The Financial Challenges Facing Offshore Wind Energy Projects

Table of Contents
High Capital Expenditure (CAPEX) and Financing
The sheer scale of offshore wind energy projects translates into enormous upfront capital costs. This high CAPEX is a primary barrier to entry for many developers.
The Cost of Installation and Infrastructure
Offshore wind farms demand specialized equipment and expertise unlike anything seen in onshore projects.
- Specialized Vessels and Equipment: Installing turbines in deep waters requires specialized, and often expensive, floating platforms, heavy-lift cranes, and underwater construction equipment. These resources are often in high demand, driving up costs.
- Challenging Weather Conditions: Offshore installations are susceptible to unpredictable weather delays and damage, leading to schedule overruns and cost escalations. Stormy conditions require downtime and potentially costly repairs.
- Supply Chain Bottlenecks and Material Price Fluctuations: The global supply chain for critical components, like turbines and subsea cables, is susceptible to delays and price volatility, impacting project budgets.
- Other CAPEX Considerations:
- Longer lead times for equipment procurement.
- Increased transportation costs for heavy components.
- Higher insurance premiums due to the inherent risks.
Securing Project Financing
Securing funding for these massive offshore wind investment projects is challenging.
- Robust Financial Models: Investors require detailed financial models that demonstrate a clear pathway to a strong Return on Investment (ROI), accounting for all potential risks and uncertainties.
- Long-Term Financing: The long lifespan of offshore wind farms necessitates long-term financing arrangements, which can be difficult to secure in volatile financial markets.
- Competition for Investment Funds: The renewable energy sector is competitive, with numerous projects vying for the same limited pool of investment capital.
- Mitigating Financial Risks:
- Government subsidies and tax incentives are crucial in reducing project risk and attracting investment.
- Effective risk mitigation strategies, such as hedging against price fluctuations and insuring against unforeseen events, are essential.
- Green bonds and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investments are increasingly important sources of financing for sustainable projects like offshore wind.
Operational Expenditure (OPEX) and Maintenance
Even after construction, significant costs persist throughout the operational life of an offshore wind farm.
Ongoing Maintenance and Repair Costs
The harsh marine environment presents unique challenges for maintenance.
- Regular Maintenance: Offshore wind turbines require regular inspections, maintenance, and repairs due to the exposure to salt spray, strong winds, and wave action.
- Specialized Vessels and Technicians: Accessing and maintaining offshore turbines often requires specialized vessels and highly skilled technicians, increasing OPEX significantly.
- Remote Locations and Challenging Weather: The remote location and challenging weather conditions can lead to costly delays and disruptions in maintenance operations.
- Other OPEX Considerations:
- High cost of specialized crew transfer vessels (CTVs) and maintenance vessels.
- Difficulty in attracting and retaining qualified technicians willing to work in offshore environments.
- Increased maintenance needs and higher costs due to the impact of extreme weather events.
Grid Connection Costs
Connecting offshore wind farms to the onshore electricity grid is a costly and complex undertaking.
- Extensive Infrastructure Development: This process requires substantial infrastructure development, including the construction of high-voltage subsea cables and onshore substations.
- Distance from Shore: The distance of the wind farm from the shore significantly impacts the length and cost of the transmission lines.
- Grid Integration Challenges: Integrating large amounts of intermittent renewable energy into the existing grid presents technical challenges that can lead to delays and cost overruns.
- Other Grid Connection Costs:
- Challenges in obtaining necessary permits and approvals.
- Environmental impact assessments required for onshore infrastructure.
- Upgrading existing onshore transmission infrastructure to handle increased capacity.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Policy Risks
Navigating the regulatory landscape adds complexity and cost to offshore wind projects.
Permitting and Licensing Processes
The lengthy and complex permitting process is a major hurdle.
- Lengthy Approval Processes: Securing all necessary permits and licenses can take years, causing significant delays and increased financing costs.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Comprehensive environmental impact assessments are required, adding time and expense to the project timeline.
- Stakeholder Consultations: Extensive consultations with local communities, environmental groups, and other stakeholders are often necessary.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations or policies can significantly impact the feasibility and profitability of a project.
Political and Economic Instability
External factors can significantly impact the financial viability of these projects.
- Changes in Government Policies: Changes in government support for renewable energy, feed-in tariffs, or tax incentives can directly impact investor confidence and project financing.
- Economic Downturns: Economic recessions or fluctuations in energy prices can affect the profitability of offshore wind projects and make securing financing more difficult.
- Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical instability, international trade disputes, and currency fluctuations can all add significant risk and uncertainty to offshore wind projects.
Conclusion
Offshore wind energy offers a crucial pathway to a sustainable energy future, but overcoming the significant financial challenges discussed above is paramount for its success. High CAPEX, substantial OPEX, and regulatory uncertainties create considerable obstacles. However, through innovative wind farm financing strategies, strong government support, technological advancements, and improved project management, these hurdles can be overcome. Investing in and mitigating the financial risks associated with offshore wind energy projects is crucial for securing a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. Learn more about the financial aspects of offshore wind energy and potential solutions by exploring industry resources and consulting with financial experts.

