Addressing The New COVID-19 LP.8.1 Variant
Table of Contents
Understanding the Spread and Transmission of the COVID-19 LP.8.1 Variant
The transmissibility of the COVID-19 LP.8.1 variant is currently under investigation. While data is still being collected and analyzed, preliminary findings suggest [insert information on transmissibility compared to other variants, e.g., "a potential increase in transmissibility compared to earlier Omicron subvariants"]. The role of vaccination status and prior immunity in influencing transmission rates is also a key area of ongoing research. Initial studies suggest [insert information about the impact of vaccination and prior infection on transmission]. Geographic areas showing higher prevalence of the LP.8.1 variant are [insert specific geographic regions if available, citing sources].
- Transmission Routes: Like previous variants, the LP.8.1 variant is believed to spread primarily through airborne transmission via respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Close contact with infected individuals also poses a risk.
- Incubation Period: The estimated incubation period is [insert estimated incubation period, citing source].
- R0 Value: The basic reproduction number (R0) for the LP.8.1 variant is [insert R0 value if available and cite source. If unavailable, state this clearly]. Further research is needed to determine the precise R0 value.
- Transmission Dynamics: Current research focuses on understanding the factors contributing to the LP.8.1 variant's spread, including its ability to evade immune responses and its potential for increased replication.
Symptoms Associated with the COVID-19 LP.8.1 Variant
While the symptoms of the COVID-19 LP.8.1 variant are largely similar to those seen in previous variants, there may be subtle differences. [Insert information on symptom similarities and differences compared to previous variants, e.g., "Many individuals experience the common symptoms seen in previous waves, including fever, cough, and fatigue. However, some reports suggest a higher prevalence of..."]. The severity of symptoms can range from mild to severe, and the long-term effects (Long COVID) are still being investigated.
- Common Symptoms: Fever, cough, fatigue, sore throat, runny nose, headache, muscle aches, loss of taste or smell.
- Less Common Symptoms: [Insert less common symptoms reported, if any, citing sources].
- Long COVID Implications: [Insert information about potential long-term implications, citing sources. If not yet known, state clearly that this is an area of ongoing research].
- Severity Compared to Other Variants: [Compare the observed severity of LP.8.1 with previous variants, referencing data on hospitalization and mortality rates].
Severity and Risk Factors of the COVID-19 LP.8.1 Variant
The severity of illness caused by the COVID-19 LP.8.1 variant is currently being assessed. Initial data suggests [insert data on hospitalization and mortality rates, citing sources]. As with previous variants, certain groups are at higher risk of severe illness.
- Hospitalization Rates and ICU Admissions: [Insert data on hospitalization and ICU admission rates, citing sources].
- Mortality Rates Compared to Other Variants: [Insert data comparing mortality rates to previous variants, citing sources].
- Risk Factors: Older adults, individuals with underlying health conditions (such as heart disease, lung disease, diabetes, and weakened immune systems), and unvaccinated individuals are at increased risk of severe illness.
- Impact on Healthcare Infrastructure: [Discuss the potential impact on healthcare systems, considering the strain on resources and capacity].
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies for the COVID-19 LP.8.1 Variant
Preventing the spread of the COVID-19 LP.8.1 variant relies on the same effective strategies used against previous variants.
- Vaccination Recommendations: Staying up-to-date with COVID-19 vaccinations, including booster shots, remains crucial for reducing the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death. [Specify recommended vaccine types and timing].
- Hand Hygiene and Respiratory Etiquette: Frequent handwashing with soap and water or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding touching your face are essential.
- Mask Recommendations: Wearing a well-fitting mask, particularly in crowded indoor settings or when interacting with vulnerable individuals, can significantly reduce transmission. [Specify recommended mask types].
- Testing Strategies: Rapid antigen tests and PCR tests can help identify infected individuals, facilitating isolation and preventing further spread.
- Isolation and Quarantine Guidelines: Following isolation and quarantine guidelines when experiencing symptoms or testing positive is vital to limiting transmission.
Conclusion: Staying Informed About the COVID-19 LP.8.1 Variant and Moving Forward
The COVID-19 LP.8.1 variant highlights the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive measures. Understanding its spread, symptoms, severity, and the importance of preventative measures is crucial for protecting ourselves and our communities. Staying informed through reliable sources like the WHO and CDC is essential. By taking proactive steps – getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, and following public health guidelines – we can collectively mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 LP.8.1 variant and future variants. Continue to monitor updates on the COVID-19 LP.8.1 variant from reputable sources and take necessary precautions to protect your health and the health of others. [Insert links to relevant WHO and CDC resources].

