Grocery Prices Soar: Inflation's Unrelenting Impact

Table of Contents
The Underlying Causes of Grocery Inflation
Several interconnected factors fuel the relentless rise in grocery prices. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial to addressing the problem effectively.
Rising Production Costs
Increased production costs across the agricultural and food processing sectors are a major driver of grocery inflation. Several key elements contribute to this:
- Higher fuel costs: Transportation of goods from farm to table is a significant expense. The soaring price of fuel directly impacts the cost of transporting agricultural products and processed foods, ultimately increasing prices for consumers.
- Elevated fertilizer prices: Fertilizers are essential for crop production. Sharp increases in fertilizer prices, influenced by global energy prices and supply chain disruptions, directly translate to higher food costs. This particularly impacts grain prices, which in turn affects the cost of bread, pasta, and other staple foods.
- Labor shortages: A shortage of workers across the agricultural and food processing industries contributes to rising labor costs, adding to the overall cost of food production. This affects everything from harvesting crops to processing and packaging.
- Impact of climate change: Extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, increasingly impact crop yields, leading to reduced supply and higher prices for certain food items. For example, wheat and corn prices have been particularly volatile due to adverse weather conditions in key producing regions. Statistics show a 20% increase in wheat prices in the last year alone.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chain disruptions continue to play a significant role in driving up grocery prices. These disruptions create bottlenecks and delays, leading to shortages and higher costs.
- Geopolitical instability: Conflicts and political tensions around the world disrupt trade routes and access to key resources, impacting the availability and price of various food products.
- Port congestion: Delays at major ports worldwide lead to longer shipping times and increased storage costs, contributing to higher prices for imported goods.
- Labor shortages in logistics: Shortages of truck drivers and other transportation workers exacerbate supply chain problems, further impacting the timely and efficient delivery of food products. This particularly affects perishable goods.
Increased Demand & Consumer Behavior
Changes in consumer demand and preferences also contribute to grocery inflation.
- Post-pandemic shifts: Changes in consumer behavior post-pandemic, including increased demand for certain food items and a shift towards home cooking, have put pressure on supply and prices.
- Organic food preference: The growing preference for organic and sustainably produced food has increased demand, pushing up prices for these products.
- Dietary trends: Shifts in dietary trends, such as the increased popularity of plant-based diets, can also affect demand and pricing for specific food items. For example, the surge in demand for plant-based meat alternatives has driven up prices in this sector.
The Impact on Consumers
The relentless rise in grocery prices has profound consequences for consumers.
Budget Strain and Food Insecurity
Higher grocery bills place a significant strain on household budgets, particularly for low-income families.
- Rising food insecurity: Statistics indicate a concerning increase in food insecurity rates, with more families struggling to afford adequate nutrition.
- Coping strategies: To cope, many families are resorting to cost-cutting measures such as shopping at discount stores, reducing food waste, and making difficult choices about which foods to buy.
- Social consequences: Food insecurity can have serious social and health consequences, including malnutrition and increased stress levels.
Changes in Shopping Habits
Consumers are adapting their shopping behaviors to mitigate the impact of rising grocery prices.
- Price comparison: Consumers are increasingly comparing prices across different retailers and brands.
- Coupon usage: The use of coupons and loyalty programs is on the rise.
- Store brands: There's an increased preference for store-brand products, which are generally cheaper than name brands.
- Meal planning & reduced waste: More people are planning their meals carefully and actively reducing food waste to save money.
Potential Solutions and Strategies
Addressing the problem of grocery inflation requires a multifaceted approach involving government intervention and consumer-level strategies.
Government Intervention
Government policies can play a vital role in mitigating the impact of grocery inflation.
- Subsidies: Government subsidies for farmers and food producers can help to lower production costs.
- Price controls: While potentially disruptive, price controls on essential food items could be considered, although they must be carefully implemented to avoid unintended consequences.
- Support programs: Existing government programs that provide food assistance to low-income families should be strengthened and expanded.
Consumer Strategies for Saving Money
Consumers can adopt various strategies to reduce their grocery bills:
- Meal planning: Careful meal planning can significantly reduce food waste and grocery spending.
