$9 Billion Budget Boost: Australia's Opposition Outlines Economic Recovery Strategy
Table of Contents
Key Pillars of the $9 Billion Economic Recovery Plan
The opposition's $9 billion economic recovery plan centers on three key pillars: creating green jobs through infrastructure investment, providing targeted support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and investing in education and skills training to address the skills gap. These initiatives aim to stimulate economic growth, reduce unemployment, and improve the overall standard of living for Australians.
-
Investment in Renewable Energy and Infrastructure Projects (Green Jobs, Infrastructure Spending): The plan earmarks significant funds for upgrading Australia's infrastructure, focusing on renewable energy projects. This includes investments in wind farms, solar energy facilities, and smart grid technologies. This strategy aims to create thousands of "green jobs" while simultaneously modernizing the nation's infrastructure. Specific projects may include the expansion of high-speed rail networks and the construction of new renewable energy generation plants.
-
Targeted Support for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) (SME Support, Small Business Recovery): Recognizing the crucial role of SMEs in the Australian economy, the plan includes substantial support for these businesses. This includes tax breaks, grants, and access to low-interest loans to help them navigate economic uncertainty and invest in growth. The plan also focuses on reducing red tape and simplifying regulations to make it easier for SMEs to operate.
-
Increased Funding for Education and Skills Training Programs (Skills Gap, Workforce Development): The plan addresses the growing skills gap in the Australian workforce by investing heavily in education and training programs. This includes funding for vocational training, apprenticeships, and university scholarships, particularly in high-demand fields like technology, healthcare, and renewable energy. The aim is to ensure the Australian workforce has the skills needed to thrive in a rapidly changing economy.
-
Measures to Address Cost of Living Pressures (Cost of Living Crisis, Inflation Relief): The plan acknowledges the significant strain on household budgets caused by rising inflation. Proposed measures include targeted tax relief for low- and middle-income earners, increased welfare payments, and initiatives to reduce the cost of essential goods and services.
Detailed Breakdown of Funding Allocations
The $9 billion budget boost is strategically allocated across the key pillars. While precise figures may vary pending parliamentary approval, preliminary allocations suggest:
-
Infrastructure Projects: Approximately $3 billion is allocated to infrastructure projects, including $1.5 billion for renewable energy initiatives and $1 billion for road and rail upgrades. This aims to stimulate economic activity and create jobs in the construction sector.
-
SME Support: $2 billion is earmarked for SMEs, with a combination of grants (up to $50,000 per business for eligible projects), low-interest loans, and tax incentives. Eligibility criteria will likely focus on businesses demonstrating strong growth potential and a commitment to job creation.
-
Education and Skills Training: $2.5 billion is allocated to enhance education and skills training programs, with specific amounts distributed based on regional needs and national skills priorities. This may include funding for university research in renewable energy and technology, as well as apprenticeships in the trades.
-
Cost of Living Relief: $1.5 billion is dedicated to mitigating the cost of living crisis, possibly through temporary tax cuts, direct welfare payments, and subsidies for essential goods. Specific mechanisms will require further detail.
Potential Economic Impacts and Challenges
The opposition's economic recovery strategy holds significant potential, but also presents challenges.
-
Projected Job Creation: The plan aims to create hundreds of thousands of jobs across various sectors, including construction, renewable energy, and technology.
-
Impact on Inflation: While stimulating economic growth, the plan’s impact on inflation needs careful consideration. Increased government spending could potentially fuel inflation, requiring careful management of monetary policy.
-
Fiscal Sustainability: The $9 billion injection will increase government debt. The long-term fiscal sustainability of this plan depends on strong economic growth and effective management of government finances.
-
Unintended Consequences: Potential unintended consequences could include distortions in specific markets due to targeted subsidies, or skills mismatches if training programs don't align perfectly with industry needs.
Comparison with the Government's Economic Strategy (Optional)
A comparison with the current government's economic strategy would require detailed analysis of the government's budget and economic policy. This could reveal key differences in approaches to infrastructure investment, SME support, and cost of living relief. For instance, the government might prioritize different infrastructure projects or offer different levels of SME support. Analyzing these differences would offer valuable insight into the comparative merits of each approach.
