Rent Freeze Plan Excludes Private Landlords

Table of Contents
The Excluded: Understanding the Scope of the Rent Freeze Plan
The proposed rent freeze plan, while aiming to alleviate the burden of rising rents, notably exempts a significant portion of the rental market: private landlords. This exclusion is crucial to understand, as it defines who benefits and who bears the brunt of the current housing crisis.
-
Defining the Excluded: The plan specifically excludes private landlords owning fewer than five rental units. Larger property management companies and landlords with significant portfolios are included under the freeze. This distinction is based on the assumption that smaller landlords are more vulnerable to the economic repercussions of rent control.
-
Rationale Behind the Exclusion: Proponents of the exclusion argue that protecting small property owners is vital. They claim a complete rent freeze could bankrupt smaller landlords, leading to property neglect and a reduction in available rental units. This could ultimately worsen the affordable housing shortage.
-
Unaffected Rental Properties: The freeze does not affect properties such as those designated as luxury apartments, government-subsidized housing, or those undergoing significant renovations. This further complicates the picture and highlights the uneven application of the proposed rent control measures.
-
Impact Statistics: Estimates suggest that approximately 60% of rental units are owned by private landlords who are exempt from the rent freeze. This means a substantial portion of tenants are left vulnerable to rising rental costs.
Impact on Tenants: Increased Rent Burden and Housing Instability
The exclusion of private landlords from the rent freeze has potentially severe consequences for tenants residing in properties not covered by the legislation.
-
Increased Rent: Tenants in properties owned by excluded landlords face the prospect of significantly higher rent increases. This can be particularly detrimental in areas already experiencing a high cost of living. The lack of rent control exacerbates the existing pressure on household budgets.
-
Low-Income Tenants: Low-income tenants are disproportionately affected, facing the difficult choice between paying exorbitant rent or facing eviction and homelessness. This amplifies existing housing insecurity for already vulnerable populations.
-
Rise in Evictions: As rents continue to rise unchecked in properties owned by private landlords, the likelihood of evictions increases significantly, leading to further housing instability and potentially impacting employment and social support networks.
-
Housing Instability: The cumulative effects of increased rent burden and the threat of eviction create widespread housing instability, forcing families to relocate frequently, disrupting children's education, and making it challenging to build stable lives.
The Private Landlord Perspective: Challenges and Concerns
While the rent freeze aims to protect tenants, it also raises significant concerns for private landlords excluded from its provisions.
-
Financial Pressures: Private landlords, especially those owning smaller properties, face increasing financial pressures due to rising property taxes, maintenance costs, and inflation. The lack of rent control limits their ability to offset these increasing expenses.
-
Property Maintenance: Without the ability to raise rents to cover expenses, some landlords may struggle to maintain their properties adequately, potentially leading to disrepair and substandard living conditions for tenants.
-
Legal Challenges: The exclusion may create legal ambiguities and potential disputes between landlords and tenants concerning rent increases. This adds complexity and risk to property management.
-
Reduced Investment: The reduced profitability from owning rental properties due to lack of rent control might deter potential investors from entering the market, ultimately contributing to a further decline in the supply of affordable rental housing.
Potential Solutions and Policy Alternatives
Addressing the affordability crisis requires comprehensive solutions that consider both tenants' and landlords' needs.
-
Targeted Rent Subsidies: Implementing targeted rent subsidies for low-income tenants could alleviate the burden of rising rents without directly controlling landlords' pricing power.
-
Increased Funding for Affordable Housing: Increasing government funding for the development and preservation of affordable housing units is crucial to address the shortage of affordable rental options. This would also reduce pressure on the existing rental market.
-
Expanding Rent Control: While controversial, carefully designed and implemented rent control measures could be extended to more landlords, but with safeguards to avoid unintended consequences.
-
Collaboration and Communication: Improved communication and collaboration between landlords, tenants, and government agencies are vital to developing and implementing fair and effective housing policies. This fosters cooperation and ensures all stakeholders are heard.
Conclusion
The exclusion of private landlords from the proposed rent freeze plan presents a complex challenge with significant consequences for both tenants and landlords. The resulting impact on affordability and housing stability underscores the urgent need for comprehensive and equitable housing policies. The current approach may inadvertently worsen the affordable housing crisis. To ensure fair and equitable housing, we need robust discussions and solutions that prioritize affordable housing for all. Continue the conversation and demand action to improve access to affordable rental properties and address the ongoing issues of rent control and the housing crisis.

