Negative European Electricity Prices: A Solar Energy Success Story?
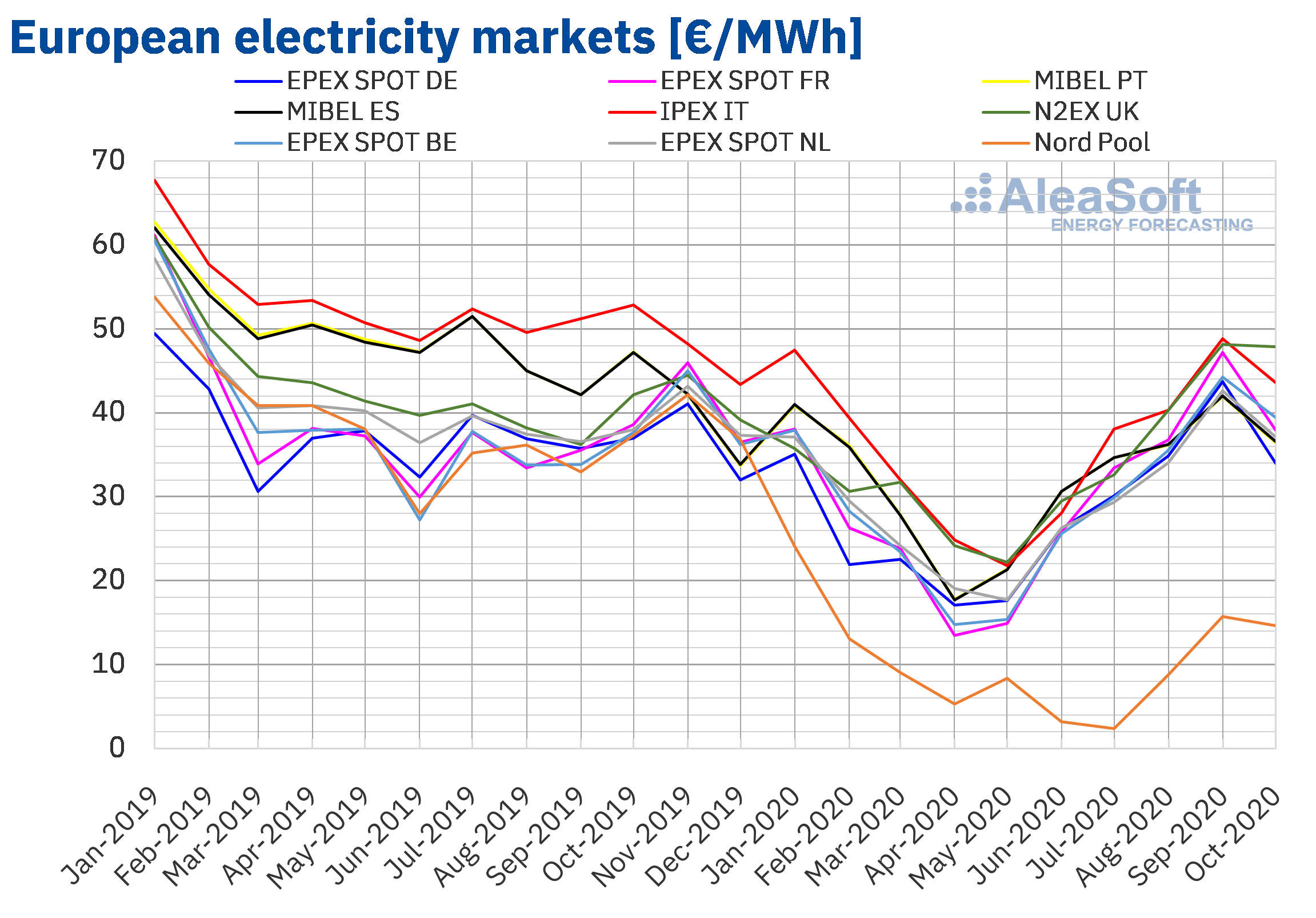
Table of Contents
The Mechanics of Negative Electricity Prices
Negative electricity prices occur when the supply of electricity significantly exceeds demand. This imbalance can lead to a situation where electricity generators, rather than receiving payment for their output, are effectively penalized for producing more than the grid can handle. Several factors contribute to this phenomenon.
The Role of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind power, play a pivotal role in creating this energy surplus. The intermittent nature of these sources means generation fluctuates throughout the day, often exceeding peak demand during periods of high solar irradiance or strong winds.
- Increased renewable energy capacity exceeding peak demand periods: The rapid expansion of solar and wind farms across Europe has significantly increased overall generation capacity. This capacity often outstrips demand during certain times, particularly during sunny midday hours.
- Intermittency of solar and wind power leading to temporary oversupply: The inherent unpredictability of solar and wind power means that generation can vary drastically, leading to periods of substantial oversupply.