Featured Posts
-
 Nigel Farages Reform Party Tory Claims Of A Sham Defection Announcement
May 04, 2025
Nigel Farages Reform Party Tory Claims Of A Sham Defection Announcement
May 04, 2025 -
 Formula Ones Explosive Growth The Role Of Ceo Stefano Domenicali
May 04, 2025
Formula Ones Explosive Growth The Role Of Ceo Stefano Domenicali
May 04, 2025 -
 Open Ais 2024 Event Easier Voice Assistant Creation Tools Unveiled
May 04, 2025
Open Ais 2024 Event Easier Voice Assistant Creation Tools Unveiled
May 04, 2025 -
 Rupert Lowes Defamation Lawsuit Against Nigel Farage False Allegations
May 04, 2025
Rupert Lowes Defamation Lawsuit Against Nigel Farage False Allegations
May 04, 2025 -
 Nat West Settles With Nigel Farage Over Account Closure
May 04, 2025
Nat West Settles With Nigel Farage Over Account Closure
May 04, 2025
Latest Posts
-
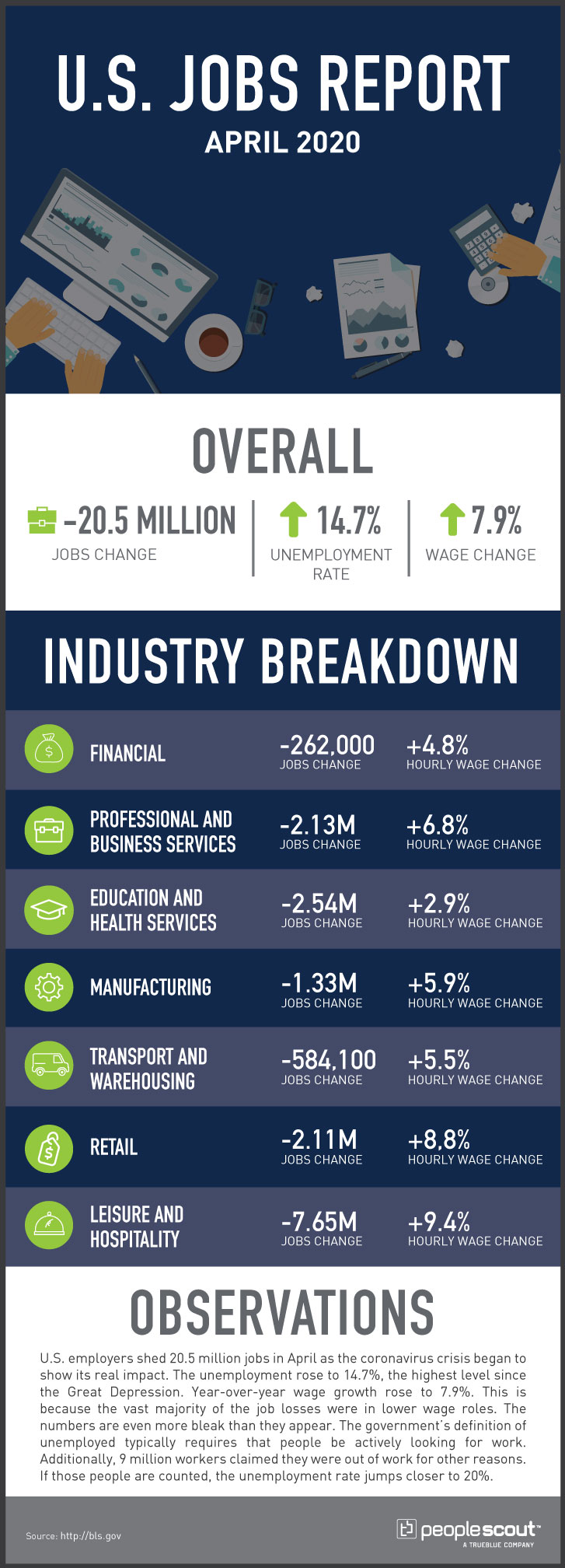 U S Jobs Report 177 000 Jobs Added In April Unemployment Steady At 4 2
May 04, 2025
U S Jobs Report 177 000 Jobs Added In April Unemployment Steady At 4 2
May 04, 2025 -
 Is Marvel Losing Its Touch A Critical Look At Recent Releases
May 04, 2025
Is Marvel Losing Its Touch A Critical Look At Recent Releases
May 04, 2025 -
 Open Ai 2024 Streamlined Voice Assistant Creation For Developers
May 04, 2025
Open Ai 2024 Streamlined Voice Assistant Creation For Developers
May 04, 2025 -
 Marvels Quality Control Addressing Criticisms Of Recent Films And Series
May 04, 2025
Marvels Quality Control Addressing Criticisms Of Recent Films And Series
May 04, 2025 -
 Voice Assistant Development Revolutionized Open Ais New Tools
May 04, 2025
Voice Assistant Development Revolutionized Open Ais New Tools
May 04, 2025