Conclusion: Analyzing Australia's Opposition $9 Billion Economic Recovery Strategy
The opposition's $9 billion economic recovery strategy presents a comprehensive plan addressing key challenges facing the Australian economy. Its focus on green jobs, SME support, education, and cost of living relief offers potential for significant economic growth and job creation. However, careful consideration of the potential inflationary pressures and long-term fiscal implications is crucial. Learning more about the details of this crucial $9 billion budget boost and its potential impact on the Australian economy is essential for informed public discourse. Share your thoughts on the effectiveness of this proposed economic recovery strategy in the comments below!

Featured Posts
-
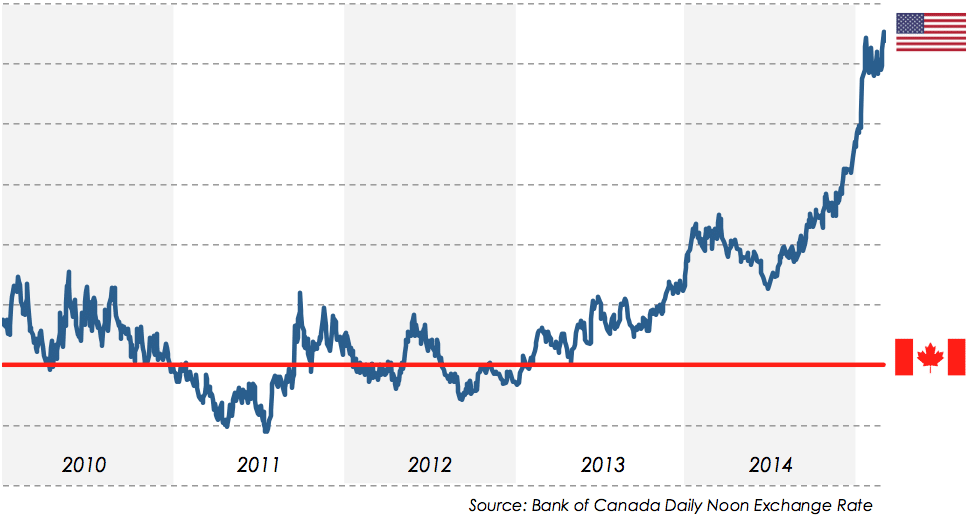 Canadian Dollar Strengthens After Trumps Carney Deal Comment
May 03, 2025
Canadian Dollar Strengthens After Trumps Carney Deal Comment
May 03, 2025 -
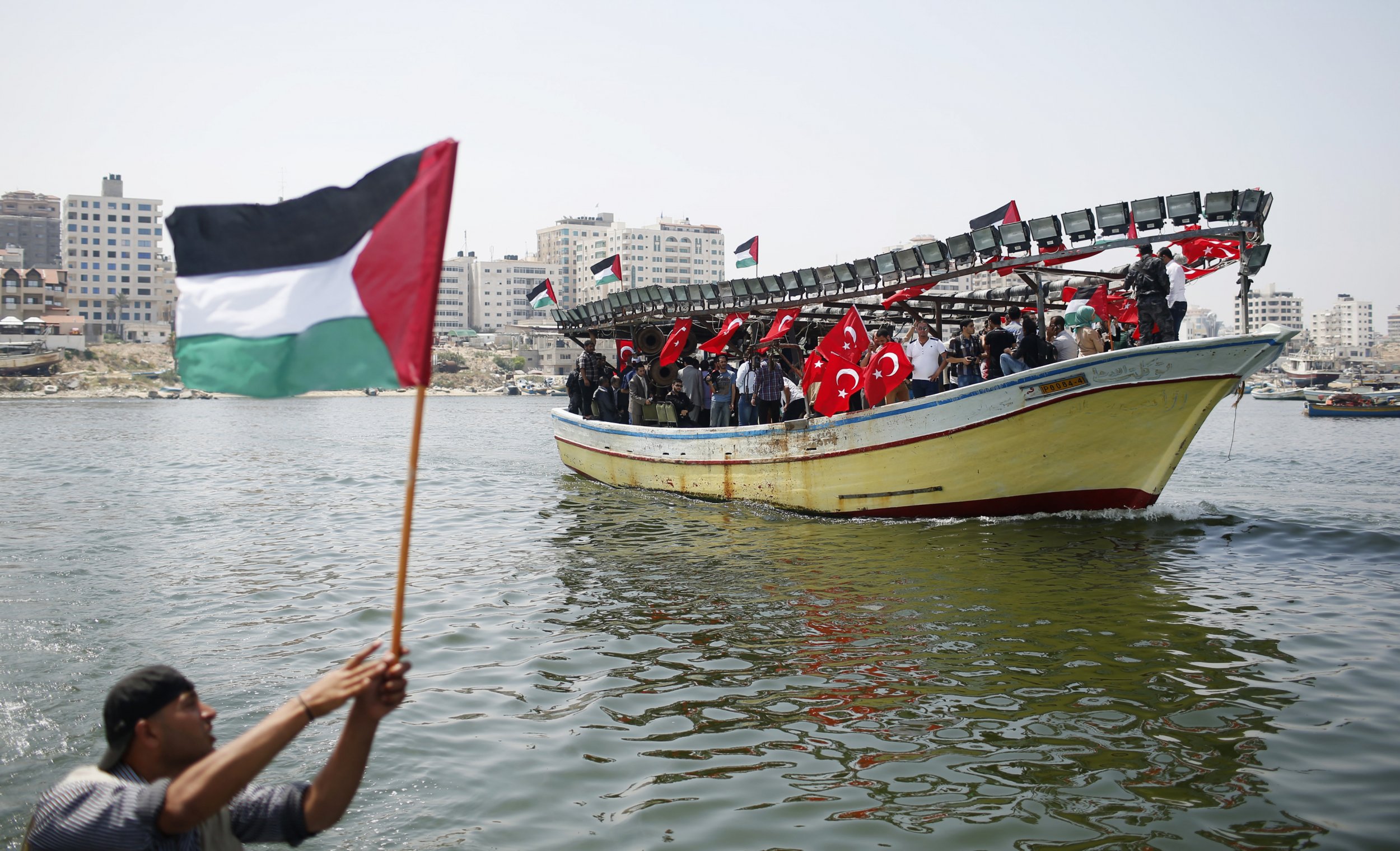 Drone Attack On Ship Near Malta Freedom Flotilla Coalitions Statement
May 03, 2025
Drone Attack On Ship Near Malta Freedom Flotilla Coalitions Statement
May 03, 2025 -
 Fortnite V34 30 Update Details Sabrina Carpenter Skin Gameplay And Downtime