Featured Posts
-
 Uk Veterinary Care The Impact Of Corporate Targets On Pet Owners
May 31, 2025
Uk Veterinary Care The Impact Of Corporate Targets On Pet Owners
May 31, 2025 -
 1 050 V Mware Price Jump At And Ts Concerns Over Broadcoms Acquisition
May 31, 2025
1 050 V Mware Price Jump At And Ts Concerns Over Broadcoms Acquisition
May 31, 2025 -
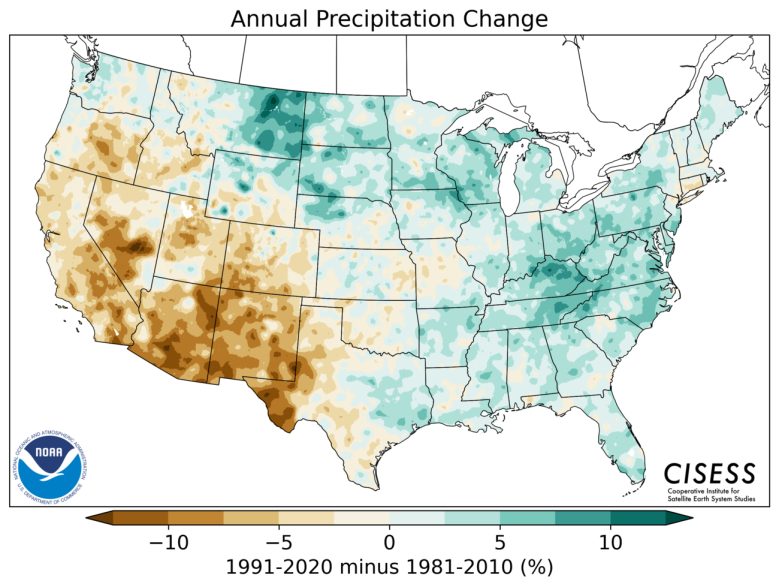 Increased Precipitation In Western Massachusetts Due To Climate Change
May 31, 2025
Increased Precipitation In Western Massachusetts Due To Climate Change
May 31, 2025 -
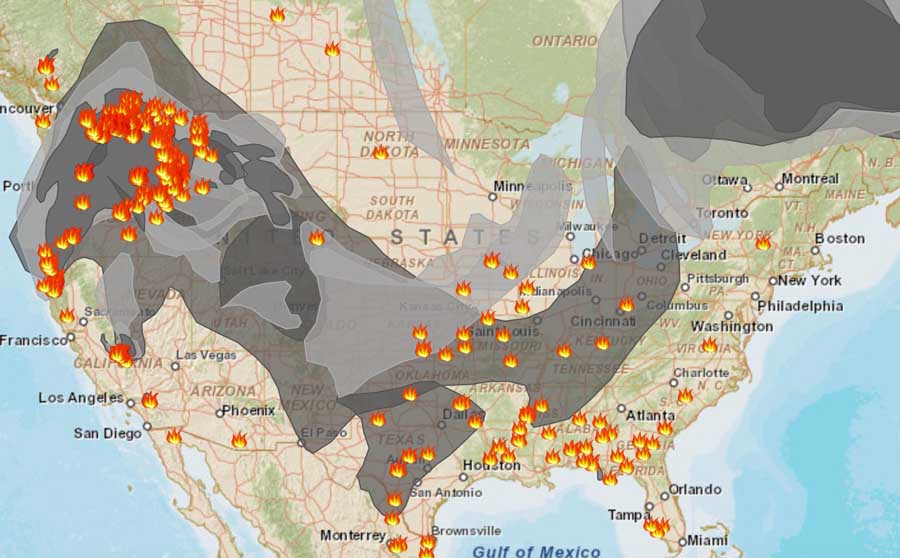 Wildfire Smoke Impact New York Citys 3 C Temperature Decrease And Elevated Air Pollutants
May 31, 2025
Wildfire Smoke Impact New York Citys 3 C Temperature Decrease And Elevated Air Pollutants
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguia Denies Doping Allegations After Positive Test
May 31, 2025
Munguia Denies Doping Allegations After Positive Test
May 31, 2025
