Trump Tariffs Resume: What It Means For The European Economy
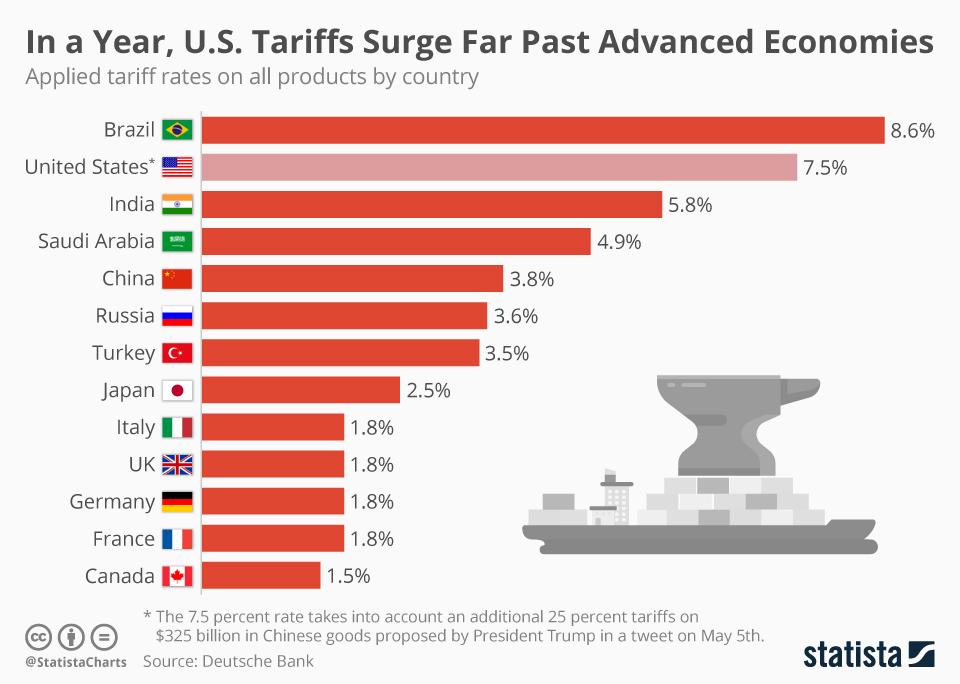
Table of Contents
Impact on Specific European Industries
The renewed imposition of Trump tariffs has triggered a ripple effect across several vital European industries. The consequences extend beyond immediate financial impacts, affecting job security, investment decisions, and long-term competitiveness.
Automotive Sector
The automotive sector, a cornerstone of many European economies, is particularly vulnerable to the reinstated tariffs. The US market is a significant export destination for European car manufacturers, and these tariffs directly impact their ability to compete effectively.
- Reduced competitiveness: Increased import costs make European cars less attractive to US consumers.
- Job losses: Reduced export volumes can lead to factory closures and job losses across the supply chain.
- Increased prices for European consumers: Retaliatory tariffs imposed by the EU could lead to higher prices for consumers in Europe.
- Retaliatory measures from the EU: The EU may implement counter-tariffs on US goods, further escalating trade tensions.
The automotive industry contributes significantly to the EU's GDP, with data indicating its contribution to be in the hundreds of billions of euros annually. The impact of these tariffs could therefore significantly impact overall economic growth.
Agricultural Products
European agricultural producers also face considerable challenges due to the Trump tariffs. Key export products like wine, cheese, and agricultural machinery are directly affected.
- Reduced export volumes: Tariffs make European agricultural products more expensive in the US market, reducing demand.
- Price drops for farmers: Reduced export opportunities can lead to oversupply and lower prices for European farmers.
- Increased competition from non-EU producers: US consumers may shift to cheaper alternatives from countries not subject to the tariffs.
- Potential subsidies needed: Governments may need to provide financial support to farmers to offset the negative impacts of the tariffs.
Comparative data on pre- and post-tariff export numbers reveal a substantial decline in agricultural exports to the US, highlighting the significant impact of these trade barriers.
Steel and Aluminum Industries
The steel and aluminum industries are particularly sensitive to trade policies. The reinstated Trump tariffs lead to increased costs and reduced competitiveness for European producers.
- Increased production costs: Tariffs make imported raw materials more expensive, increasing overall production costs.
- Reduced profitability: Higher production costs squeeze profit margins and threaten the viability of some businesses.
- Potential plant closures: Reduced profitability can lead to factory closures and job losses.
- Job losses in related industries: The impact extends beyond steel and aluminum production, affecting related industries and the broader economy.
EU steel and aluminum production and export volumes have been significantly affected, necessitating proactive measures to mitigate the negative impact of these trade restrictions.
Economic and Political Ramifications for the EU
The economic and political repercussions of the resumed Trump tariffs extend far beyond specific industries. The broader effects on the EU economy and its global relationships are significant.
GDP Growth
The Trump tariffs pose a considerable threat to EU GDP growth. The combination of decreased exports, reduced consumer spending, and diminished business investment contributes to a negative outlook.
- Reduced consumer spending: Higher prices on imported goods can decrease consumer spending and hamper economic growth.
- Decreased business investment: Uncertainty about future trade relations can lead to decreased business investment.