May 03, 2025
Fortnite V34 30 Update Details Sabrina Carpenter Skin Gameplay And Downtime
May 03, 2025 -
 Fortnite Server Status How Long Will Chapter 6 Season 2 Maintenance Last
May 03, 2025
Fortnite Server Status How Long Will Chapter 6 Season 2 Maintenance Last
May 03, 2025 -
 This Iconic Band Will Only Play At A Music Festival Under One Extreme Condition
May 03, 2025
This Iconic Band Will Only Play At A Music Festival Under One Extreme Condition
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Malta Coast Attack Gaza Freedom Flotilla Reports Incident
May 03, 2025
Malta Coast Attack Gaza Freedom Flotilla Reports Incident
May 03, 2025 -
 Graeme Souness On Manchester Uniteds Failed Transfer Strategy
May 03, 2025
Graeme Souness On Manchester Uniteds Failed Transfer Strategy
May 03, 2025 -
 Gaza Flotilla Under Attack Latest Updates From Malta
May 03, 2025
Gaza Flotilla Under Attack Latest Updates From Malta
May 03, 2025 -
 Freedom Flotilla Coalition Reports Drone Attack Off Maltese Coast
May 03, 2025
Freedom Flotilla Coalition Reports Drone Attack Off Maltese Coast
May 03, 2025 -
 Souness Condemns Manchester Uniteds Latest Transfer Move
May 03, 2025
Souness Condemns Manchester Uniteds Latest Transfer Move
May 03, 2025
