Will The Fed Hold Rates? Analyzing Current Economic Pressures On Monetary Policy
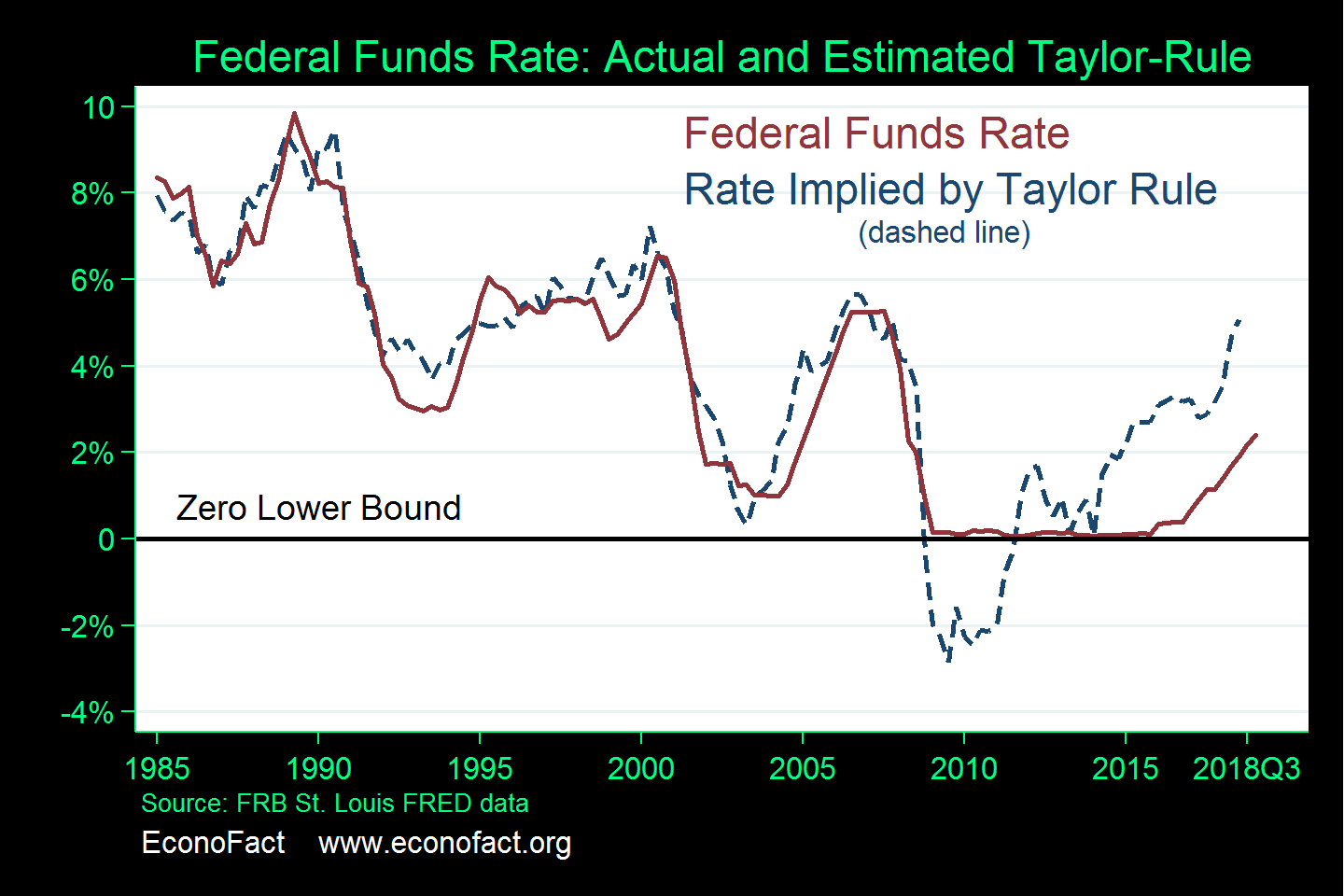
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures: A Persistent Challenge
The Federal Reserve's primary mandate is price stability. Therefore, understanding inflationary pressures is key to predicting whether the Fed will hold rates or adjust them. The current inflation landscape is multifaceted and presents a significant challenge.
Core Inflation Remains Sticky
Despite headline inflation showing some cooling, core inflation—a measure that excludes volatile food and energy prices—remains stubbornly high. This indicates that underlying inflationary pressures persist, raising concerns about the Fed's ability to achieve its 2% inflation target.
- Sticky wage growth: Strong wage growth, while positive for workers, contributes significantly to persistent core inflation. As businesses face higher labor costs, they often pass these costs on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Lingering supply chain disruptions: Although supply chain issues have eased considerably since their peak, some bottlenecks remain, still exerting upward pressure on prices for certain goods and services. These lingering disruptions add to inflationary pressures.
