A New Cold War: The Rare Earth Minerals Struggle
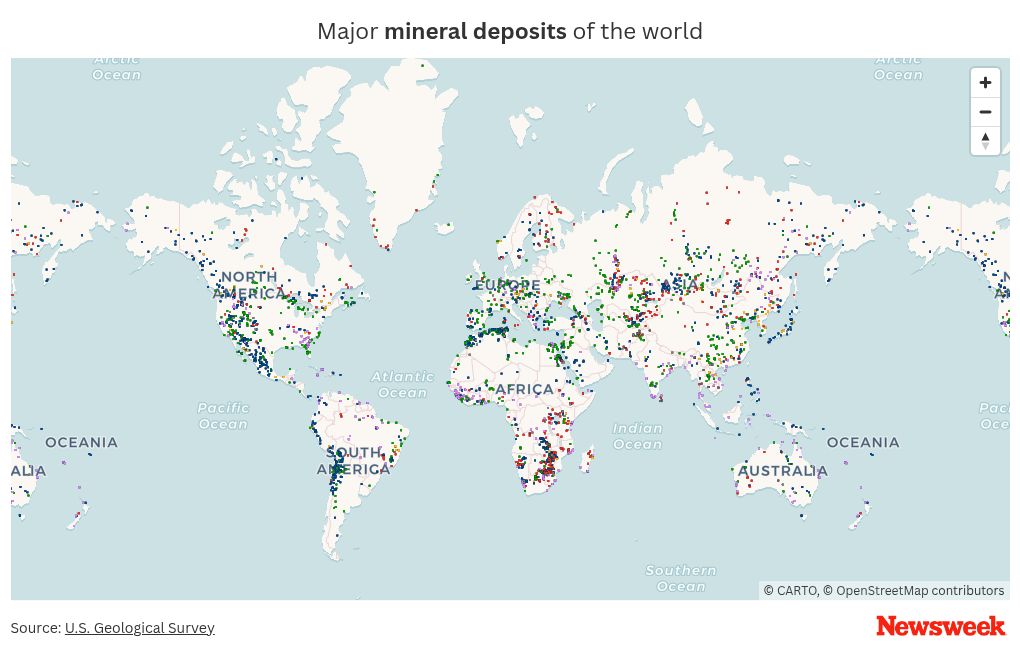
Table of Contents
The Importance of Rare Earth Minerals in Modern Technology
Rare earth minerals are not rare in the geological sense, but their extraction and processing are complex and costly. Their unique magnetic, luminescent, and catalytic properties are indispensable for a vast array of modern technologies. Without them, our digital world, renewable energy infrastructure, and national defense systems would grind to a halt.
- Specific examples: Smartphones, wind turbines, electric vehicle motors, hard disk drives, military guidance systems, fiber optic cables, and medical imaging equipment all rely heavily on rare earth elements (REEs).
- Growing demand: The global demand for rare earth minerals is projected to increase exponentially in the coming decades, driven by the growth of renewable energy, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates a significant rise in demand for REEs by 2040.
- Specific REEs and applications: Neodymium (Nd) and praseodymium (Pr) are critical for powerful permanent magnets in wind turbines and electric vehicles. Dysprosium (Dy) enhances the performance of these magnets at high temperatures. Europium (Eu) is vital for the red phosphors in LED lighting.
Geopolitical Control and the Concentration of Rare Earth Mineral Production
The production and processing of rare earth minerals are geographically concentrated, leading to significant geopolitical vulnerabilities. China currently holds a dominant position, controlling a substantial portion of the global supply chain, from mining to refining. This concentration creates significant risks for nations reliant on these materials.
- China's dominance: China's control over the rare earth market raises concerns about supply chain security and potential for economic coercion. This dominance is not just due to large reserves but also sophisticated processing capabilities.
- Environmental and social impacts: The extraction and processing of rare earth minerals can have severe environmental consequences, including water pollution, soil degradation, and radioactive waste. Social impacts on local communities, including displacement and health issues, are also significant concerns. Sustainable mining practices are crucial for mitigating these negative effects.
- Other significant producers: While China is the leading producer, other countries like Australia, the United States, Brazil, and Vietnam possess significant rare earth mineral reserves. However, the gap between reserves and refined material production remains substantial. The development of these alternative sources is crucial for reducing geopolitical risk.
