The Economic Impact Of Trump's China Tariffs: A Deep Dive Into Inflation And Supply Chain Disruptions
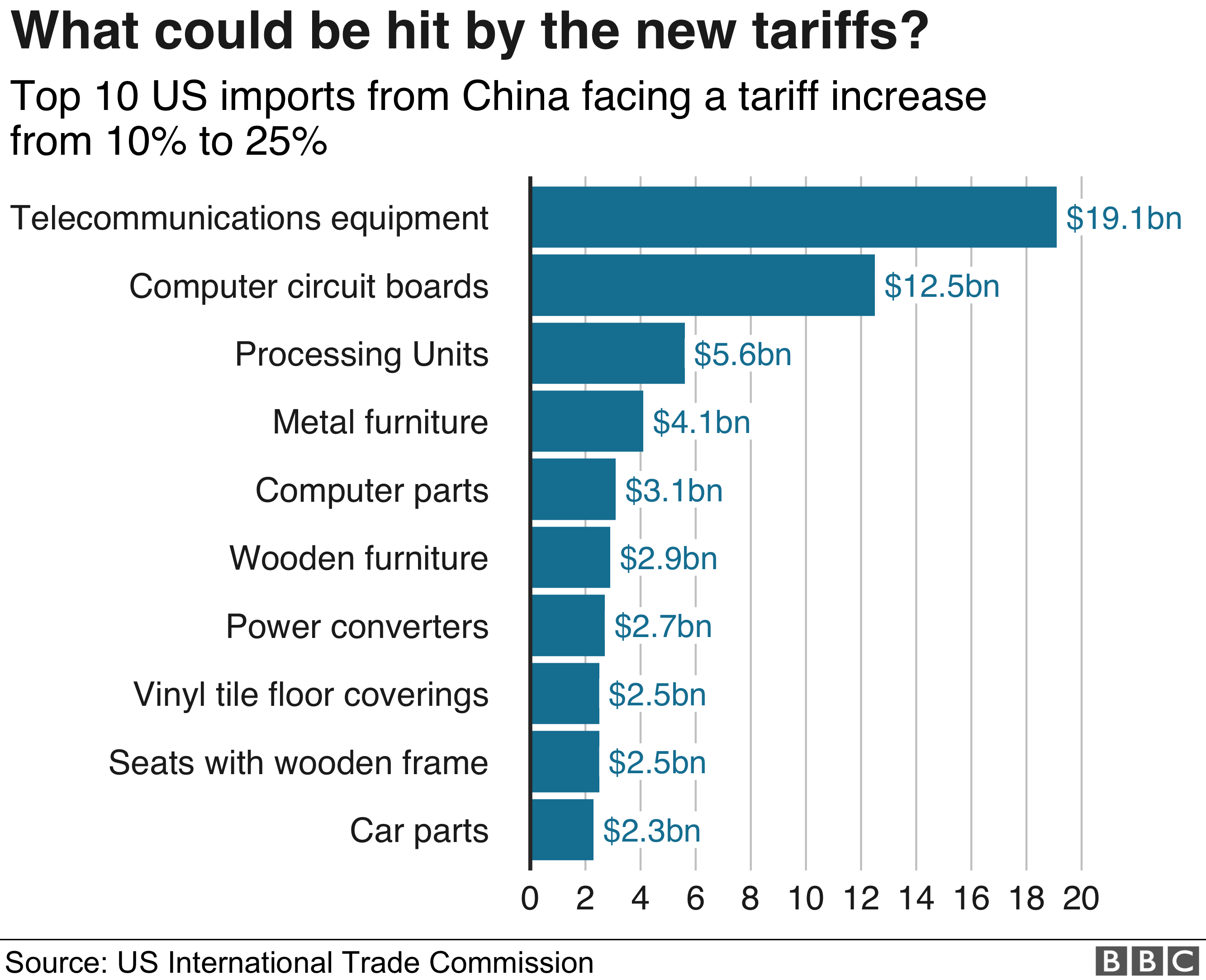
Table of Contents
The US inflation rate surged to a 40-year high in 2022, leaving many wondering about the contributing factors. While numerous elements played a role, the impact of Trump's China tariffs, implemented starting in 2018, deserves significant scrutiny. This article analyzes the economic consequences of these tariffs, focusing on their contribution to inflation and the widespread disruptions they caused to global supply chains. We will explore the direct and indirect effects, examining how these policies influenced consumer prices, business decisions, and the overall structure of international trade.
H2: The Direct Impact of Tariffs on Prices
H3: Increased Consumer Prices
Trump's China tariffs directly increased the price of numerous imported goods. These tariffs, essentially taxes on imports, were levied on a vast range of products, leading to immediate price increases for consumers.
- Examples: Electronics (smartphones, laptops), furniture, clothing, toys, and certain agricultural products experienced notable price hikes.
- Data Points: Studies from organizations like the Peterson Institute for International Economics have estimated that these tariffs increased consumer prices by several percentage points, impacting household budgets significantly. The precise impact varied depending on the product and consumer demand.
- Consumer Demand and Elasticity: The extent to which consumers absorbed these price increases depended on the price elasticity of demand for each product. Essential goods saw less of a demand reduction compared to luxury items.
H3: Impact on Businesses and Producers
Businesses relying on Chinese imports faced significant challenges. Increased import costs squeezed profit margins, forcing many to raise prices, absorb losses, or reduce production.
- Examples: Retailers selling imported goods, manufacturers using Chinese components, and wholesalers all felt the pinch.
- Profit Margins and Investment: Reduced profit margins impacted investment decisions, hindering growth and potentially leading to job losses in certain sectors.
