Electric Motor Independence: Breaking Free From China's Grip
Table of Contents
The Current State of Electric Motor Dependence on China
China's dominance in the electric motor industry is multifaceted, stemming from control over both raw materials and manufacturing processes. This dependence creates significant risks for global supply chains.
China's Dominance in Rare Earth Minerals
China controls a significant portion of the mining and processing of rare earth minerals, crucial for the production of high-performance electric motors. These minerals, including neodymium and dysprosium, are essential for the powerful permanent magnets found in many electric motors.
- Statistics: China currently controls over 70% of global rare earth mineral production and processing.
- Geopolitical Implications: This dominance grants China considerable leverage in global markets, influencing pricing and potentially disrupting supply.
- Price Manipulation: The concentrated control allows for potential price manipulation, impacting the cost and availability of electric motors worldwide. This control extends beyond just the raw materials; processing these minerals into usable forms for magnets is also highly concentrated in China.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Concentration
Beyond raw materials, a significant portion of electric motor manufacturing and component production is concentrated in China. This creates further vulnerabilities in the global supply chain.
- Key Chinese Manufacturers: Numerous major electric motor manufacturers and component suppliers are based in China, solidifying its position in the global market.
- Supply Chain Complexity: The intricate global supply chains for electric motors often rely heavily on Chinese manufacturing hubs, leading to potential bottlenecks.
- Transportation Bottlenecks: Reliance on specific Chinese ports and transportation infrastructure for shipping components adds another layer of risk, making the system vulnerable to disruptions.
Strategies for Achieving Electric Motor Independence
Breaking free from China's grip on the electric motor industry requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on diversification, domestic manufacturing, and technological innovation.
Diversifying Raw Material Sources
Reducing dependence on Chinese rare earth minerals necessitates exploring and developing alternative sources.
- Investment in Mining and Processing: Increased investment in mining and processing operations in other countries, such as Australia, the US, and Canada, is crucial.
- Recycling and Reuse: Developing robust recycling and reuse programs for rare earth elements will help reduce reliance on new mining and improve sustainability.
- Challenges: Establishing new supply chains presents challenges, including the environmental impact of mining and geopolitical considerations in securing stable access to resources.
Fostering Domestic Manufacturing
Governments can play a vital role in supporting the growth of domestic electric motor manufacturing.
- Government Incentives: Providing tax breaks, subsidies, and other incentives to attract electric motor manufacturers to domestic markets.
- Research and Development: Investing heavily in research and development to improve domestic manufacturing capabilities and technological advancements.
- Skills Development: Implementing training programs to develop the skilled workforce needed for domestic electric motor production.
- Economic Benefits: Reshoring electric motor production creates jobs, boosts domestic GDP, and fosters technological advancement.
Technological Innovation
Innovation in electric motor design and materials science can significantly reduce reliance on rare earth elements.
- Alternative Motor Designs: Research and development efforts focused on alternative motor designs that require fewer or no rare earth elements.
- Material Science Advancements: Exploring and developing alternative materials, such as silicon carbide, for use in electric motor components.
- Permanent Magnet Technology: Advancements in permanent magnet technology that utilize less rare earth materials while maintaining high performance. These innovations improve sustainability and reduce dependence on volatile global markets.
The Economic and Geopolitical Implications of Electric Motor Independence
Achieving electric motor independence offers significant economic and geopolitical advantages.
Enhanced National Security
Reduced dependence on a single nation for critical technologies strengthens national security.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Diversification minimizes the risk of supply chain disruptions caused by geopolitical instability or other unforeseen events.
- Geopolitical Leverage: Reducing China's leverage in the electric motor market enhances a nation's overall geopolitical standing.
- Technological Self-Reliance: It fosters technological self-reliance, a critical aspect of national security in the modern era.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
Domestic electric motor production can stimulate economic growth and create high-skilled jobs.
- Investment Opportunities: The development of a domestic electric motor industry attracts investment and stimulates related industries.
