Grocery Inflation: Three Months Of Price Hikes Outpacing Overall Inflation
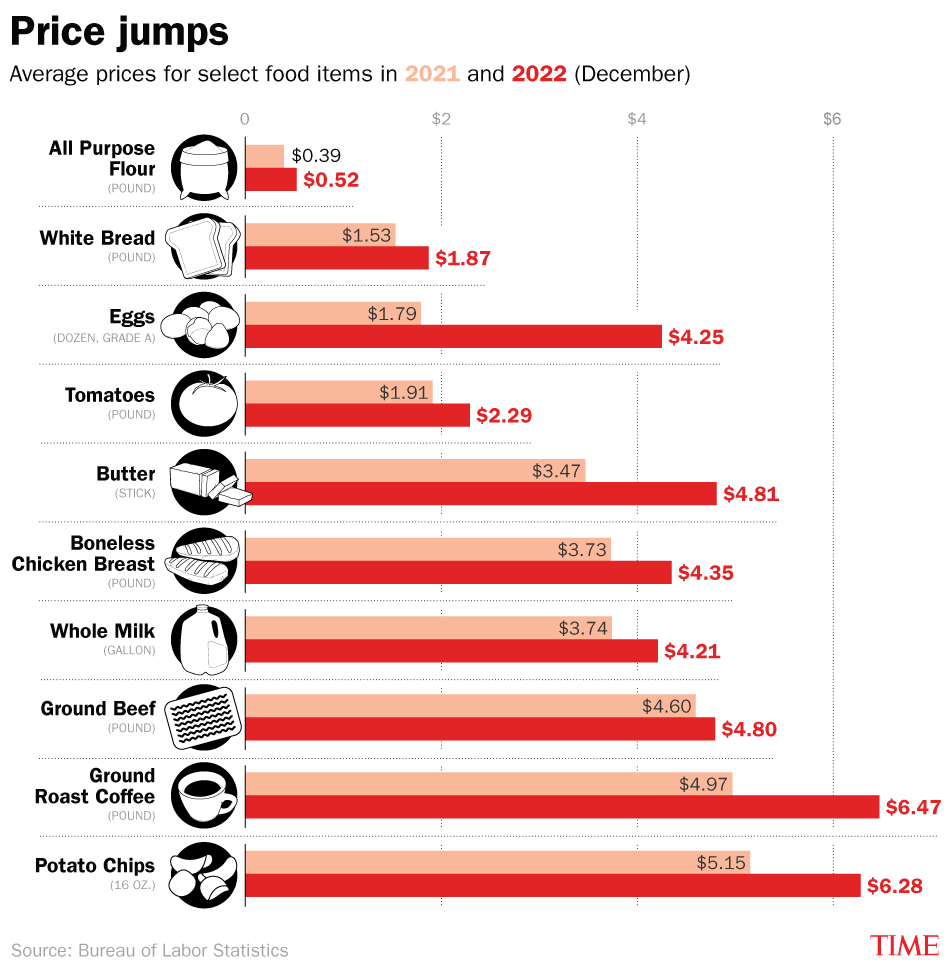
Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to Accelerated Grocery Inflation
Several interconnected factors have fueled the recent acceleration of grocery inflation. Understanding these elements is crucial to addressing the problem effectively.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Ongoing supply chain bottlenecks continue to plague the food industry, leading to significant price increases. These disruptions ripple through the entire process, from farm to table.
- Increased Transportation Costs: Fuel prices have skyrocketed, increasing the cost of transporting goods from farms and processing plants to distribution centers and supermarkets.
- Labor Shortages: A lack of workers across the supply chain, from farmhands to truck drivers, has slowed down production and distribution.
- Port Congestion: Delays in unloading cargo at ports have created further bottlenecks, leading to shortages and increased costs.
- Packaging Material Shortages: Shortages of cardboard, plastic, and other packaging materials have hampered production and increased packaging costs.
Specific examples include significant price increases in certain fruits and vegetables due to transportation delays and labor shortages in agricultural regions. The cost of canned goods has also risen due to metal packaging shortages.
Rising Energy Costs
The surge in energy prices – fuel, electricity, and natural gas – has a profound impact on food production, processing, and transportation. These increased energy costs are directly passed on to consumers.
- Higher Fertilizer Prices: The production of fertilizers is energy-intensive, and rising energy costs have led to a significant increase in fertilizer prices, directly affecting crop yields and food prices.
- Increased Fuel Costs for Farming Equipment: Farmers rely heavily on machinery and equipment, and higher fuel prices directly increase their operational costs, which are eventually reflected in food prices.
- Energy-Intensive Food Processing: Many food processing plants require substantial energy to operate, leading to higher costs for processed foods as energy prices rise.
Data shows a strong correlation between energy price increases and grocery inflation; as energy costs climb, so do grocery prices.
Increased Demand and Shifting Consumer Behavior
Changes in consumer buying habits have also contributed to the current grocery inflation.
- Increased Demand for Certain Items: The pandemic shifted consumer preferences, leading to increased demand for certain pantry staples, frozen foods, and home-cooking ingredients. This heightened demand outpaced supply, resulting in price increases.
- Effect of Restaurant Closures: With many restaurants closed or operating at reduced capacity, more people turned to grocery shopping, further increasing demand.
These shifts in consumer behavior are likely to have long-term implications for grocery pricing and could permanently alter the demand for certain food products.
