Reduced Apple Yields: The Impact Of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation
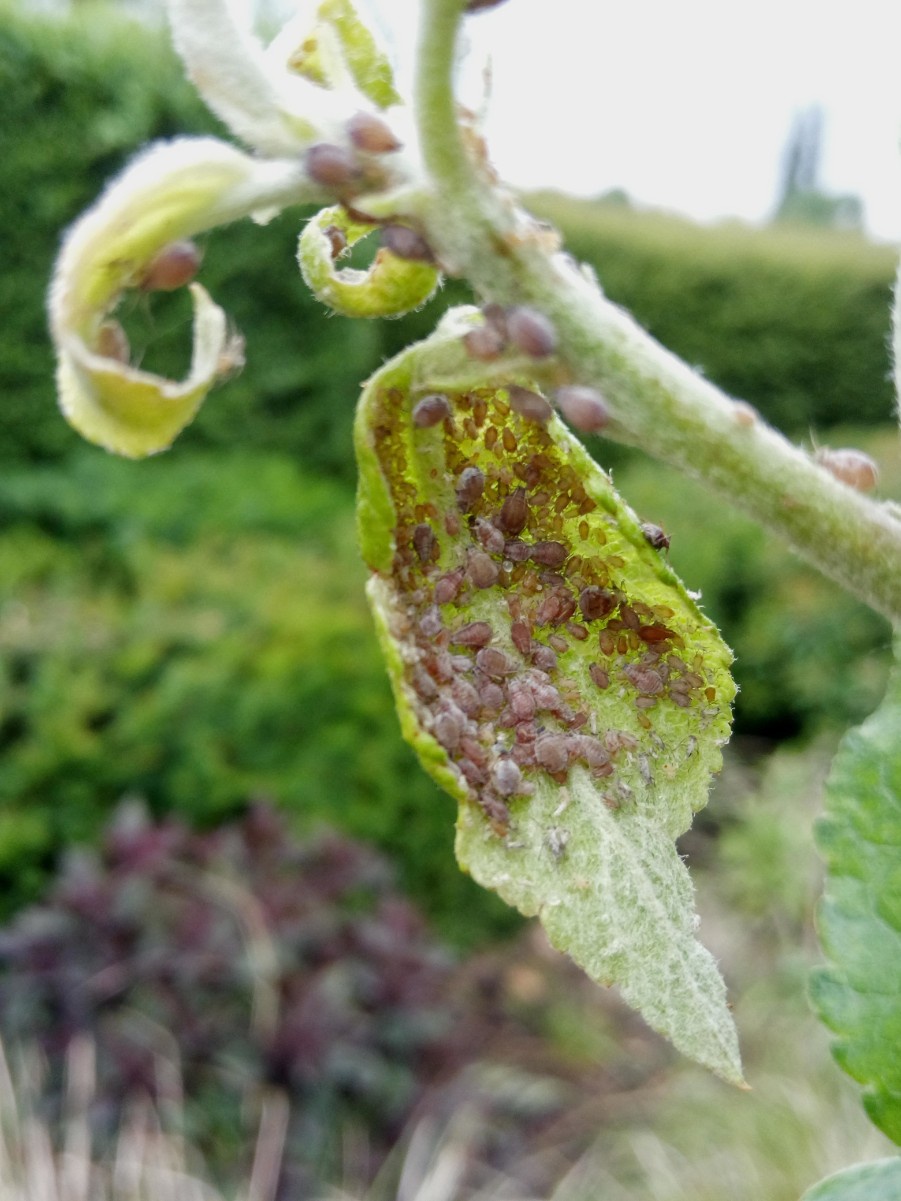

Table of Contents
Understanding the Rosy Apple Aphid and its Life Cycle
The rosy apple aphid (Dysaphis plantaginea) is a serious pest of apple trees worldwide. Understanding its life cycle is crucial for effective control.
Identifying Rosy Apple Aphids
Rosy apple aphids are small, typically measuring only a few millimeters in length. Their distinctive pinkish-red color, often with a powdery coating, makes them relatively easy to identify. They are usually found clustered on the undersides of leaves, particularly young, tender leaves, and along shoots. They may also be found on the fruit itself, especially during early development. (Insert image of rosy apple aphids here)
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Rosy apple aphids exhibit a complex life cycle, with several generations developing throughout the growing season. They overwinter as eggs laid on the twigs of apple trees. In spring, these eggs hatch into nymphs, which begin feeding and rapidly reproducing. They reproduce asexually through parthenogenesis, meaning they don't require males to produce offspring. This results in an exponential increase in aphid numbers within a short period. Multiple generations can be produced during a single growing season, leading to devastating infestations if left unchecked.