Featured Posts
-
 Jannik Sinner And Italian Open Good News On Grand Slam Participation Amidst Ban
May 28, 2025
Jannik Sinner And Italian Open Good News On Grand Slam Participation Amidst Ban
May 28, 2025 -
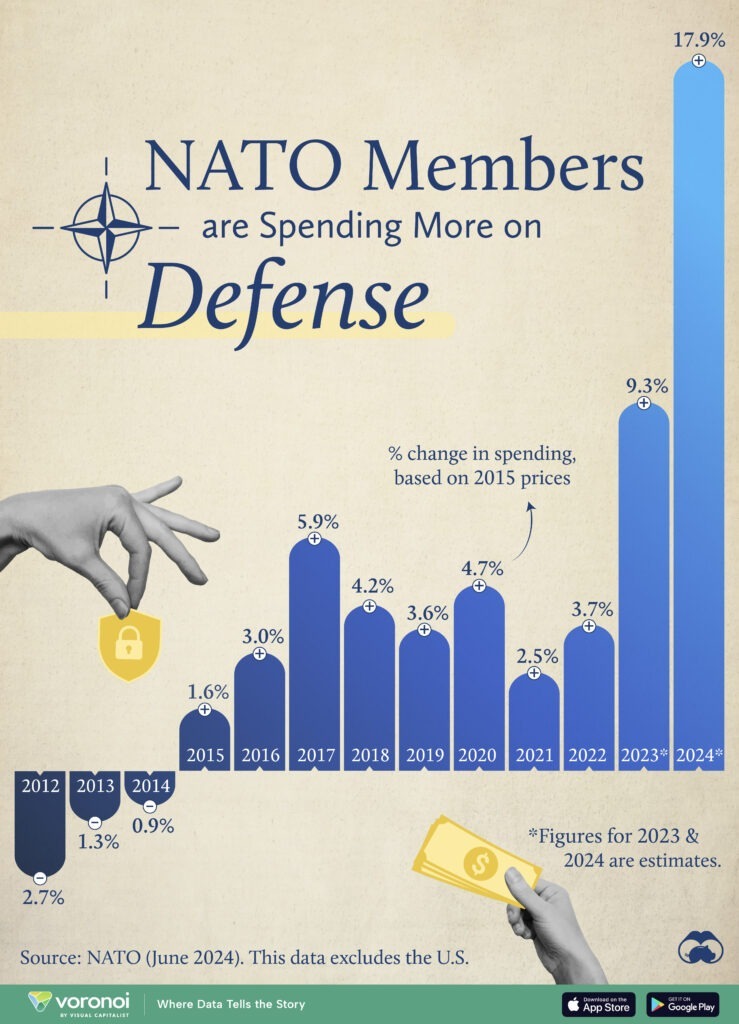 Nato Secretary General Rutte On Defense Spending Increase
May 28, 2025
Nato Secretary General Rutte On Defense Spending Increase
May 28, 2025 -
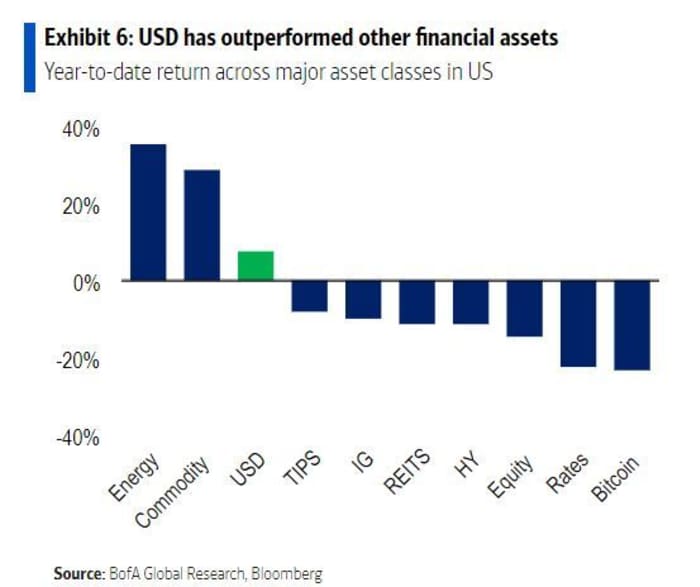 Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof A Offers Reassurance To Investors
May 28, 2025
Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof A Offers Reassurance To Investors
May 28, 2025 -
 Hujan Petir Landa Jawa Timur Prakiraan Cuaca Besok 29 Maret 2024
May 28, 2025
Hujan Petir Landa Jawa Timur Prakiraan Cuaca Besok 29 Maret 2024
May 28, 2025 -
 Tueketici Kredileri Patlamasi Abd De Beklentileri Asan Rakamlar
May 28, 2025
Tueketici Kredileri Patlamasi Abd De Beklentileri Asan Rakamlar
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Where To Invest A Geographic Analysis Of Promising Business Locations
May 29, 2025
Where To Invest A Geographic Analysis Of Promising Business Locations
May 29, 2025 -
 The China Market Hurdles For Bmw Porsche And Other Automakers
May 29, 2025
The China Market Hurdles For Bmw Porsche And Other Automakers
May 29, 2025 -
 Putin Criticism From Trump Russias Response And Its Implications
May 29, 2025
Putin Criticism From Trump Russias Response And Its Implications
May 29, 2025 -
 Kremlin Dismissal Of Trumps Putin Critique An Emotional Reaction
May 29, 2025
Kremlin Dismissal Of Trumps Putin Critique An Emotional Reaction
May 29, 2025 -
 Russia Calls Trumps Putin Criticism An Emotional Response
May 29, 2025
Russia Calls Trumps Putin Criticism An Emotional Response
May 29, 2025