Impact of Grocery Inflation on Consumers
The impact of grocery inflation is far-reaching, placing a significant strain on household budgets and forcing consumers to adapt.
Budgetary Strain on Households
Higher grocery prices disproportionately impact low-income families, forcing them to make difficult choices between food and other essential expenses.
- Impact on Low-Income Families: For low-income families, a significant portion of their income is already allocated to groceries. Grocery inflation further reduces their disposable income, potentially leading to food insecurity.
- Percentage of Household Income Spent on Groceries: Statistics show a clear upward trend in the percentage of household income spent on groceries, highlighting the growing financial burden.
Consumers are adopting various strategies to cope, including reducing food waste, buying store brands, and looking for discounts.
Changes in Shopping Habits
Rising grocery prices are prompting consumers to change their shopping habits significantly.
- Increased Shopping at Discount Stores: More consumers are turning to discount stores and budget-friendly grocery options to save money.
- Purchasing Store Brands: The popularity of store-brand products, which are generally cheaper than name-brand items, has increased considerably.
- Reducing Food Waste: Consumers are becoming more mindful of food waste, aiming to utilize all purchased groceries to maximize value.
- Changing Dietary Habits: Some consumers are adapting their diets, choosing cheaper alternatives or reducing their overall food consumption to manage costs.
These changes impact food choices and may affect overall nutritional intake.
Potential Long-Term Effects
Sustained high grocery inflation could have severe long-term consequences.
- Increased Food Insecurity: Prolonged high prices could lead to increased food insecurity, impacting the health and well-being of vulnerable populations.
- Changes in Long-Term Dietary Patterns: Consumers may permanently alter their dietary habits, potentially impacting their long-term health.
- Overall Economic Consequences: High grocery inflation can negatively affect overall economic growth as consumers reduce spending on other goods and services.
Government Intervention and Potential Solutions
Addressing grocery inflation requires a multi-pronged approach involving government intervention and industry collaboration.
Government Policies and Support
Governments can play a crucial role in mitigating the effects of grocery inflation.
- Subsidies: Government subsidies for farmers and food producers could help reduce production costs and stabilize prices.
- Targeted Assistance Programs: Expanding existing food assistance programs and creating new ones can help vulnerable populations afford groceries.
However, government price controls are usually complex to implement and can have unintended consequences.
Industry Strategies
The grocery industry also needs to actively work towards solutions.
- Increased Efficiency: Improving efficiency in the supply chain, reducing waste, and optimizing logistics can help lower costs.
- Partnerships to Streamline the Supply Chain: Collaboration among stakeholders can help identify and address bottlenecks more effectively.
- Reducing Waste: Minimizing food waste throughout the supply chain can significantly reduce costs and increase the availability of food.
Conclusion: Navigating the Challenge of Grocery Inflation
Several interconnected factors – supply chain disruptions, rising energy costs, and shifting consumer behavior – are driving the current surge in grocery inflation. This has a substantial impact on household budgets, forcing consumers to make difficult choices and potentially impacting their health and well-being. The potential long-term consequences of sustained high grocery inflation are significant. Understanding the dynamics of grocery inflation is crucial for managing household budgets. Stay informed, adapt your shopping strategies, and advocate for solutions to mitigate this critical issue. We must collectively work towards addressing the root causes of grocery inflation to ensure affordable and accessible food for everyone.

Featured Posts
-
 Restauration Du Patrimoine Breton Plouzane Et Clisson Beneficient De La Mission Patrimoine 2025
May 22, 2025
Restauration Du Patrimoine Breton Plouzane Et Clisson Beneficient De La Mission Patrimoine 2025
May 22, 2025 -
 David Walliams And Britains Got Talent A Look At Recent Events
May 22, 2025
David Walliams And Britains Got Talent A Look At Recent Events
May 22, 2025 -
 Barry Ward Interview The Irish Actor On Roles And Type Casting
May 22, 2025
Barry Ward Interview The Irish Actor On Roles And Type Casting
May 22, 2025 -
 Nato Membership For Ukraine A Eurocommissioner Highlights Key Risks
May 22, 2025
Nato Membership For Ukraine A Eurocommissioner Highlights Key Risks
May 22, 2025 -
 Sses Revised Spending Plan 3 Billion Cut Reflects Economic Uncertainty
May 22, 2025
Sses Revised Spending Plan 3 Billion Cut Reflects Economic Uncertainty
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Historic Win Zimbabwe Claims First Away Test Victory Since 2021 In Sylhet
May 23, 2025
Historic Win Zimbabwe Claims First Away Test Victory Since 2021 In Sylhet
May 23, 2025 -
 First Away Test Win Since 2021 Zimbabwes Sylhet Victory
May 23, 2025
First Away Test Win Since 2021 Zimbabwes Sylhet Victory
May 23, 2025 -
 Grand Ole Opry A Royal Albert Hall Concert And Global Broadcast Premiere
May 23, 2025
Grand Ole Opry A Royal Albert Hall Concert And Global Broadcast Premiere
May 23, 2025 -
 Londons Royal Albert Hall To Host Grand Ole Oprys Inaugural International Broadcast
May 23, 2025
Londons Royal Albert Hall To Host Grand Ole Oprys Inaugural International Broadcast
May 23, 2025 -
 Sylhet Thriller Zimbabwes First Away Test Win Since 2021
May 23, 2025
Sylhet Thriller Zimbabwes First Away Test Win Since 2021
May 23, 2025
