The Justice Department And The Future Of School Desegregation
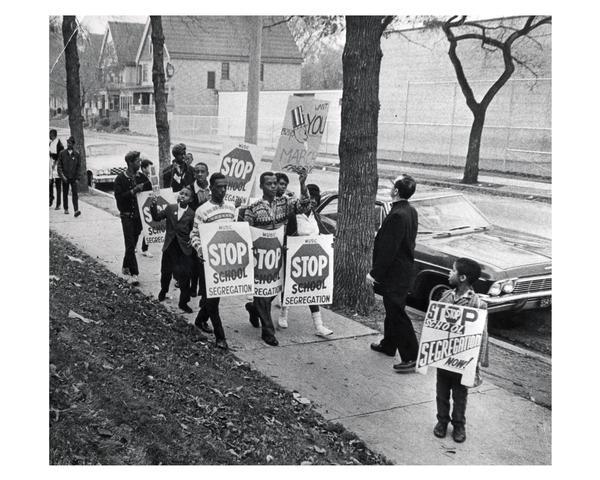

Table of Contents
The Legal History of School Desegregation and the DOJ's Role
The legal battle for school desegregation is a long and complex one. Brown v. Board of Education (1954) declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. However, this landmark decision faced significant resistance, and the Justice Department played a pivotal role in enforcing desegregation orders.
-
Key Supreme Court cases and their impact: Following Brown, cases like Green v. County School Board (1968) and Swann v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education (1971) further clarified the requirements for desegregation, including busing and other remedial measures. These rulings significantly impacted the DOJ’s approach to enforcing desegregation.
-
Examples of DOJ interventions in specific school districts: The DOJ intervened in numerous school districts across the South and beyond, filing lawsuits, negotiating settlements, and monitoring compliance with court orders. These interventions often involved significant resources and legal expertise.
-
The evolution of DOJ strategies over time: The DOJ's strategies have evolved over time, adapting to changing legal landscapes and social realities. Early efforts focused on dismantling de jure segregation (segregation mandated by law), while later interventions addressed the more subtle forms of de facto segregation.
Current Challenges to School Desegregation
While de jure segregation has largely been eradicated, de facto segregation remains a significant problem. This type of segregation, stemming from residential patterns, socioeconomic disparities, and other factors, continues to create racially isolated schools.
-
Examples of modern-day segregation practices: Subtle forms of segregation, such as selective school admissions policies, school boundary lines drawn along racial lines, and unequal resource allocation, contribute to the persistent problem of racial imbalance in schools.
-
Statistical data on racial disparities in school resources and achievement: Numerous studies demonstrate significant disparities in school funding, teacher quality, and academic achievement between predominantly white schools and schools with predominantly minority student populations. This data underscores the ongoing need for interventions.
-
The impact of residential segregation on school demographics: Residential segregation remains a major driver of school segregation. Concentrated poverty and racial residential segregation often lead to unequal access to quality education. Addressing this requires a multifaceted approach that tackles both housing and education policies.
The Justice Department's Current Approach to School Desegregation
The DOJ's current approach to school desegregation involves a combination of litigation, investigations, and technical assistance. The department actively investigates complaints of discrimination and takes legal action when necessary.
-
Recent DOJ actions related to school desegregation cases: The DOJ continues to file lawsuits and intervene in cases involving discriminatory school practices, although the frequency and scope of such interventions have varied across different administrations.
-
Analysis of the DOJ's budget allocation for desegregation efforts: The budget allocated to school desegregation efforts varies and is often influenced by the political climate and prioritization of civil rights issues.
-
Evaluation of the success rate of DOJ interventions in desegregation cases: Measuring the success of DOJ interventions is complex. While some cases result in significant improvements in school integration, others face persistent challenges, highlighting the need for more holistic and long-term strategies.