- High reproductive rate leads to rapid infestation.
- Multiple generations per season, with overlapping life stages.
- Overwintering eggs on twigs and branches ensure survival through cold periods.
The Impact of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation on Apple Trees
A heavy rosy apple aphid infestation can severely impact apple tree health and productivity. The consequences are both direct and indirect.
Direct Damage
Direct damage from rosy apple aphids is primarily caused by their feeding. They pierce the leaves and stems with their mouthparts, sucking out sap. This leads to several observable effects:
- Leaf curling: Infested leaves often become curled and distorted, reducing their photosynthetic capacity. (Insert image of curled leaves due to rosy apple aphid infestation here)
- Stunting: Severe infestations can stunt the growth of young shoots and branches.
- Distorted fruit: Aphid feeding on young fruit can cause malformation and reduced fruit size.
Indirect Damage
Beyond the direct damage, rosy apple aphids also cause indirect harm to apple trees:
-
Honeydew production: Rosy apple aphids excrete large quantities of honeydew, a sticky, sugary substance. This honeydew provides a medium for the growth of sooty mold, a black fungus that further reduces the photosynthetic efficiency of the leaves and renders the fruit unmarketable.
-
Virus transmission: While not a primary concern, rosy apple aphids can potentially transmit certain apple viruses during feeding, adding another layer of complexity to orchard management.
-
Reduced fruit size and quality.
-
Premature fruit drop.
-
Increased susceptibility to other pests and diseases, like apple scab.
Managing Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations for Improved Yields
Effective management of rosy apple aphid infestations requires a multi-pronged approach based on Integrated Pest Management (IPM) principles.
Monitoring and Early Detection
Regular orchard monitoring is crucial for early detection of rosy apple aphid infestations. Scouting should be conducted throughout the growing season, with a particular focus on spring and early summer when aphid populations are expanding. Visual inspection of leaves and shoots, looking for the characteristic pinkish-red aphids and signs of damage, is essential.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
IPM emphasizes a combination of strategies to control pests while minimizing environmental impact:
-
Biological control: Introducing natural predators such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps can help suppress aphid populations. These beneficial insects prey on aphids, reducing their numbers naturally.
-
Cultural control: Orchard sanitation, which includes removing weeds and fallen leaves that serve as overwintering sites for aphids, plays a vital role. Pruning to improve air circulation within the orchard canopy can help reduce aphid populations.
-
Chemical control: Insecticides should be used as a last resort, employing selective insecticides that target aphids without harming beneficial insects. Always follow label instructions carefully. Consider using environmentally friendly options such as insecticidal soaps or horticultural oils.
-
Regular monitoring is crucial for timely intervention.
-
Use of natural predators offers a sustainable approach.
-
Strategic pruning improves airflow and reduces favorable aphid habitats.
-
Consider using selective insecticides as a last resort, focusing on targeted applications.
Economic Impact of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations on Apple Production
Rosy apple aphid infestations have substantial economic consequences for apple growers.
Reduced Yields and Revenue
Heavy aphid infestations can lead to significant reductions in apple yields. Studies have shown reductions ranging from 10% to 50% depending on the severity of the infestation and the effectiveness of control measures. This directly translates to lower revenue for growers.
Increased Production Costs
The cost of managing rosy apple aphids adds another layer of economic pressure on growers. This includes expenses associated with monitoring, employing biological control agents, applying insecticides (if necessary), and the increased labor required for these interventions.
- Significant reduction in apple production and associated revenue.
- Increased operational costs for pest management.
- Potential market price fluctuations due to reduced supply.
Conclusion
The rosy apple aphid poses a serious threat to apple production, leading to reduced yields and significant economic losses for growers. Effective management strategies, utilizing integrated pest management techniques, are crucial for minimizing infestations and protecting apple crops. By implementing regular monitoring, utilizing biological controls where possible, and employing targeted chemical interventions only when necessary, apple growers can significantly mitigate the impact of the rosy apple aphid and maintain profitable yields. Don't let the rosy apple aphid ruin your harvest – take action today to protect your apple orchards and ensure healthy, high-yielding trees. Learn more about effective rosy apple aphid control strategies and protect your investment.

