deforestation, driving species extinction and further disrupting delicate ecosystems. Recovery is slow and challenging.
- Temperate Forests: Damage to water cycles and soil stability. Loss of timber resources and economic impact on local communities.
The Economic and Social Costs:
The economic and social costs of these record-breaking wildfires are staggering. Damage to infrastructure, lost timber resources, and the downturn in tourism represent significant economic losses. Communities are displaced, livelihoods are destroyed, and the health impacts of wildfire smoke are far-reaching.
- Economic Losses: Billions of dollars in damage to property, infrastructure, and lost timber revenue (provide specific estimates if possible).
- Displacement: Thousands of people displaced from their homes, requiring substantial humanitarian aid and resettlement efforts.
- Health Impacts: Increased respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular issues, and other health problems linked to prolonged exposure to wildfire smoke.
Underlying Causes: The Complex Interplay of Factors
The intensification of wildfires is not a single-cause phenomenon. It’s a complex interplay of climate change, human activities, and increasingly extreme weather patterns.
Climate Change and its Role:
Rising global temperatures are creating drier conditions, extending wildfire seasons, and increasing the intensity of fires. This creates a dangerous feedback loop: wildfires release vast amounts of carbon dioxide, further accelerating climate change and fueling future fire events.
- Rising Temperatures: Increased frequency and intensity of heatwaves lead to drier vegetation, creating highly flammable conditions.
- Drought Conditions: Extended periods of drought leave forests parched and vulnerable to ignition.
- Feedback Loop: Wildfires release significant amounts of carbon dioxide, exacerbating climate change and increasing the risk of future wildfires.
Human Activities and Deforestation:
Human activities such as deforestation, land-clearing for agriculture, and unsustainable forest management practices contribute significantly to wildfire risk. Removing trees creates drier, more flammable landscapes, increasing the speed and intensity of fire spread.
- Deforestation: Removal of trees creates continuous fuel for fires, increasing the intensity and spread of wildfires.
- Land-Clearing: Agricultural practices and urbanization often encroach on forested areas, leading to fragmentation and increased wildfire risk.
- Poor Forest Management: Lack of controlled burns and inadequate forest thinning can lead to the buildup of flammable material, making forests more susceptible to intense wildfires.
Extreme Weather Patterns:
Heatwaves, droughts, and strong winds create "perfect storms" for wildfires. The increased frequency and intensity of these extreme weather events, linked to climate change, are exacerbating the problem.
- Heatwaves: Extreme heat dries out vegetation, creating highly flammable conditions and increasing the risk of spontaneous ignition.
- Droughts: Prolonged periods of drought leave forests exceptionally vulnerable, creating ideal fuel for intense wildfires.
- Strong Winds: High winds rapidly spread wildfires, making them extremely difficult to control and increasing the area burned.
Consequences of Wildfire Intensification: Beyond Immediate Damage
The consequences of intensified wildfires extend far beyond the immediate damage. The impact on biodiversity, air quality, and long-term ecological health are profound and long-lasting.
Biodiversity Loss:
Wildfires cause devastating biodiversity loss, impacting countless plant and animal species. Habitat destruction, direct mortality, and disruption of ecological processes lead to long-term consequences for ecosystems.
- Habitat Loss: Wildfires destroy vital habitats, leading to population declines and potentially extinctions of vulnerable species.
- Direct Mortality: Many animals are killed directly by the fires, while others are injured or displaced.
- Disrupted Ecosystems: Wildfires can significantly alter the structure and function of ecosystems, impacting food webs and ecological processes.
Air Quality Degradation:
Wildfire smoke contains harmful pollutants that severely impact air quality, posing significant health risks to humans and animals. Exposure to wildfire smoke can cause respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues.
- Respiratory Illnesses: Wildfire smoke can trigger asthma attacks, bronchitis, and other respiratory problems.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Exposure to fine particulate matter in wildfire smoke increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Other Health Problems: Wildfire smoke can also cause eye irritation, skin problems, and other health issues.
Long-Term Ecological Impacts:
The long-term ecological consequences of wildfires can be substantial. Soil erosion, changes in water quality, and reduced carbon sequestration capacity affect forest regeneration and ecosystem services.
- Soil Erosion: Wildfires remove vegetation cover, leaving soil exposed to erosion and degradation.
- Water Quality Degradation: Ash and other pollutants from wildfires can contaminate water sources, affecting water quality and availability.
- Reduced Carbon Sequestration: Damaged forests have a reduced capacity to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Conclusion:
The record-breaking wildfire activity of 2023 underscores the severity of the global forest loss crisis. Climate change, human activities, and extreme weather patterns are synergistically driving this escalating problem. The consequences— biodiversity loss, air pollution, and long-term ecological damage— are profound and demand immediate action. We must fight against global forest loss by addressing the root causes of wildfires. Learn more about the issue and support organizations working on forest conservation, reforestation efforts, and climate action to combat record-breaking wildfire events. Take action against wildfires today; the future of our forests depends on it. Advocate for stronger policies promoting sustainable forest management practices and mitigating the effects of climate change. Join the fight against global forest loss and help protect our planet's precious resources.