- Tariffs as a Negotiating Tool: The administration presented these tariffs as a negotiating tool to secure better trade deals with China. However, the effectiveness of this approach remains a subject of ongoing debate among economists.
H2: Supply Chain Disruptions and Their Ripple Effects
H3: Increased Transportation Costs and Delays
The tariffs contributed to significant disruptions in global supply chains. Increased import costs and uncertainty led to longer shipping times and higher freight costs.
- Port Congestion and Logistical Challenges: Port congestion worsened, further delaying the delivery of goods and exacerbating existing supply chain bottlenecks.
- Data Points: Reports from shipping companies and logistics providers documented significant increases in both shipping times and costs during this period.
- Geopolitical Factors: The added complexity of navigating these trade restrictions highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains to geopolitical instability.
H3: Reshoring and Nearshoring
In response to the tariffs and supply chain disruptions, some companies attempted to "reshor" (bring manufacturing back to the US) or "nearshore" (move production to nearby countries).
- Challenges of Finding Alternative Suppliers: Finding suitable and cost-effective alternatives to Chinese suppliers proved challenging for many businesses.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth: While reshoring and nearshoring had the potential to create jobs in the US and other countries, the overall economic impact was complex and not uniformly positive.
- Data Points: Data on the growth of reshoring initiatives can provide insights into the scale of this shift, although measuring its overall economic effect is challenging.
H3: Impact on Global Trade
Trump's China tariffs ignited a trade war, with China and other countries imposing retaliatory tariffs. This negatively affected global trade relations and economic interdependence.
- Retaliatory Tariffs: China imposed tariffs on US goods, leading to a decline in bilateral trade and impacting US businesses.
- International Cooperation and Multilateral Trade Agreements: The trade war undermined international cooperation and created uncertainty about the future of multilateral trade agreements.
- Data Points: Statistics on global trade volumes during this period show a clear decline, highlighting the negative impact of the trade conflict.
H2: The Inflationary Pressure from Trump's China Tariffs
H3: The Transmission of Tariffs to Consumer Prices
The impact of tariffs on consumer prices wasn't immediate or uniform. Several factors influenced how these price increases were passed on.
- Market Structures and Price Transmission: The degree of price transmission varied depending on the market structure (e.g., perfectly competitive markets vs. monopolies).
- Inflationary Expectations: The expectation of further price increases could also contribute to inflationary pressures.
- Data Points: Analyzing Consumer Price Index (CPI) data can reveal the extent to which tariffs contributed to overall inflation.
H3: The Interaction with Other Inflationary Factors
Isolating the precise contribution of Trump's China tariffs to inflation is difficult because several other factors were at play.
- Difficulty of Isolating the Effect of Tariffs: Energy price shocks, supply chain bottlenecks due to the pandemic, and other macroeconomic factors all contributed to inflation.
- Econometric Models: Economists use econometric models to attempt to disentangle the various factors affecting inflation, but arriving at a definitive conclusion is challenging.
- Data Points: Examining macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth, unemployment rates, and energy prices provides a broader context for understanding inflationary pressures.
Conclusion:
Trump's China tariffs had a significant and multifaceted impact on the US economy. They directly increased consumer prices for various imported goods, disrupted global supply chains, and contributed to inflationary pressures. While the tariffs aimed to leverage trade as a negotiating tool, their consequences included increased costs for businesses, reduced competitiveness, and a decline in international cooperation. The long-term effects of these policies on economic stability and global trade relations continue to unfold, and understanding their full impact requires ongoing research and analysis. To further your understanding of this complex issue, we encourage you to explore resources from reputable economic institutions and engage in further discussion on the lasting consequences of Trump's China tariffs and their broader implications for trade policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Lynas Texas Refinery Us Aid Request As Costs Escalate
Apr 29, 2025
Lynas Texas Refinery Us Aid Request As Costs Escalate
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Huaweis New Ai Chip A Bid To Rival Nvidias Dominance In The Exclusive Market
Apr 29, 2025
Huaweis New Ai Chip A Bid To Rival Nvidias Dominance In The Exclusive Market
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Food Fuel And Water Scarcity In Gaza Fuel Calls To End Israeli Aid Ban
Apr 29, 2025
Food Fuel And Water Scarcity In Gaza Fuel Calls To End Israeli Aid Ban
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Anthony Edwards Nba Imposes 50 K Fine For Offensive Remarks To Fan
Apr 29, 2025
Anthony Edwards Nba Imposes 50 K Fine For Offensive Remarks To Fan
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Increased Rent In La After Fires Price Gouging Allegations Surface
Apr 29, 2025
Increased Rent In La After Fires Price Gouging Allegations Surface
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Impact Of Zombie Office Buildings On Chicagos Real Estate Market
Apr 29, 2025
The Impact Of Zombie Office Buildings On Chicagos Real Estate Market
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Key Republican Groups Threaten To Block Trumps Tax Bill
Apr 29, 2025
Key Republican Groups Threaten To Block Trumps Tax Bill
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Zombie Buildings In Chicago Understanding The Office Real Estate Collapse
Apr 29, 2025
Zombie Buildings In Chicago Understanding The Office Real Estate Collapse
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Can Trumps Tax Cuts Survive Internal Republican Opposition
Apr 29, 2025
Can Trumps Tax Cuts Survive Internal Republican Opposition
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Chicagos Office Market Meltdown The Rise Of Zombie Buildings
Apr 29, 2025
Chicagos Office Market Meltdown The Rise Of Zombie Buildings
Apr 29, 2025
