Ontario's $14.6 Billion Deficit: Tariff Impacts And Economic Outlook
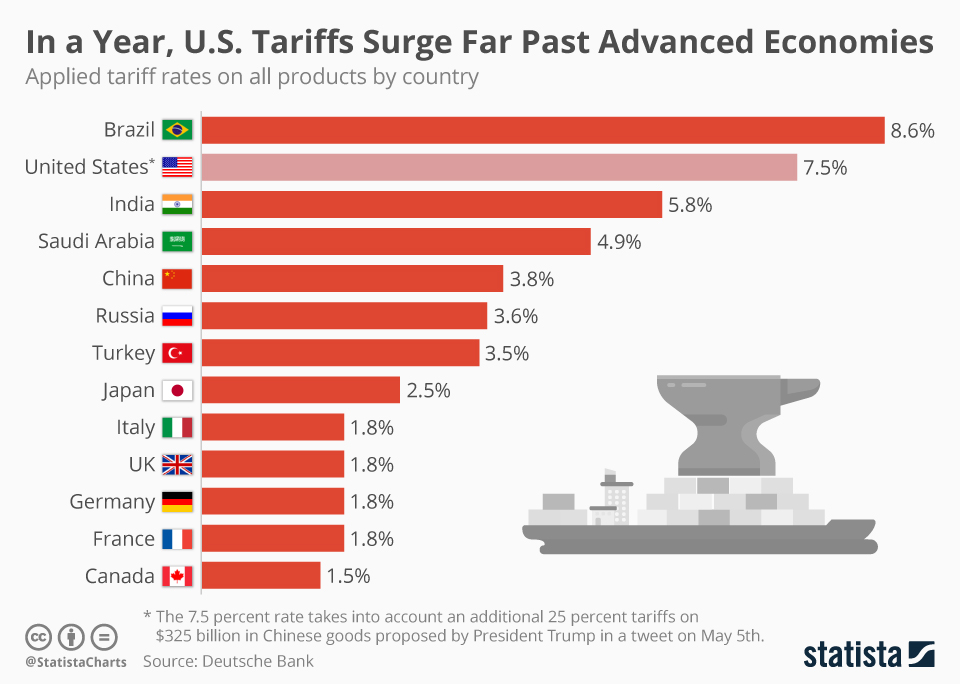
Table of Contents
The Impact of Tariffs on Ontario's Economy
Tariffs, taxes imposed on imported goods, have significantly contributed to Ontario's burgeoning deficit. Their effects ripple through the economy, impacting businesses and consumers alike.
Increased Costs for Businesses and Consumers
Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods for businesses. This added expense often translates into higher production costs, which are subsequently passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Automotive Industry: The automotive sector, a major player in the Ontario economy, relies heavily on imported parts. Tariffs on these components have increased manufacturing costs, leading to higher vehicle prices and reduced competitiveness.
- Manufacturing Sector: Many Ontario manufacturers depend on imported raw materials and intermediate goods. Tariffs on these inputs inflate production costs, impacting profitability and potentially leading to job losses.
- Statistics: For example, a recent study by [insert credible source here] indicated that tariffs on steel increased the price of cars by an average of X% and reduced sales by Y%. (Replace X and Y with actual or estimated data). This directly impacts consumer spending and overall economic activity.
The increased cost of living due to tariffs reduces consumer spending, further dampening economic growth and contributing to the Ontario deficit.
Reduced Export Opportunities
Retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries on Ontario goods are another significant consequence. When Ontario levies tariffs, other nations may respond in kind, harming Ontario's export-oriented industries.
- Agricultural Products: Ontario's agricultural sector, a significant contributor to the province's economy, has experienced decreased export opportunities due to retaliatory tariffs imposed by trading partners.
- Manufacturing Exports: Similarly, Ontario's manufacturing exports have suffered as a result of trade disputes and retaliatory tariffs, reducing revenue and hindering economic growth.
- Data: [Insert data here showing the decrease in exports due to retaliatory tariffs]. This decline in exports directly contributes to the widening Ontario deficit and negatively impacts job creation.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Tariffs disrupt global supply chains, creating significant challenges for businesses that rely on imported components or raw materials.
- Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Many businesses operate on just-in-time manufacturing models, relying on timely delivery of imported parts. Tariffs and resulting delays disrupt these processes, leading to production slowdowns and increased costs.
- Increased Uncertainty: The uncertainty surrounding tariffs makes it difficult for businesses to plan for the future, hindering investment and economic growth. This uncertainty adds to the overall economic instability and contributes to the Ontario deficit.