Featured Posts
-
 Pivdenniy Mist Detali Remontu Pidryadniki Ta Finansuvannya
May 23, 2025
Pivdenniy Mist Detali Remontu Pidryadniki Ta Finansuvannya
May 23, 2025 -
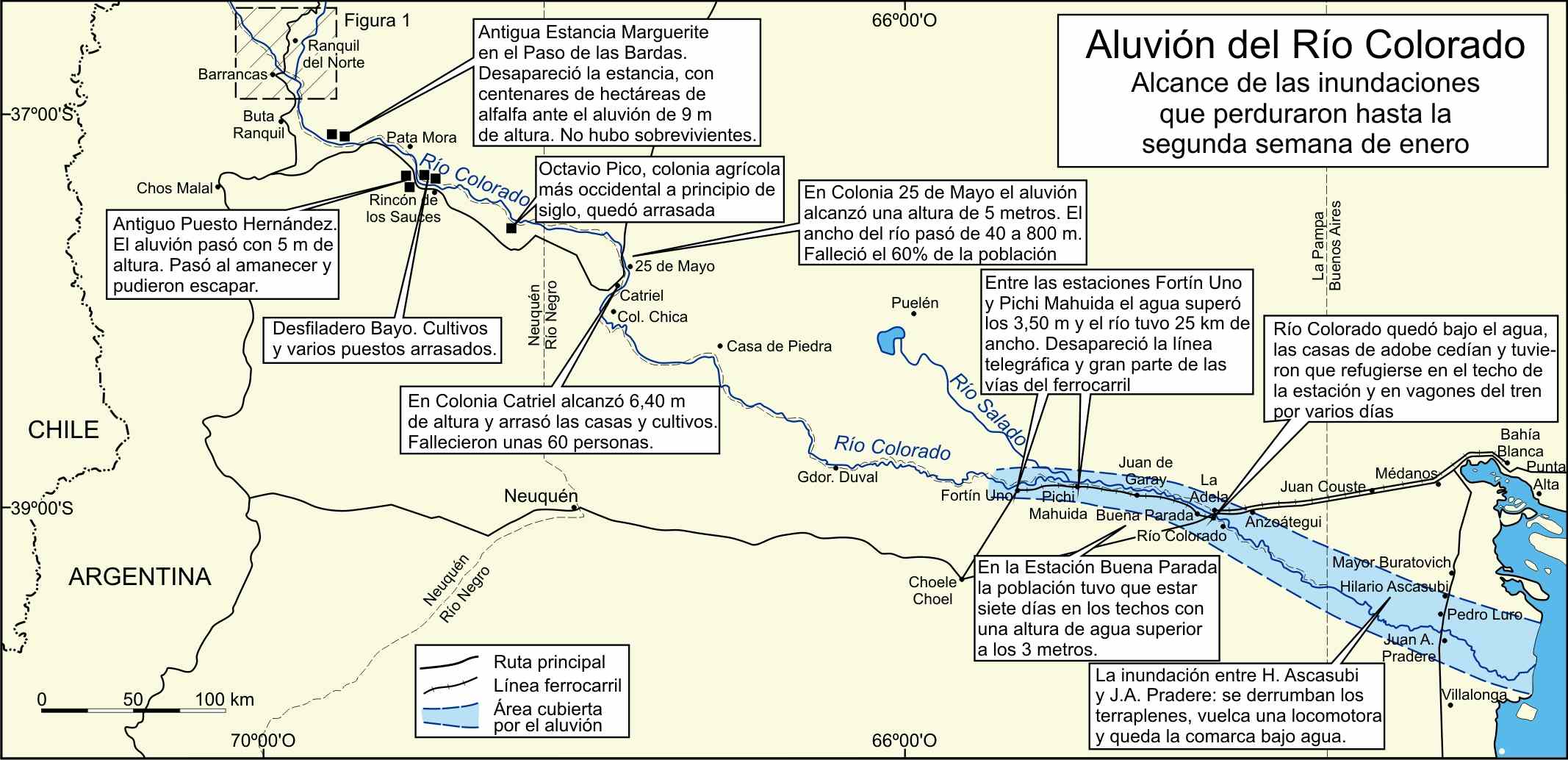 Real Sociedad Sin Descanso Ahogada Por El Aluvion De Partidos Del Virus Fifa
May 23, 2025
Real Sociedad Sin Descanso Ahogada Por El Aluvion De Partidos Del Virus Fifa
May 23, 2025 -
 Effondrement De Route A Seoul Un Motard Perd La Vie
May 23, 2025
Effondrement De Route A Seoul Un Motard Perd La Vie
May 23, 2025 -
 Police Source Kartel Restrictions For His Own Protection Trinidad And Tobago Newsday
May 23, 2025
Police Source Kartel Restrictions For His Own Protection Trinidad And Tobago Newsday
May 23, 2025 -
 El Virus Fifa La Real Sociedad Atrapada En Un Calendario Incesante
May 23, 2025
El Virus Fifa La Real Sociedad Atrapada En Un Calendario Incesante
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 2025 Memorial Day Weekend Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 23, 2025
2025 Memorial Day Weekend Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 23, 2025 -
 Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 23, 2025 -
 Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Ocean City Rehoboth And Sandy Point Beach Forecast
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Ocean City Rehoboth And Sandy Point Beach Forecast
May 23, 2025 -
 2025 Umd Graduation Kermit The Frog To Deliver Commencement Address
May 23, 2025
2025 Umd Graduation Kermit The Frog To Deliver Commencement Address
May 23, 2025 -
 University Of Maryland Graduation A Notable Amphibians Inspiring Speech
May 23, 2025
University Of Maryland Graduation A Notable Amphibians Inspiring Speech
May 23, 2025
