Gas Prices Up 20 Cents: What's Driving The Increase?
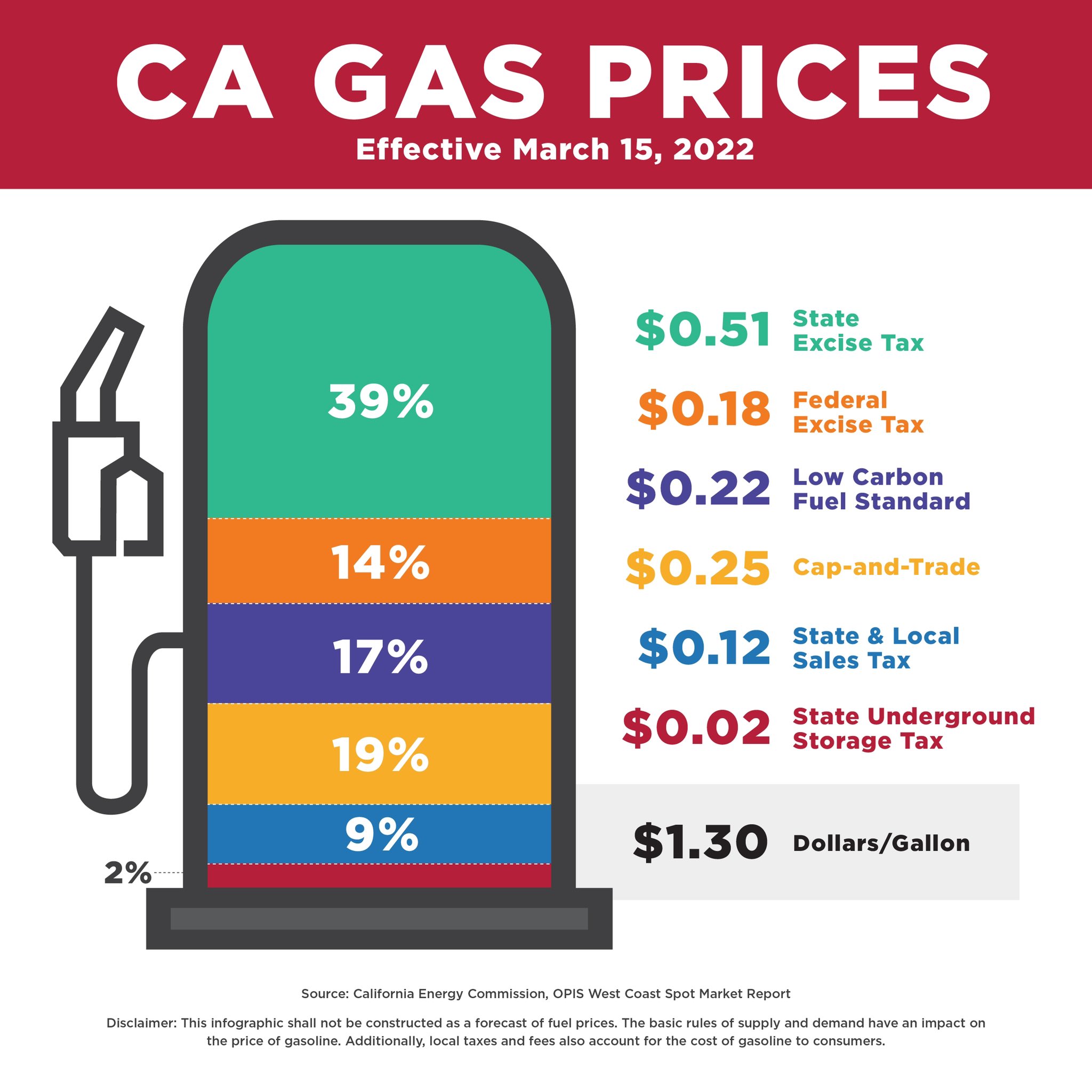
Table of Contents
The Role of Crude Oil Prices
The price of gasoline is intrinsically linked to the price of crude oil. Crude oil is the raw material used to produce gasoline, so fluctuations in its cost directly impact fuel prices. Several factors influence crude oil prices, creating a ripple effect that reaches our gas pumps. These include:
-
OPEC+ Production Decisions: The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), along with its allies (OPEC+), plays a significant role in regulating global oil supply. Production cuts by OPEC+ can restrict the availability of crude oil, leading to higher prices. This has been a major factor influencing recent gasoline price increases.
-
Geopolitical Instability and Sanctions: Geopolitical events, such as wars, sanctions, and political instability in oil-producing regions, can severely disrupt the global oil supply. For example, sanctions on Russian oil exports have created a supply crunch, pushing crude oil prices higher.
-
Global Supply and Demand Dynamics: The balance between global oil supply and demand significantly impacts pricing. Increased global demand, particularly from rapidly developing Asian economies, can outpace supply, driving prices upward. Conversely, a surplus in oil production can lead to lower prices.
-
Speculation and Trading in the Oil Market: The oil market is highly susceptible to speculation and trading activity. Futures contracts and investor sentiment can significantly influence crude oil prices, leading to price volatility and unpredictable fluctuations in gasoline prices.
