Navigating The Chinese Market: The BMW And Porsche Case Study

Table of Contents
Market Entry Strategies: A Tale of Two Approaches
BMW and Porsche, while both luxury brands, adopted distinct market entry strategies in China. Their approaches highlight the flexibility required when entering such a diverse and dynamic market.
BMW's Gradual Expansion:
BMW opted for a phased approach, prioritizing long-term sustainability over rapid expansion. This involved a strategic combination of organic growth and strategic partnerships.
- Building a Robust Dealer Network: BMW invested heavily in establishing a widespread and reliable dealer network across China. This ensured accessibility for customers and efficient after-sales service.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with local suppliers helped BMW integrate into the Chinese automotive ecosystem, reducing costs and improving supply chain efficiency. This minimized risks associated with navigating unfamiliar regulatory environments.
- Phased Product Introduction: BMW didn't flood the market immediately. Instead, they carefully introduced models, tailoring specifications to Chinese consumer preferences. This included longer wheelbases in some models to cater to the preference for spacious rear seating.
- Early Investment in Local Production: Establishing local production facilities was a key element of BMW's strategy. This reduced import costs, shortened delivery times, and improved responsiveness to local demands within the China business environment.
- Leveraging Global Brand Recognition: BMW leveraged its existing global brand recognition, building upon its established reputation for quality and innovation. However, they carefully adapted their marketing messages to resonate with the Chinese market.
Porsche's Targeted Luxury Positioning:
Porsche employed a more targeted approach, focusing on high-end segments where their brand resonated strongly. Their strategy was centered around exclusivity and superior customer experience.
- Concentrated Luxury Focus: Porsche initially concentrated its efforts on major metropolitan areas with high concentrations of affluent consumers, optimizing resource allocation.
- Exclusive Dealership Network: Porsche emphasized establishing exclusive dealerships offering superior customer service and a premium brand experience. This reinforced their image as a luxury marque.
- Strong Digital Marketing: Recognizing the importance of digital channels in China, Porsche invested heavily in a robust digital marketing strategy targeting affluent Chinese consumers online through platforms like WeChat.
- Highlighting Brand Heritage and Performance: Porsche leveraged its brand heritage and performance capabilities in its marketing, resonating with Chinese consumers who appreciate quality, status, and sophisticated engineering.
Localization and Brand Building: Adapting to Chinese Preferences
Successfully navigating the Chinese market requires deep understanding of cultural nuances and effective brand localization. Both BMW and Porsche demonstrated mastery in this area.
Understanding Cultural Nuances:
- Adapting to Chinese Driving Preferences: BMW adapted models and features to better suit Chinese road conditions and consumer preferences, showcasing sensitivity to local needs. This included focusing on rear passenger comfort.
- Emphasizing Exclusivity and Status: Porsche meticulously cultivated its image as a symbol of success and prestige, understanding and catering to the Chinese appreciation of luxury goods and status symbols.
- Localized Marketing Campaigns: Both brands employed localized marketing campaigns utilizing culturally relevant messaging and channels, ensuring impactful communication. This is a critical aspect of China business strategy.
Leveraging Digital Channels:
- Social Media Engagement: Both brands extensively utilized major social media platforms like WeChat and Weibo to directly engage with Chinese consumers, building brand loyalty and collecting valuable feedback.
- Targeted Online Advertising: Precisely targeted online advertising campaigns ensured efficient allocation of marketing resources, maximizing ROI within the China business landscape.
- E-commerce Integration: Seamless e-commerce integration simplified the purchasing process, enhancing convenience for the tech-savvy Chinese consumer. This is crucial for a smooth customer journey.
Building Strong Relationships:
- Community Engagement and CSR: Both BMW and Porsche invested in community engagement and corporate social responsibility initiatives, building positive brand perception and trust.
- Influencer Marketing: Cultivating relationships with key influencers and media outlets helped spread brand awareness and build positive sentiment within the Chinese market.
- Exceptional Customer Service: Providing superior customer service tailored to the expectations of Chinese consumers has been essential for both brands in maintaining loyalty and fostering positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Overcoming Challenges: Competition and Regulatory Hurdles
The Chinese market is fiercely competitive, with established domestic brands and other international players vying for market share. Regulatory hurdles also pose significant challenges.
Intense Competition:
- Differentiation Strategies: Both brands employed distinct differentiation strategies to stand out from competitors, emphasizing unique features, technological innovation, and superior brand experience.
- Maintaining Brand Prestige: Preserving brand exclusivity and prestige in a highly competitive environment required consistent delivery of quality and exceptional customer service.
- Continuous Innovation: Continuous product development and innovation are vital to remain ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge within the Chinese market.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape:
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict adherence to Chinese government regulations and standards is paramount for operating legally and sustainably in China.
- Trade Barrier Management: Understanding and navigating import tariffs and other trade barriers is crucial for cost management and profitability.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Protecting intellectual property rights in the Chinese market requires proactive measures and careful legal counsel.
Conclusion:
Successfully navigating the Chinese market requires a nuanced understanding of consumer preferences, a robust localization strategy, and a sustained commitment to building strong relationships. BMW and Porsche's case studies highlight the critical importance of adapting to the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this dynamic market. By analyzing their successes and challenges, businesses can gain valuable insights into developing effective strategies for their own market entry into China. To learn more about crafting a successful strategy for the Chinese market, continue your research and consider consulting with experts on navigating the Chinese market.