- Producer Price Index (PPI) analysis: Monitoring the Producer Price Index (PPI), which measures inflation at the wholesale level, provides valuable insight into future inflation trends. A persistently high PPI suggests that inflationary pressures may continue to build.
The Fed's Inflation Target
The Fed's stated goal is to achieve 2% inflation. This target is crucial because it influences their monetary policy decisions. Any significant deviation from this target, whether above or below, will likely trigger a response.
- Commitment to price stability: The Fed's commitment to achieving price stability is unwavering. They view persistent inflation as detrimental to long-term economic health.
- Consequences of missing the target: Failing to meet the inflation target can lead to various negative consequences, including erosion of purchasing power, increased uncertainty, and potential damage to the credibility of the central bank.
Economic Growth and Recessionary Risks
The Fed’s decision on whether to hold rates is also heavily influenced by the state of economic growth and the risk of a recession. These factors introduce a crucial element of trade-off into the equation.
Slowing GDP Growth
Recent economic data reveals slowing GDP growth, raising concerns about the possibility of an economic recession. This slowdown is largely attributable to the Fed's previous interest rate hikes.
- Analysis of GDP growth figures and forecasts: Analyzing recent GDP figures and various economic forecasts helps to assess the current state of the economy and the likelihood of a recession.
- Impact of rising interest rates: Rising interest rates curb consumer spending and business investment, slowing down economic growth. This is a deliberate consequence of the Fed's efforts to control inflation.
Labor Market Dynamics
While the unemployment rate remains low, signifying economic strength, robust wage growth remains a concern fueling inflation. The labor market's health is a significant consideration for the Fed.
- Labor market tightness: A tight labor market, characterized by low unemployment and high demand for workers, contributes to upward pressure on wages and inflation.
- Potential labor market softening: The Fed might hope to see some softening in the labor market as a consequence of its rate hikes, helping to alleviate inflationary pressures without triggering a significant recession.
Geopolitical Factors and Global Uncertainty
External factors such as geopolitical events and global economic uncertainty significantly influence the US economy and the Fed's decisions. These external pressures add another layer of complexity to the already intricate situation.
Global Economic Slowdown
Global economic uncertainty stemming from events like the war in Ukraine directly impacts US economic growth and inflation through various channels.
- Impact of the war in Ukraine: The war in Ukraine has caused significant disruptions to energy markets and global supply chains, contributing to inflationary pressures worldwide.
- Influence of global economic conditions: Global economic slowdowns can negatively impact US export growth and investment, potentially affecting the Fed’s decisions on whether to hold rates or adjust.
Financial Market Volatility
Volatility in financial markets can influence the Fed's actions. Significant market fluctuations can increase systemic risk and potentially necessitate a more cautious approach to monetary policy.
- Impact of interest rate hikes on bond yields and equity markets: Interest rate hikes typically lead to increased bond yields and potentially decreased equity market valuations.
- Potential for financial instability: The Fed must consider the potential for financial instability to influence its policy decisions. A sharp market downturn could force them to adopt a more accommodative stance.
Conclusion
The decision of whether the Fed will hold rates is a complex balancing act. While inflation shows some signs of cooling, persistent core inflation and the risk of recession remain significant challenges. The Fed must carefully balance the need to control inflation with the need to avoid triggering a significant economic downturn. Ultimately, the path of monetary policy will depend on incoming economic data and the Fed's assessment of the risks. To stay informed on the latest developments and understand the implications for your financial decisions, continue monitoring the economic indicators and the Fed's official communications regarding their interest rate policy. Stay updated on the latest news regarding the Fed's hold rates policy and its potential impact on your investments and financial planning.

Featured Posts
-
 Trumps Plan To Limit Migrant Detention Challenges
May 10, 2025
Trumps Plan To Limit Migrant Detention Challenges
May 10, 2025 -
 La Fire Aftermath Investigation Into Landlord Price Gouging Practices
May 10, 2025
La Fire Aftermath Investigation Into Landlord Price Gouging Practices
May 10, 2025 -
 Dakota Johnsons Family Supports Her At Materialist La Screening
May 10, 2025
Dakota Johnsons Family Supports Her At Materialist La Screening
May 10, 2025 -
 Pakistan Sri Lanka Bangladesh Pledge Closer Capital Market Ties
May 10, 2025
Pakistan Sri Lanka Bangladesh Pledge Closer Capital Market Ties
May 10, 2025 -
 Palantir Technologies Stock A Detailed Investment Analysis For 2024 And Beyond
May 10, 2025
Palantir Technologies Stock A Detailed Investment Analysis For 2024 And Beyond
May 10, 2025