Refinery Capacity and Operational Issues
Beyond the price of crude oil, the capacity and efficiency of domestic refineries play a crucial role in determining gasoline prices. Several issues can impact refinery output and contribute to price increases:
-
Planned and Unplanned Refinery Shutdowns: Refineries require regular maintenance, and planned shutdowns can temporarily reduce gasoline production. However, unplanned closures due to unforeseen circumstances, such as equipment failures or accidents, can have a more significant impact on supply and prices.
-
Increased Transportation Costs for Gasoline: Getting gasoline from refineries to gas stations involves transportation, a process impacted by fuel costs themselves and trucking logistics. Increased trucking costs, driven by higher diesel prices, contribute to the overall price at the pump.
-
Labor Shortages Impacting Refinery Operations: A shortage of skilled labor can hinder refinery operations, leading to reduced output and potentially higher prices.
-
Impact of Aging Refinery Infrastructure: Many US refineries are aging, requiring significant investment in upgrades and maintenance. This can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased costs, affecting the final price of gasoline.
Seasonal Demand and Summer Driving
The demand for gasoline fluctuates throughout the year, with a significant surge during the summer driving season. This peak demand period drives up prices as more people hit the road for vacations, road trips, and other summer activities.
-
Increased Road Travel During Summer Vacations: Summer vacation periods see a sharp increase in road travel, leading to higher fuel consumption and increased demand.
-
Higher Demand During Peak Holiday Periods: Major holidays, such as Memorial Day, the Fourth of July, and Labor Day, further intensify demand, pushing gasoline prices higher.
-
Impact of Tourism on Fuel Consumption: Tourism, particularly in areas with popular vacation destinations, contributes significantly to increased gasoline consumption and higher prices during the peak summer season.
Government Regulations and Taxes
Government regulations and taxes also play a role in shaping gasoline prices. These include:
-
Federal and State Gasoline Taxes: Federal and state governments impose taxes on gasoline, which directly adds to the price consumers pay at the pump. These taxes fund various infrastructure projects and programs.
-
Impact of Carbon Emission Regulations: Regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions from vehicles can affect gasoline production and pricing. For instance, the introduction of stricter emissions standards might lead to changes in gasoline formulation and increased production costs.
-
Effect of Environmental Policies on Fuel Production: Environmental policies, such as those aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, can impact the production process and potentially increase the cost of gasoline.
Conclusion
The recent 20-cent surge in gas prices is a result of a complex interplay of factors. Increased crude oil prices due to global supply chain issues and geopolitical tensions, coupled with refinery operational challenges, seasonal demand, and government regulations, all contribute to the higher cost of gasoline. Understanding these factors driving gas prices, like this recent 20-cent surge, allows you to make informed decisions about your fuel consumption and budget. To stay updated on fuel price fluctuations in your area and find tips for saving money on gas, check out [link to a gas price tracking website or fuel saving tips].

Featured Posts
-
 The David Walliams Simon Cowell Britains Got Talent Dispute What Happened
May 22, 2025
The David Walliams Simon Cowell Britains Got Talent Dispute What Happened
May 22, 2025 -
 Fastest Crossing Of Australia On Foot A New Record Is Set
May 22, 2025
Fastest Crossing Of Australia On Foot A New Record Is Set
May 22, 2025 -
 Analysis The Chicago Sun Times Ai Reporting Failures
May 22, 2025
Analysis The Chicago Sun Times Ai Reporting Failures
May 22, 2025 -
 British Ultrarunner Attempts Australian Speed Record
May 22, 2025
British Ultrarunner Attempts Australian Speed Record
May 22, 2025 -
 Tuyen Duong Huyet Mach Tp Hcm Ba Ria Vung Tau Huong Dan Di Chuyen
May 22, 2025
Tuyen Duong Huyet Mach Tp Hcm Ba Ria Vung Tau Huong Dan Di Chuyen
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Senatori Vklyuchayuchi Lindsi Grema Vimagayut Vid Trampa Konfiskatsiyi Rosiyskikh Aktiviv
May 22, 2025
Senatori Vklyuchayuchi Lindsi Grema Vimagayut Vid Trampa Konfiskatsiyi Rosiyskikh Aktiviv
May 22, 2025 -
 Ukrayina Ta Viyskova Dopomoga Klyuchova Rol Linsi Grema
May 22, 2025
Ukrayina Ta Viyskova Dopomoga Klyuchova Rol Linsi Grema
May 22, 2025 -
 Lindsi Grem Ta Senatori Zaklikayut Do Konfiskatsiyi Aktiviv Rf Vimogi Do Trampa
May 22, 2025
Lindsi Grem Ta Senatori Zaklikayut Do Konfiskatsiyi Aktiviv Rf Vimogi Do Trampa
May 22, 2025 -
 Viyskova Dopomoga Ukrayini Linsi Grem Vistupaye Za Yiyi Vidnovlennya
May 22, 2025
Viyskova Dopomoga Ukrayini Linsi Grem Vistupaye Za Yiyi Vidnovlennya
May 22, 2025 -
 Viyskova Dopomoga Ukrayini Grem Zaklikaye Do Yiyi Vidnovlennya
May 22, 2025
Viyskova Dopomoga Ukrayini Grem Zaklikaye Do Yiyi Vidnovlennya
May 22, 2025