- Lack of sufficient energy storage infrastructure to manage fluctuating energy production: Europe currently lacks the large-scale energy storage capacity needed to effectively manage the fluctuations in renewable energy generation. This inability to store excess energy exacerbates the oversupply issue.
- Impact of government subsidies and renewable energy mandates: Government policies promoting renewable energy adoption, including subsidies and mandates, have driven rapid growth in solar and wind power, contributing to the surplus generation capacity.
Solar Energy's Contribution to the Phenomenon
Solar energy is a major contributor to the surplus electricity that drives negative pricing. The dramatic increase in solar power generation across Europe, fueled by technological advancements and cost reductions, is a key factor. Data from [insert source with relevant statistics on European solar power generation] shows a significant rise in solar energy output, directly correlating with periods of negative electricity prices.
Technological Advancements and Cost Reductions
The solar energy industry has experienced remarkable advancements, leading to significantly lower costs and increased efficiency.
- Increased efficiency of solar panels: Modern solar panels are far more efficient than their predecessors, generating more electricity per unit area.
- Falling costs of solar panel installation and maintenance: The cost of installing and maintaining solar panels has plummeted in recent years, making solar power increasingly accessible and affordable.
- Government incentives and tax breaks promoting solar adoption: Government support through tax breaks and other incentives has significantly boosted solar energy adoption across Europe.
The Geographic Distribution of Solar Power
Regions in Europe with high solar irradiance and significant solar power installations, such as Southern Europe, are most frequently affected by negative electricity prices. This correlation underscores the strong link between solar energy growth and the occurrence of negative pricing.
Implications and Challenges of Negative Prices
Negative electricity prices have significant implications for electricity producers, consumers, and the overall energy market.
Challenges for Conventional Power Plants
Negative prices present major challenges for conventional power plants reliant on fossil fuels and nuclear energy.
- Reduced profitability for conventional power plants: When electricity prices are negative, these plants face financial losses if they continue operating.
- Potential for plant closures or reduced operation: Many conventional power plants may find it economically unviable to operate under these conditions, potentially leading to closures or reduced operating hours.
- Increased pressure to transition to more sustainable energy sources: Negative prices highlight the economic challenges faced by traditional energy sources and accelerate the transition to more sustainable alternatives.
Opportunities for Energy Storage and Grid Management
The challenge of negative pricing presents significant opportunities for advancements in energy storage and smarter grid management.
- The need for efficient energy storage solutions to absorb surplus renewable energy and release it during peak demand periods is becoming increasingly critical.
- Improved grid management strategies are needed to better balance supply and demand, mitigating the occurrence of negative pricing and maximizing the utilization of renewable energy sources.
Conclusion
Negative European electricity prices, while initially surprising, are a strong indication of the growing success and integration of solar energy into the European energy mix. The phenomenon highlights both the challenges and opportunities presented by the rapid expansion of renewable energy sources. While posing challenges for traditional power plants, negative prices ultimately signal a significant step towards a more sustainable energy future. The need for improved energy storage and smart grid management is paramount to fully harness the potential of solar energy and manage the fluctuations inherent in renewable energy generation. Learn more about how negative European electricity prices are shaping the future of solar energy and its role in a sustainable energy transition. [Insert link to relevant resources here]

Featured Posts
-
 See Bob Dylan And Billy Strings Live Willie Nelsons Outlaw Music Festival In Portland
Apr 29, 2025
See Bob Dylan And Billy Strings Live Willie Nelsons Outlaw Music Festival In Portland
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Us Attorney Generals Warning To Minnesota Compliance With Transgender Athlete Ban
Apr 29, 2025
Us Attorney Generals Warning To Minnesota Compliance With Transgender Athlete Ban
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Will Us Trade Policy Influence The Canadian Election
Apr 29, 2025
Will Us Trade Policy Influence The Canadian Election
Apr 29, 2025 -
 North Koreas Ukraine Involvement Troop Deployment Confirmed
Apr 29, 2025
North Koreas Ukraine Involvement Troop Deployment Confirmed
Apr 29, 2025 -
 U S Companies Slash Costs Amid Tariff Uncertainty
Apr 29, 2025
U S Companies Slash Costs Amid Tariff Uncertainty
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks Canceled Ohio River Flooding
Apr 29, 2025
Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks Canceled Ohio River Flooding
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Louisville Restaurants Struggle Amid River Road Construction
Apr 29, 2025
Louisville Restaurants Struggle Amid River Road Construction
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The January 29th Dc Air Disaster Uncovering The Untold Story
Apr 29, 2025
The January 29th Dc Air Disaster Uncovering The Untold Story
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Louisvilles Early 2025 Disaster A Confluence Of Snow Tornadoes And Floods
Apr 29, 2025
Louisvilles Early 2025 Disaster A Confluence Of Snow Tornadoes And Floods
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Snow Tornadoes And Historic Flooding On Louisville In 2025
Apr 29, 2025
The Impact Of Snow Tornadoes And Historic Flooding On Louisville In 2025
Apr 29, 2025