The Emerging Scramble for Rare Earth Minerals: Diversification and New Discoveries
Recognizing the risks associated with over-reliance on a single source, countries are actively pursuing diversification strategies, including investing in new discoveries and developing innovative technologies. This "scramble" for rare earth minerals is shaping the geopolitical landscape.
- Investments outside China: Several nations are investing heavily in rare earth mining and processing facilities to reduce their dependence on China. The US, Australia, and the EU are among the key players in this effort. This includes government subsidies and incentives to encourage domestic production.
- Rare earth recycling: Recycling and reuse of rare earth minerals from end-of-life products represent a critical strategy for reducing reliance on primary mining and enhancing resource sustainability. Technological advancements in this area are essential for improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Alternative materials: Research and development efforts are focusing on identifying and developing alternative materials that can replace rare earth elements in certain applications. However, this is a long-term process with significant technological hurdles.
The Role of International Cooperation and Trade Policy
Securing a stable and sustainable supply of rare earth minerals requires international cooperation and well-defined trade policies. This necessitates collaboration among nations to address environmental concerns, promote fair trade practices, and prevent conflicts over resource control.
- International agreements and initiatives: Several international organizations are working to promote sustainable rare earth mining and responsible supply chains. However, comprehensive international agreements are still lacking.
- Trade policies and tariffs: Trade policies and tariffs can significantly impact the rare earth market. Tariffs and export restrictions can create artificial scarcity and distort global supply chains.
- Potential for conflict and cooperation: The competition for rare earth minerals presents a significant risk of geopolitical conflict. However, international cooperation in responsible resource management can create opportunities for mutually beneficial partnerships. Resource diplomacy will be crucial in navigating these complexities.
Conclusion
The "rare earth minerals struggle" is a multifaceted challenge with profound implications for global security, technological advancement, and environmental sustainability. China's dominant position necessitates a multi-pronged approach involving diversified sourcing, innovative recycling technologies, and strengthened international cooperation. Understanding the intricacies of this struggle is crucial for navigating the 21st-century geopolitical landscape. We must prioritize the development of sustainable and ethically sourced rare earth minerals and implement strategies to mitigate the inherent risks associated with this critical resource. Let's work together to responsibly manage the future of rare earth minerals and ensure a secure and sustainable supply for generations to come.

Featured Posts
-
 Breens Lighthearted Taunts Of Bridges Playing Time Concerns
May 17, 2025
Breens Lighthearted Taunts Of Bridges Playing Time Concerns
May 17, 2025 -
 New York Knicks The Landry Shamet Conundrum
May 17, 2025
New York Knicks The Landry Shamet Conundrum
May 17, 2025 -
 5 Key Dos And Don Ts To Succeed In The Private Credit Market
May 17, 2025
5 Key Dos And Don Ts To Succeed In The Private Credit Market
May 17, 2025 -
 Two Decades On Ichiro Suzukis Continued Impact On The Seattle Mariners And Baseball
May 17, 2025
Two Decades On Ichiro Suzukis Continued Impact On The Seattle Mariners And Baseball
May 17, 2025 -
 Ontarios 14 6 Billion Deficit Tariff Impacts And Economic Outlook
May 17, 2025
Ontarios 14 6 Billion Deficit Tariff Impacts And Economic Outlook
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Severance Season 3 Lehigh Valley Live Coms Prediction
May 17, 2025
Severance Season 3 Lehigh Valley Live Coms Prediction
May 17, 2025 -
 Severance Tv Series Ben Stiller On Lumon Industries And The Apple Comparison
May 17, 2025
Severance Tv Series Ben Stiller On Lumon Industries And The Apple Comparison
May 17, 2025 -
 Is Severance Renewed For Season 3 Lehigh Valley Live Com News
May 17, 2025
Is Severance Renewed For Season 3 Lehigh Valley Live Com News
May 17, 2025 -
 Lumon Industries Vs Apple Ben Stillers Severance And Corporate Culture
May 17, 2025
Lumon Industries Vs Apple Ben Stillers Severance And Corporate Culture
May 17, 2025 -
 Is There Going To Be A Severance Season 3
May 17, 2025
Is There Going To Be A Severance Season 3
May 17, 2025