Featured Posts
-
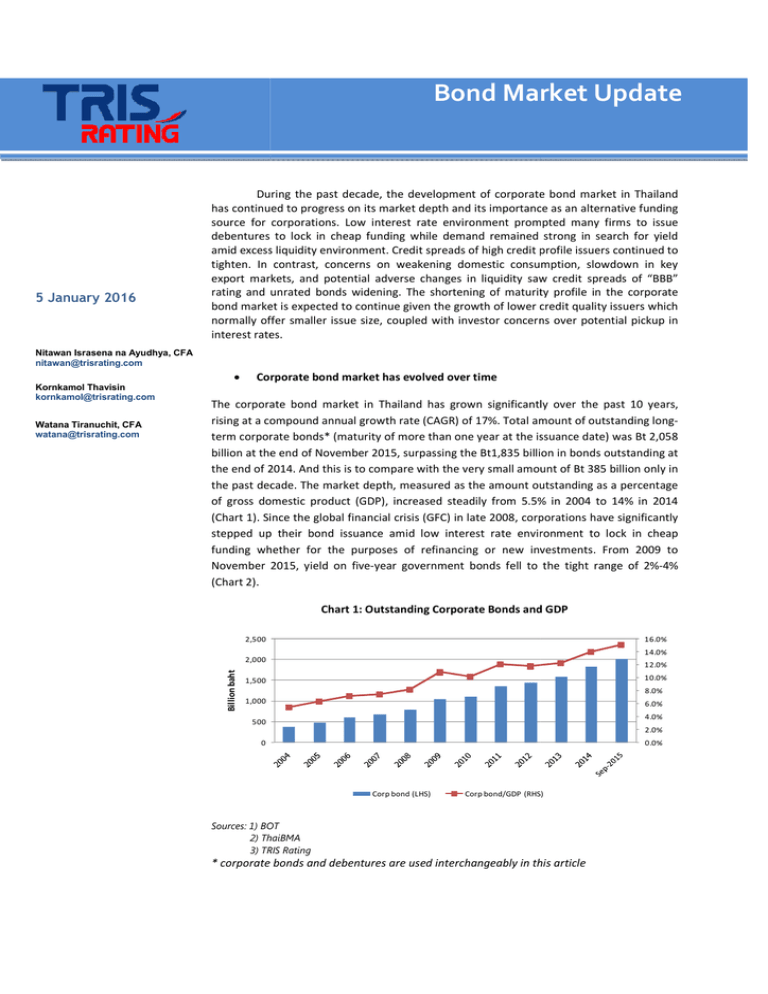 Sovereign Bond Market Update Swissquote Banks Perspective
May 19, 2025
Sovereign Bond Market Update Swissquote Banks Perspective
May 19, 2025 -
 Affordable Luxury Exploring The Rich Flavors Of Minervois Wines
May 19, 2025
Affordable Luxury Exploring The Rich Flavors Of Minervois Wines
May 19, 2025 -
 This Weekends Ufc 313 A Closer Look At Pereira Vs Ankalaev
May 19, 2025
This Weekends Ufc 313 A Closer Look At Pereira Vs Ankalaev
May 19, 2025 -
 Get The Answers Nyt Mini Crossword March 16 2025
May 19, 2025
Get The Answers Nyt Mini Crossword March 16 2025
May 19, 2025 -
 Experience Orlandos Longest Running Arts Festival At Loch Haven Park
May 19, 2025
Experience Orlandos Longest Running Arts Festival At Loch Haven Park
May 19, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Gazze De Yerinden Edilmenin Filistinliler Uezerindeki Etkisi
May 19, 2025
Gazze De Yerinden Edilmenin Filistinliler Uezerindeki Etkisi
May 19, 2025 -
 Filistinli Muelteciler Gazze Deki Varolus Muecadelesi
May 19, 2025
Filistinli Muelteciler Gazze Deki Varolus Muecadelesi
May 19, 2025 -
 Resultats Q4 2024 Credit Mutuel Am Impact Et Perspectives
May 19, 2025
Resultats Q4 2024 Credit Mutuel Am Impact Et Perspectives
May 19, 2025 -
 Gazze Deki Filistin Mueltecilerinin Yasam Kosullari Ve Zorluklari
May 19, 2025
Gazze Deki Filistin Mueltecilerinin Yasam Kosullari Ve Zorluklari
May 19, 2025 -
 Gazze Skandali Trump Dansoezler Altin Ve Elon Musk In Baglantisi
May 19, 2025
Gazze Skandali Trump Dansoezler Altin Ve Elon Musk In Baglantisi
May 19, 2025
