The Harmful Effects Of School Suspensions: A Critical Look

Table of Contents
Negative Impact on Academic Performance
Suspensions significantly harm a student's academic progress, creating a cycle of disadvantage that extends far beyond the period of suspension itself. The effects manifest in several crucial ways:
Increased Absenteeism and Missed Instruction
- Disrupted Learning: Suspensions lead to substantial missed class time, disrupting the continuity of learning and negatively impacting academic performance. Students miss crucial lessons, assignments, and assessments, falling behind their peers.
- Academic Failure: The cumulative effect of missed learning creates a cycle of academic failure. Students struggle to catch up, leading to decreased motivation, lower grades, and increased frustration. This is especially detrimental for students already struggling academically, widening the achievement gap.
- Long-Term Impact: The long-term consequences of repeated suspensions can include reduced graduation rates and decreased future academic opportunities. The disruption to their education profoundly impacts their future prospects.
Reduced Graduation Rates
- Increased Dropout Risk: Students facing repeated suspensions are far more likely to drop out of school. The negative experiences associated with suspensions, such as feelings of isolation and unfair treatment, contribute to a sense of alienation and disengagement from school.
- Consequences of Dropping Out: Dropping out of school has significant long-term consequences, including reduced earning potential, increased unemployment, and a higher risk of involvement with the justice system. This highlights the far-reaching impact of seemingly minor disciplinary actions.
- Breaking the Cycle: Addressing the root causes of behavioral issues and providing supportive interventions is essential to preventing suspensions and reducing dropout rates. Early intervention and preventative measures are crucial for a student's future.
Detrimental Effects on Social-Emotional Well-being
School suspensions have devastating consequences for a student's social and emotional development, often exacerbating existing mental health challenges and creating new ones.
Increased Trauma and Mental Health Issues
- Traumatic Experience: Suspension can be a deeply traumatic experience, particularly for students with pre-existing mental health conditions. The isolation, feeling of punishment, and potential stigma associated with suspension can trigger or worsen anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems.
- Lack of Support: The absence of crucial support systems during and after a suspension can further exacerbate these mental health issues. Students may feel abandoned and unsupported, intensifying their feelings of isolation and hopelessness.
- Long-Term Mental Health: The long-term effects of repeated suspensions can include chronic mental health problems, impacting their ability to maintain healthy relationships and succeed in life. Addressing mental health needs is paramount for preventing future suspensions.
Damage to Self-Esteem and Behavior
- Negative Self-Perception: Suspension can significantly damage a student's self-esteem and reinforce negative self-perceptions. Being labeled as a troublemaker can lead to internalized stigma and a sense of worthlessness.
- Increased Defiance: Rather than promoting positive behavior change, suspensions can often lead to increased aggression and defiance. Students may feel unfairly treated and respond with resentment, creating a vicious cycle of disciplinary action.
- Lack of Positive Role Models: The absence of positive adult role models and supportive relationships during and after suspension can further exacerbate negative behaviors. A lack of guidance and support can lead to increased risk-taking and engagement in harmful activities.
Contribution to the School-to-Prison Pipeline
The overuse of school suspensions, particularly its disproportionate application, significantly contributes to the school-to-prison pipeline.
Disproportionate Impact on Minority Students
- Systemic Bias: Minority students, particularly Black and Hispanic students, are disproportionately suspended compared to their white peers. This disparity reflects underlying biases within school disciplinary practices and perpetuates systemic inequalities.
- Increased Risk of Incarceration: The increased suspension rates for minority students directly increase their risk of involvement with the juvenile justice system, creating a pathway from school to prison.
- Addressing Bias: Addressing these biases through equitable disciplinary practices and culturally responsive interventions is vital to breaking the school-to-prison pipeline.
Lack of Support and Resources
- Inadequate Support: Suspended students often lack access to the support services and resources necessary to address the underlying causes of their behavioral issues. The absence of positive interventions increases the likelihood of future disciplinary problems.
- Investment in Alternatives: Investing in restorative justice programs, conflict resolution training, and increased access to mental health services is crucial for preventing suspensions and promoting positive behavior change. Focusing on support rather than punishment is key.
- Creating Safe Schools: Creating safe and supportive school environments, where students feel valued and respected, is crucial for preventing the need for suspensions in the first place.
Conclusion
The detrimental effects of school suspensions are undeniable, significantly impacting academic achievement, social-emotional well-being, and contributing to the school-to-prison pipeline. The data overwhelmingly supports the need for a significant shift away from punitive disciplinary measures towards more supportive and restorative approaches. We must advocate for effective alternatives to school suspensions, such as restorative justice practices, conflict resolution training, positive behavior interventions and support (PBIS), and increased access to mental health services. Let's work together to create safer, more inclusive, and effective learning environments for all students by reducing the reliance on school suspensions and building a better future for our children. Let's find better alternatives to school suspensions and implement truly positive behavior interventions.