- Negative impact on overall economic confidence: Trade tensions can undermine overall economic confidence, leading to further economic slowdown.
Economic forecasts and models suggest that the reinstated tariffs could shave several percentage points off EU GDP growth in the coming years.
Trade Relations with the US
The renewed tariffs exacerbate already strained trade relations between the EU and the US. This creates a risk of further escalation and retaliatory measures.
- Increased trade barriers: The tariffs serve as a barrier to trade, restricting the flow of goods and services.
- Potential for trade wars: Retaliatory tariffs from both sides could trigger a broader trade war, negatively impacting global trade.
- Strained diplomatic relations: Trade disputes can strain diplomatic relations and complicate cooperation on other issues.
- Impact on future trade agreements: The current tensions could hinder progress on future trade agreements between the EU and the US.
Current EU-US trade negotiations are hampered by the uncertainty surrounding these tariffs, making the path towards a resolution even more challenging.
Geopolitical Implications
The Trump tariffs have far-reaching geopolitical implications for the EU. The EU must consider its relationships with other trading partners and adapt its trade strategies accordingly.
- Shifting trade alliances: The EU may seek to strengthen ties with other trading partners to reduce its reliance on the US.
- Increased reliance on other trading blocs: The EU may explore deeper integration with other trading blocs, such as the Asian or Latin American markets.
- Potential for strengthened EU-China trade relations: Trade tensions with the US could lead to a closer relationship between the EU and China.
- Diversification of trade partners: The EU is likely to pursue a strategy of diversifying its trade partners to reduce vulnerability to trade disputes with any single country.
Mitigation Strategies for European Businesses
European businesses must adopt proactive strategies to mitigate the negative consequences of the resumed Trump tariffs. This includes diversification, cost optimization, and effective advocacy.
Diversification of Markets
Reducing reliance on the US market is crucial. European businesses should explore alternative export markets to mitigate the impact of tariffs.
- Expanding into Asian markets: The Asian market offers significant growth potential for many European businesses.
- Strengthening ties with Latin American countries: Latin America presents another attractive market for European exports.
- Focusing on domestic consumption: Businesses can also focus on strengthening their domestic markets to reduce reliance on exports.
Successful diversification strategies require thorough market research, strategic partnerships, and adaptation to local market conditions.
Cost Optimization and Efficiency Improvements
Businesses must identify ways to improve efficiency and reduce costs to remain competitive in the face of increased tariffs.
- Investing in automation: Automation can help increase productivity and reduce labor costs.
- Streamlining supply chains: Optimizing supply chains can reduce transportation costs and improve efficiency.
- Reducing waste: Minimizing waste throughout the production process can reduce costs and improve sustainability.
- Exploring government support programs: Businesses should explore government aid packages and incentives designed to support industries affected by the tariffs.
Government support programs and incentives can play a crucial role in assisting businesses to adapt to new realities imposed by trade barriers.
Lobbying and Advocacy
Industry associations and businesses themselves must actively participate in lobbying and advocacy efforts to influence policy decisions.
- Negotiating with the EU: Businesses should work with the EU to advocate for policies that mitigate the negative impact of the tariffs.
- Influencing policy decisions: Active engagement in policy discussions is essential to shape trade policy that benefits European businesses.
- Raising awareness of the impact of tariffs: Effective communication is key to raising awareness among policymakers and the public.
Successful lobbying efforts can lead to policy changes that protect the interests of affected industries and alleviate the negative impacts of these trade restrictions.
Conclusion
The resumed Trump tariffs pose significant challenges to the European economy, impacting key industries such as automotive, agriculture, and steel and aluminum. These tariffs have far-reaching economic and political ramifications, potentially affecting GDP growth, trade relations with the US, and the EU's geopolitical standing. European businesses must adopt proactive strategies, including market diversification, cost optimization, and lobbying, to mitigate the negative impacts. Policymakers need to collaborate with industries and consider comprehensive solutions to address these challenges and navigate the complexities of a changing global trade landscape. To learn more about the specific implications for your industry or region, and to contribute to informed discussions about potential solutions and policy responses related to Trump tariffs and their ongoing impact on the EU, we encourage further research into relevant EU and industry reports. The ongoing impact of Trump tariffs requires constant vigilance and proactive engagement from all stakeholders.

Featured Posts
-
 Heatwave Advisory For Outdoor Workers Ghaziabad And Noida Take Action
May 13, 2025
Heatwave Advisory For Outdoor Workers Ghaziabad And Noida Take Action
May 13, 2025 -
 3 S And P 500 Gain Positive Impact Of Us China Trade Deal
May 13, 2025
3 S And P 500 Gain Positive Impact Of Us China Trade Deal
May 13, 2025 -
 New Muslim Community In Texas Faces Setbacks After Mosque Restrictions
May 13, 2025
New Muslim Community In Texas Faces Setbacks After Mosque Restrictions
May 13, 2025 -
 Funeral For Teenager Killed In School Stabbing
May 13, 2025
Funeral For Teenager Killed In School Stabbing
May 13, 2025 -
 Aws Pokoryaet
May 13, 2025
Aws Pokoryaet
May 13, 2025
