Ohio Train Derailment: The Prolonged Impact Of Toxic Chemical Contamination On Buildings
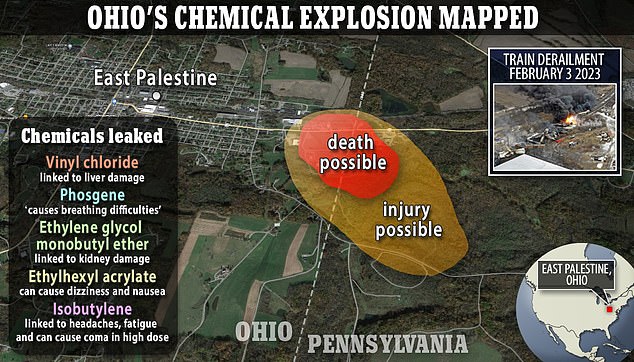
Table of Contents
Types of Chemical Contamination and Their Impact on Building Materials
The derailment released a cocktail of chemicals, but vinyl chloride stands out due to its known carcinogenic properties and its potential for widespread contamination.
Vinyl Chloride's Effects
Vinyl chloride, a colorless gas used in the production of PVC plastics, is highly volatile and readily penetrates building materials. Exposure can lead to various health problems, including liver damage, liver cancer, and brain tumors.
- Chemical Reactions and Damage: Vinyl chloride can react with certain building materials, causing degradation and weakening. For example, it can leach into plastics, potentially making them brittle and prone to cracking. It can also interact with paints and coatings, altering their chemical structure and compromising their protective qualities.
- Long-Term Structural Weaknesses: The insidious nature of vinyl chloride contamination means that damage may not be immediately apparent. Long-term exposure can lead to subtle but significant structural weaknesses in buildings, increasing the risk of collapse or failure over time. This necessitates thorough and ongoing inspection and potential remediation efforts.
- Scientific Evidence: Numerous studies by organizations like the National Cancer Institute and the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) link vinyl chloride exposure to serious health risks, further highlighting the urgency of addressing contamination. [Insert links to relevant studies here]
Other Contaminating Chemicals
While vinyl chloride is a primary concern, other chemicals released during the derailment may also have significant impacts on building materials. The synergistic effects of multiple chemicals interacting with each other and building components could exacerbate the damage.
- Synergistic Effects: The combined effect of different chemicals might be more destructive than the sum of their individual impacts. Further research is needed to fully understand these complex interactions.
- Unique Challenges: Each chemical presents unique challenges for remediation. Some may be more easily removed than others, requiring different approaches and technologies.
- Affected Building Materials: Depending on the specific chemical and its properties, various building materials are at risk. This includes not just plastics and paints, but also insulation, wood, and even concrete, depending on the level and type of contamination.
Assessing and Mitigating Contamination in Buildings
Effective remediation requires a multi-pronged approach, starting with thorough assessment and followed by appropriate cleanup strategies.
Identifying Contamination
Accurate identification of the extent and nature of the toxic chemical contamination is crucial for effective remediation.
- Environmental Testing: Professional environmental testing is paramount. This includes air quality testing to measure airborne concentrations of hazardous substances and material sampling to identify contaminated building components.
- Regulatory Oversight: Regulatory agencies like the EPA play a critical role in overseeing the testing process and ensuring that it is conducted according to established protocols.
- Comprehensive Assessment: The assessment must not only focus on the interior of buildings but also consider potential contamination pathways, such as contaminated soil entering the building through cracks or foundations.
Remediation Strategies
Several strategies are available for addressing contamination, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
- Decontamination: This involves cleaning or treating contaminated surfaces to remove or neutralize hazardous substances. The effectiveness depends on the type and extent of contamination.
- Demolition and Replacement: In cases of severe contamination, demolition and replacement of affected building materials may be the only viable option. This is a costly but potentially necessary approach to ensure safety.