- Coupon usage: Take advantage of coupons and discounts offered by retailers.
- Bulk buying (when appropriate): Buying in bulk can be cost-effective for non-perishable items.
- Discount stores: Utilize budget-friendly grocery stores and discount supermarkets.
- Reduce food waste: Implement strategies to minimize food spoilage and waste.
Conclusion
Soaring grocery prices are a result of a complex interplay of rising production costs, persistent supply chain disruptions, and increased demand. The impact on consumers is substantial, particularly for vulnerable populations facing increased food insecurity. Addressing this requires both government intervention to support producers and consumers, and individual strategies to manage household budgets effectively. Understanding the drivers of grocery inflation is crucial for managing your household budget. Stay informed and adopt effective strategies to combat rising grocery costs!

Featured Posts
-
 The Goldbergs Behind The Scenes Look At Production And Cast
May 22, 2025
The Goldbergs Behind The Scenes Look At Production And Cast
May 22, 2025 -
 Bp Executive Compensation A 31 Reduction
May 22, 2025
Bp Executive Compensation A 31 Reduction
May 22, 2025 -
 Karin Polman Benoemd Tot Directeur Hypotheken Voor Abn Amro Florius En Moneyou Een Belangrijke Stap Voor De Hypotheekmarkt
May 22, 2025
Karin Polman Benoemd Tot Directeur Hypotheken Voor Abn Amro Florius En Moneyou Een Belangrijke Stap Voor De Hypotheekmarkt
May 22, 2025 -
 Broadcoms Extreme V Mware Price Increase At And T Sounds The Alarm On 1 050 Jump
May 22, 2025
Broadcoms Extreme V Mware Price Increase At And T Sounds The Alarm On 1 050 Jump
May 22, 2025 -
 India Creates History 19 Paddlers At Wtt Star Contender Chennai
May 22, 2025
India Creates History 19 Paddlers At Wtt Star Contender Chennai
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
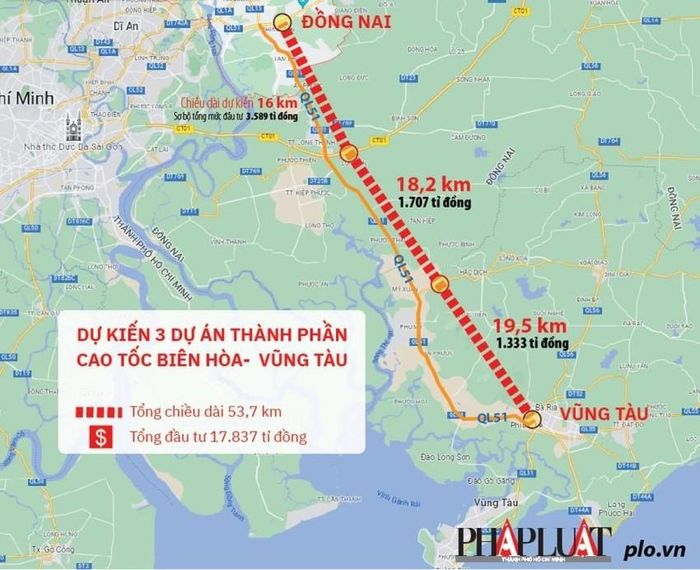 Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Thong Xe Du Kien 2 9
May 22, 2025
Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Thong Xe Du Kien 2 9
May 22, 2025 -
 The Future Of Core Weave Stock Predictions And Projections
May 22, 2025
The Future Of Core Weave Stock Predictions And Projections
May 22, 2025 -
 Whats Driving Core Weave Stocks Current Price
May 22, 2025
Whats Driving Core Weave Stocks Current Price
May 22, 2025 -
 Core Weave Stock Performance Factors Influencing Its Trajectory
May 22, 2025
Core Weave Stock Performance Factors Influencing Its Trajectory
May 22, 2025 -
 Deconstructing Core Weaves Crwv Impressive Stock Performance Last Week
May 22, 2025
Deconstructing Core Weaves Crwv Impressive Stock Performance Last Week
May 22, 2025