- Skilled Labor: The industry requires a skilled workforce, creating jobs in engineering, manufacturing, and related fields.
- Economic Benefits: The economic benefits extend beyond job creation, including increased GDP, export potential, and technological advancements.
Conclusion
Achieving electric motor independence is crucial for national security, economic resilience, and a stable global supply chain. By diversifying raw material sources, fostering domestic manufacturing, and driving technological innovation, nations can break free from over-reliance on any single nation. This requires a concerted effort from governments, industries, and researchers to prioritize electric motor independence and actively invest in building a resilient and diversified ecosystem. Take the first step towards electric motor independence today—invest in domestic production and support sustainable supply chains.

Featured Posts
-
 Au Roeulx Eneco Lance Le Plus Grand Projet De Stockage D Energie De Belgique
May 04, 2025
Au Roeulx Eneco Lance Le Plus Grand Projet De Stockage D Energie De Belgique
May 04, 2025 -
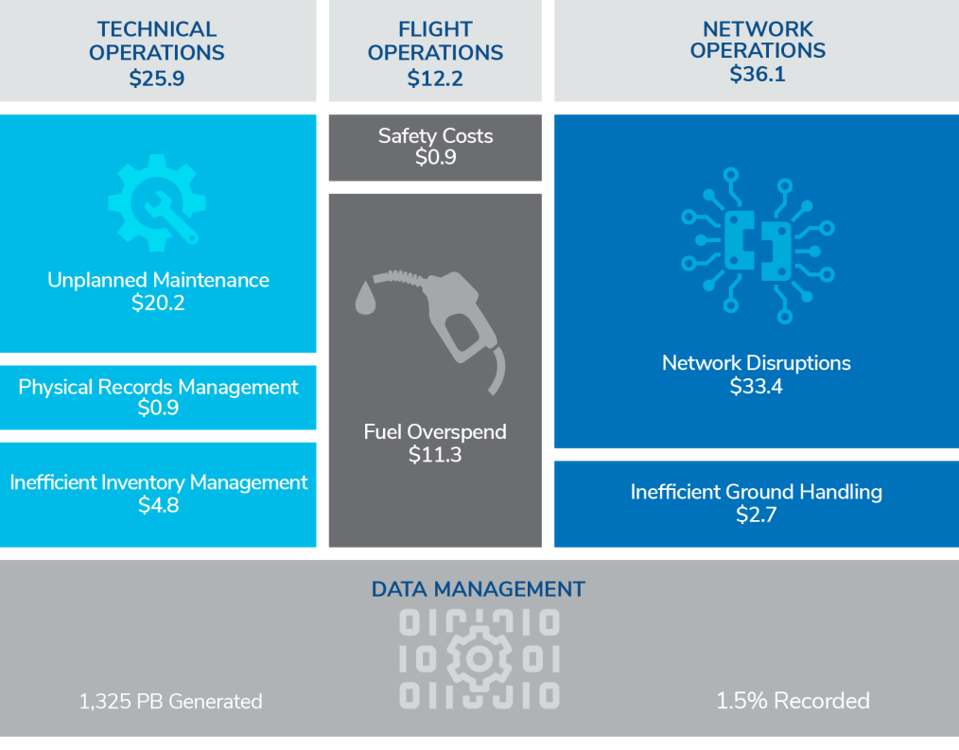 The Impact Of Oil Supply Instability On Airline Operations And Finances
May 04, 2025
The Impact Of Oil Supply Instability On Airline Operations And Finances
May 04, 2025 -