Featured Posts
-
 Dont Miss Out Glastonbury 2025 Resale Tickets
May 03, 2025
Dont Miss Out Glastonbury 2025 Resale Tickets
May 03, 2025 -
 Comprendre La Creme De La Crim L Univers De Joseph Sur Tf 1
May 03, 2025
Comprendre La Creme De La Crim L Univers De Joseph Sur Tf 1
May 03, 2025 -
 Access To Birth Control Examining The Post Roe Otc Landscape
May 03, 2025
Access To Birth Control Examining The Post Roe Otc Landscape
May 03, 2025 -
 Trump Et Macron Au Vatican Les Coulisses D Une Rencontre Difficile
May 03, 2025
Trump Et Macron Au Vatican Les Coulisses D Une Rencontre Difficile
May 03, 2025 -
 Laura Keller Em Retiro De Tantra Yoga Fotos Do Biquini
May 03, 2025
Laura Keller Em Retiro De Tantra Yoga Fotos Do Biquini
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
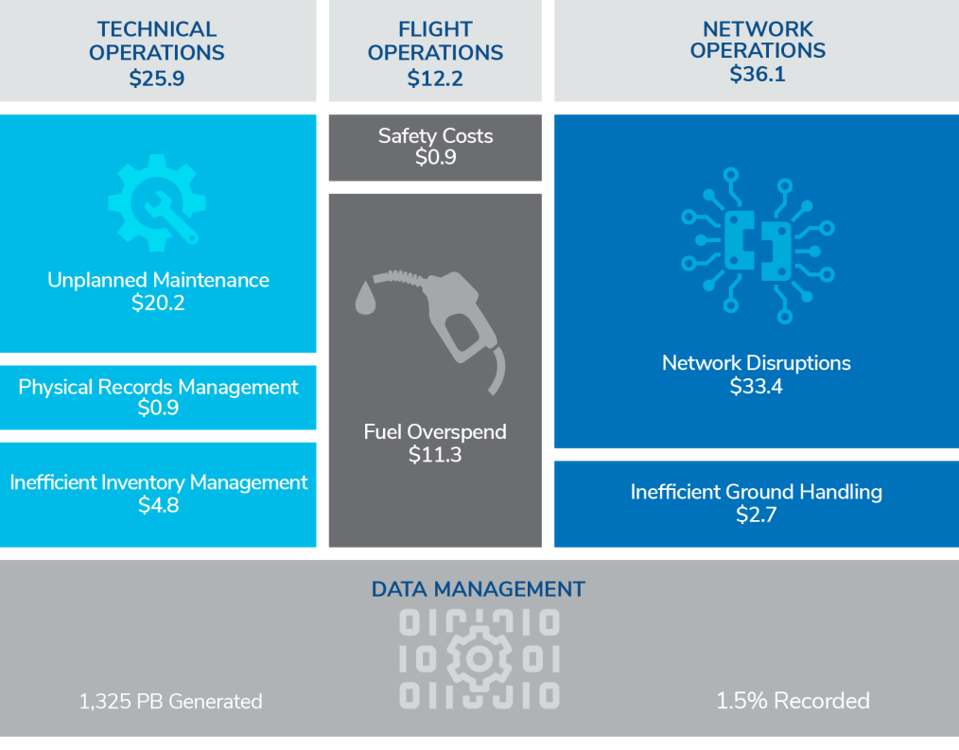 The Impact Of Oil Supply Instability On Airline Operations And Finances
May 04, 2025
The Impact Of Oil Supply Instability On Airline Operations And Finances
May 04, 2025 -
 Fabio Christen Se Impone En La Vuelta Ciclista A La Region De Murcia
May 04, 2025
Fabio Christen Se Impone En La Vuelta Ciclista A La Region De Murcia
May 04, 2025 -
 Oil Crisis Navigating The Turbulent Waters For Airlines
May 04, 2025
Oil Crisis Navigating The Turbulent Waters For Airlines
May 04, 2025 -
 45 Vuelta Ciclista A La Region De Murcia Victoria Para Fabio Christen
May 04, 2025
45 Vuelta Ciclista A La Region De Murcia Victoria Para Fabio Christen
May 04, 2025 -
 Soaring Fuel Costs The Airline Industrys Struggle With Oil Supply Shocks
May 04, 2025
Soaring Fuel Costs The Airline Industrys Struggle With Oil Supply Shocks
May 04, 2025