- Examples: The imposition of tariffs on specific components can cause delays and shortages for manufacturers relying on these imported parts. This can affect production schedules, leading to lost revenue and decreased economic output.
Other Contributing Factors to Ontario's Deficit
While tariffs play a significant role, Ontario's deficit is also influenced by other factors:
Government Spending
Increased government spending on social programs, infrastructure projects, and other initiatives contributes to the deficit. Balancing the need for essential services with fiscal responsibility is a crucial challenge.
Economic Slowdown
A slowdown in economic activity reduces tax revenue, making it harder for the government to meet its financial obligations, thus widening the Ontario deficit.
Interest Payments on Debt
The province's accumulated debt requires substantial interest payments each year, a significant drain on public funds and a major contributor to the ongoing deficit.
Demographic Shifts and Aging Population
The aging population of Ontario puts increasing strain on healthcare and pension systems, leading to higher government expenditure and further contributing to the fiscal imbalance.
Economic Outlook and Potential Solutions
Addressing Ontario's deficit requires a multifaceted approach:
Projected Economic Growth
Forecasts for Ontario's economic growth in the coming years are crucial for assessing the province's ability to reduce its deficit. Positive economic growth generates higher tax revenue, aiding deficit reduction. However, uncertain global economic conditions make accurate forecasting challenging.
Government Strategies for Deficit Reduction
The government may implement various strategies such as:
- Spending cuts: Identifying areas where government spending can be reduced without compromising essential services.
- Tax increases: Increasing taxes on individuals or corporations to generate additional revenue.
- Economic stimulus programs: Investing in infrastructure projects and other initiatives to stimulate economic growth.
The Role of Private Sector Investment
Private sector investment plays a vital role in driving economic growth, creating jobs, and generating tax revenue, all of which contribute to reducing the Ontario deficit.
Long-Term Fiscal Sustainability
Implementing long-term fiscal sustainability measures, including responsible budgeting, effective debt management, and diversification of the economy, is crucial for ensuring Ontario's long-term financial health.
Conclusion
Ontario's $14.6 billion deficit is a serious issue stemming from a complex interplay of factors, with tariffs significantly impacting the province's economy. Increased costs for businesses and consumers, reduced export opportunities, and supply chain disruptions all contribute to this substantial shortfall. Other factors, such as government spending, economic slowdown, interest payments on debt, and demographic shifts, further exacerbate the situation. Addressing Ontario's deficit requires a comprehensive strategy involving government initiatives, private sector investment, and a focus on long-term fiscal sustainability. Understanding Ontario's deficit and the role of tariffs is crucial for informed decision-making. Stay informed about the evolving economic situation and the government's response to address Ontario's deficit. Further research into the specifics of tariff impacts on your industry or sector is highly recommended. Continue reading about solutions to address Ontario's deficit to better understand the challenges and opportunities ahead.

Featured Posts
-
 Knicks Win Over Pistons Nba Officials Admit To Crucial Missed Call
May 17, 2025
Knicks Win Over Pistons Nba Officials Admit To Crucial Missed Call
May 17, 2025 -
 Giants Vs Mariners Impact Of Injuries On The April 4 6 Series
May 17, 2025
Giants Vs Mariners Impact Of Injuries On The April 4 6 Series
May 17, 2025 -
 From The Pitch To The Podium Josh Cavallos Post Coming Out Activism
May 17, 2025
From The Pitch To The Podium Josh Cavallos Post Coming Out Activism
May 17, 2025 -
 Analyzing Cassie Venturas Testimony In Sean Combs Case
May 17, 2025
Analyzing Cassie Venturas Testimony In Sean Combs Case
May 17, 2025 -
 Mlb Betting Mariners Vs Reds Game Predictions And Best Odds
May 17, 2025
Mlb Betting Mariners Vs Reds Game Predictions And Best Odds
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Black Americans Reactions To Trumps Student Loan Plan
May 17, 2025
Black Americans Reactions To Trumps Student Loan Plan
May 17, 2025 -
 How Student Loan Debt Impacts Your Ability To Buy A House
May 17, 2025
How Student Loan Debt Impacts Your Ability To Buy A House
May 17, 2025 -
 Buying A House How Student Loans Affect Your Mortgage
May 17, 2025
Buying A House How Student Loans Affect Your Mortgage
May 17, 2025 -
 The Ultimate Guide To Refinancing Federal Student Loans
May 17, 2025
The Ultimate Guide To Refinancing Federal Student Loans
May 17, 2025 -
 Federal Student Loan Refinancing Pros Cons And Considerations
May 17, 2025
Federal Student Loan Refinancing Pros Cons And Considerations
May 17, 2025