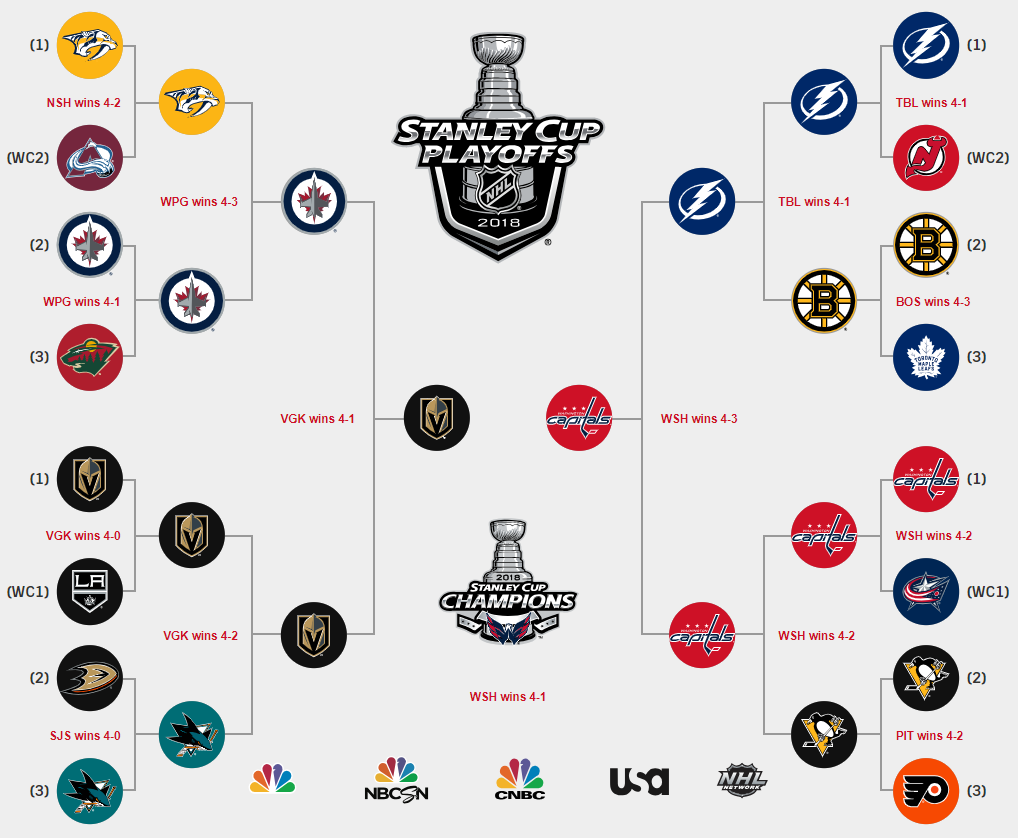 Nhl Stanley Cup Playoffs What To Expect In The First Round
May 04, 2025
Nhl Stanley Cup Playoffs What To Expect In The First Round
May 04, 2025 -
 Zakharova O Situatsii S Makronami Kommentariy I Reaktsiya
May 04, 2025
Zakharova O Situatsii S Makronami Kommentariy I Reaktsiya
May 04, 2025 -
 How Rising Oil Prices Are Impacting Airlines And Passengers
May 04, 2025
How Rising Oil Prices Are Impacting Airlines And Passengers
May 04, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Anna Kendricks Body Language During Blake Lively Interview Sparks Fan Discussion
May 04, 2025
Anna Kendricks Body Language During Blake Lively Interview Sparks Fan Discussion
May 04, 2025 -
 Anna Kendrick Silent On Blake Lively Lawsuit At Premiere
May 04, 2025
Anna Kendrick Silent On Blake Lively Lawsuit At Premiere
May 04, 2025 -
 Understanding The Alleged Blake Lively And Anna Kendrick Dispute
May 04, 2025
Understanding The Alleged Blake Lively And Anna Kendrick Dispute
May 04, 2025 -
 The Blake Lively And Anna Kendrick Feud Truth Or Fiction
May 04, 2025
The Blake Lively And Anna Kendrick Feud Truth Or Fiction
May 04, 2025 -
 Is Anna Kendrick Essential For The Accountant 3 Evidence From The Accountant 2
May 04, 2025
Is Anna Kendrick Essential For The Accountant 3 Evidence From The Accountant 2
May 04, 2025