The Role of Civil Rights Enforcement
The Civil Rights Division of the DOJ plays a central role in enforcing federal civil rights laws related to education. Specific sections within the division are dedicated to investigating and litigating cases involving school discrimination. Their mandates cover a broad range of issues impacting school desegregation, including access to facilities, equal educational opportunities, and discriminatory discipline practices.
The Impact of Political Climate on School Desegregation Enforcement
The political climate significantly influences the DOJ's approach to school desegregation. Changes in administration can lead to shifts in priorities, resource allocation, and enforcement strategies. This fluctuating political landscape presents a significant challenge to maintaining consistent and effective desegregation efforts.
Future Directions for School Desegregation and the DOJ's Role
Achieving truly integrated and equitable schools requires a multi-pronged approach. The DOJ can play a critical role by:
-
Potential legislative solutions to address segregation: Legislative action could address issues such as funding disparities, school assignment policies, and discriminatory practices.
-
Innovative approaches to promoting school integration: Exploring innovative approaches such as magnet schools, school choice programs (with careful consideration to avoid re-segregation), and inter-district cooperation can promote integration.
-
The importance of community buy-in for successful desegregation initiatives: Community engagement is crucial for the success of any desegregation initiative. Local partnerships and collaboration with school districts, community organizations, and parents are essential.
Conclusion
The Justice Department has a long and complex history of involvement in school desegregation. While significant progress has been made, de facto segregation continues to create unequal educational opportunities for many students. The DOJ's role remains crucial in addressing these challenges through litigation, investigation, and technical assistance. However, achieving truly integrated and equitable schools necessitates a sustained commitment from all stakeholders. The fight for school desegregation requires sustained effort and commitment. Understanding the Justice Department's role and advocating for effective policies are crucial steps toward ensuring equal educational opportunities for all children. Learn more about how you can contribute to the ongoing work towards effective school desegregation.

Featured Posts
-
 Reforme Des Partis Politiques En Algerie Positions Du Pt Ffs Rcd Et Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025
Reforme Des Partis Politiques En Algerie Positions Du Pt Ffs Rcd Et Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025 -
 1 Mayis Emek Ve Dayanisma Guenue Tarihsel Arbedeler Ve Guenuemuez Yansimalari
May 03, 2025
1 Mayis Emek Ve Dayanisma Guenue Tarihsel Arbedeler Ve Guenuemuez Yansimalari
May 03, 2025 -
 Saudi Arabias Abs Market A Post Reform Analysis
May 03, 2025
Saudi Arabias Abs Market A Post Reform Analysis
May 03, 2025 -
 Lotto Plus 1 And 2 Results Find The Latest Winning Numbers
May 03, 2025
Lotto Plus 1 And 2 Results Find The Latest Winning Numbers
May 03, 2025 -
 Trump Et Macron Au Vatican Les Coulisses D Une Rencontre
May 03, 2025
Trump Et Macron Au Vatican Les Coulisses D Une Rencontre
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Reducing Emissions And Energy Costs The Case For Wind Powered Trains
May 04, 2025
Reducing Emissions And Energy Costs The Case For Wind Powered Trains
May 04, 2025 -
 The Future Of Rail Exploring The Potential Of Wind Powered Trains
May 04, 2025
The Future Of Rail Exploring The Potential Of Wind Powered Trains
May 04, 2025 -
 Wind Energy For Trains A Sustainable Solution For Rail Transport
May 04, 2025
Wind Energy For Trains A Sustainable Solution For Rail Transport
May 04, 2025 -
 Lion Storage Secures Funding For 1 4 G Wh Bess Project In Netherlands
May 04, 2025
Lion Storage Secures Funding For 1 4 G Wh Bess Project In Netherlands
May 04, 2025 -
 Harnessing The Wind How Wind Powered Trains Can Reduce Pollution And Save Energy
May 04, 2025
Harnessing The Wind How Wind Powered Trains Can Reduce Pollution And Save Energy
May 04, 2025