- Material Replacement: Selective replacement of severely contaminated materials, such as insulation or flooring, can be a more cost-effective alternative to complete demolition in certain situations.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Even after remediation, ongoing monitoring is crucial to ensure that contamination levels remain within acceptable limits and to detect any recurrence. This long-term commitment is essential for protecting the health and safety of residents.
Long-Term Health and Environmental Consequences
The consequences of the toxic chemical contamination extend far beyond the immediate aftermath of the derailment.
Health Risks for Occupants
Exposure to the released chemicals poses significant long-term health risks for those living or working in contaminated buildings.
- Respiratory Problems: Inhalation of hazardous substances can lead to various respiratory problems, including asthma, bronchitis, and other lung diseases.
- Cancer Risks: Several of the chemicals released are known carcinogens, increasing the risk of various types of cancer over time.
- Health Monitoring: Ongoing health monitoring for affected populations is essential to identify and address any health problems that may arise as a result of exposure. Resources from the CDC and other public health organizations are vital for affected individuals. [Insert links to relevant health organizations and resources here]
Environmental Impact Beyond Buildings
The environmental consequences extend far beyond the buildings themselves.
- Soil and Water Contamination: The released chemicals have contaminated soil and water sources, posing a threat to the surrounding ecosystem.
- Wildlife and Agriculture: Contamination can harm wildlife and impact agricultural productivity, creating long-term ecological damage.
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment's toxic chemical contamination presents a significant and long-lasting challenge to the affected community. The impact on buildings, from structural integrity to long-term habitability, demands immediate and comprehensive remediation efforts. Ongoing health monitoring of residents and thorough environmental assessment are critical. We must learn from this tragedy to prevent future incidents and strengthen regulations protecting communities from hazardous materials transportation and handling. Support organizations working on the toxic chemical remediation in East Palestine and advocate for stronger safety standards to prevent future occurrences of this type of devastating chemical contamination. Stay informed about the ongoing situation and support the affected communities in their recovery efforts. [Insert links to relevant organizations and resources here]

Featured Posts
-
 Investing In Amundi Msci World Ii Ucits Etf Dist Monitoring The Nav
May 24, 2025
Investing In Amundi Msci World Ii Ucits Etf Dist Monitoring The Nav
May 24, 2025 -
 Apple Stock Suffers Setback Amidst 900 Million Tariff Projection
May 24, 2025
Apple Stock Suffers Setback Amidst 900 Million Tariff Projection
May 24, 2025 -
 Amundi Msci World Catholic Principles Ucits Etf Acc Daily Nav Updates And Analysis
May 24, 2025
Amundi Msci World Catholic Principles Ucits Etf Acc Daily Nav Updates And Analysis
May 24, 2025 -
 A Successful Escape To The Country Top Tips And Considerations
May 24, 2025
A Successful Escape To The Country Top Tips And Considerations
May 24, 2025 -
 Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Classy Response
May 24, 2025
Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Classy Response
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Broadway Buzz Jonathan Groffs Just In Time And The Raw Energy Of Bobby Darin
May 24, 2025
Broadway Buzz Jonathan Groffs Just In Time And The Raw Energy Of Bobby Darin
May 24, 2025 -
 Just In Time Musical Review Groffs Performance And The 60s Vibe
May 24, 2025
Just In Time Musical Review Groffs Performance And The 60s Vibe
May 24, 2025 -
 Jonathan Groffs Just In Time Performance Bobby Darin Primal Instincts And Broadway Buzz
May 24, 2025
Jonathan Groffs Just In Time Performance Bobby Darin Primal Instincts And Broadway Buzz
May 24, 2025 -
 Jonathan Groffs Just In Time A 1965 Inspired Musical Triumph
May 24, 2025
Jonathan Groffs Just In Time A 1965 Inspired Musical Triumph
May 24, 2025 -
 Jonathan Groff On Just In Time Channeling Bobby Darin And The Power Of Performance
May 24, 2025
Jonathan Groff On Just In Time Channeling Bobby Darin And The Power Of Performance
May 24, 2025