Featured Posts
-
 Analysis Of Financing Strategies For A 270 M Wh Bess Project In The Belgian Merchant Market
May 03, 2025
Analysis Of Financing Strategies For A 270 M Wh Bess Project In The Belgian Merchant Market
May 03, 2025 -
 Exclusive Which A Lister Wants Access To Melissa Gorgas Beach House
May 03, 2025
Exclusive Which A Lister Wants Access To Melissa Gorgas Beach House
May 03, 2025 -
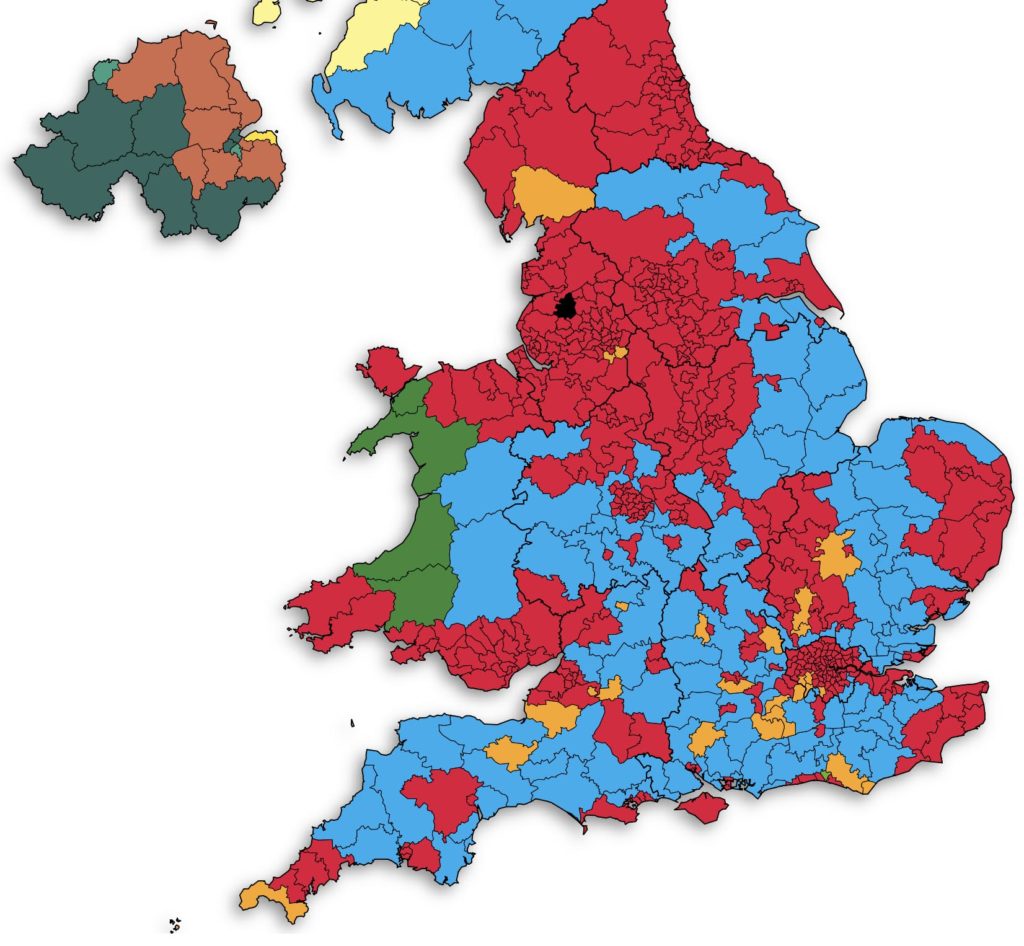 Farages Reform Party Faces The Heat Uk Local Election Results
May 03, 2025
Farages Reform Party Faces The Heat Uk Local Election Results
May 03, 2025 -
 Lakazet S 157 Gola Lion Se Priblizhava Do Vrkha Vv Frantsiya
May 03, 2025
Lakazet S 157 Gola Lion Se Priblizhava Do Vrkha Vv Frantsiya
May 03, 2025 -
 Grab Free Captain America Gear Fortnite Item Shops Limited Time Event
May 03, 2025
Grab Free Captain America Gear Fortnite Item Shops Limited Time Event
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Rupert Lowe On X Effectiveness Of Messaging For Uk Reform Examined
May 03, 2025
Rupert Lowe On X Effectiveness Of Messaging For Uk Reform Examined
May 03, 2025 -
 Channel Swim Graeme Sounesss Bold Commitment To Islas Cause
May 03, 2025
Channel Swim Graeme Sounesss Bold Commitment To Islas Cause
May 03, 2025 -
 Arsenals Title Failure Souness Pinpoints The Crucial Role
May 03, 2025
Arsenals Title Failure Souness Pinpoints The Crucial Role
May 03, 2025 -
 Sounesss Double Channel Swim A Daring Feat For Isla
May 03, 2025
Sounesss Double Channel Swim A Daring Feat For Isla
May 03, 2025 -
 Graeme Sounesss Channel Swim Challenge A Fiery Dedication To Isla
May 03, 2025
Graeme Sounesss Channel Swim Challenge A Fiery Dedication To Isla
May 03, 2025
