Air Traffic Control System Failures: Causes, Consequences, And Prevention Strategies

Table of Contents
Causes of Air Traffic Control System Failures
Air traffic control system failures stem from a complex interplay of technological shortcomings, human error, and environmental factors. Understanding these contributing elements is crucial for developing effective preventative measures.
Technological Failures
Technological failures are a significant contributor to ATC system disruptions. These failures can manifest in various forms:
-
Hardware Malfunctions: Radar system failures, communication network outages (e.g., loss of VHF radio communication), and malfunctioning ground-based navigation aids (e.g., Instrument Landing System - ILS) can severely impact air traffic management. A failure in a single component can trigger a cascade of problems, impacting the entire system.
-
Software Glitches and Bugs: Software bugs, system crashes, and data corruption can lead to inaccurate information being presented to air traffic controllers, resulting in potentially dangerous situations. Out-of-date software can introduce vulnerabilities and increase the likelihood of failures.
-
Outdated Technology: Aging infrastructure and outdated technology are a major concern. The reliance on legacy systems that lack the resilience and capabilities of modern technologies increases the vulnerability to failures. Regular upgrades and proactive maintenance are vital for preventing these issues.
-
Examples:
- The 2015 FAA nationwide ground stop due to a computer failure in the En Route Automation Modernization (ERAM) system.
- Localized radar outages impacting specific airports, causing delays and diversions.
Human Error
Human error remains a significant factor in ATC system failures, despite the implementation of advanced technologies. Several human factors contribute to these incidents:
-
Controller Fatigue: Long working hours, irregular shifts, and high-pressure situations can lead to fatigue, reducing controllers’ alertness and increasing the likelihood of errors.
-
Improper Training: Inadequate training programs that do not equip controllers with the necessary skills to handle complex situations can result in mistakes with serious consequences.
-
Communication Breakdowns: Miscommunication between controllers, pilots, and other stakeholders can lead to misunderstandings and potentially hazardous situations. Effective communication protocols and training are crucial.
-
Examples:
- Errors in issuing clearances or instructions to pilots.
- Failure to adequately monitor airspace, leading to near-miss incidents.
- Inadequate response to unexpected events or emergencies.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also significantly impact ATC system performance and reliability. These include:
-
Severe Weather: Thunderstorms, heavy snow, and extreme temperatures can disrupt radar signals, impair communication links, and impact the operation of ground-based navigation systems.
-
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): EMI from various sources can interfere with radio communication and navigation signals, causing disruptions to ATC operations.
-
Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, floods, and wildfires can cause significant damage to ATC infrastructure, leading to widespread system outages.
-
Examples:
- Reduced visibility due to fog or heavy snow reducing the effectiveness of radar systems.
- Lightning strikes damaging communication equipment.
- Flooding causing power outages at ATC facilities.
Consequences of Air Traffic Control System Failures
The consequences of air traffic control system failures are multifaceted and far-reaching, impacting safety, the economy, and operational efficiency.
Safety Risks
Air traffic control system failures pose significant safety risks, potentially leading to:
-
Mid-air Collisions: System failures can result in loss of situational awareness, increasing the risk of aircraft colliding mid-air.
-
Runway Incursions: Errors in ground guidance can cause aircraft to deviate from assigned routes, leading to runway incursions and potential collisions.
-
Loss of Life and Property Damage: The consequences of major ATC failures can be devastating, resulting in significant loss of life and substantial property damage.
-
Examples (Illustrative, requiring factual data):
- Statistical data on near-miss incidents attributed to ATC system failures.
- Case studies of accidents directly linked to ATC system malfunctions.
Economic Impacts
The economic impact of ATC system failures is substantial, affecting various stakeholders:
-
Flight Delays and Cancellations: System failures lead to delays, cancellations, and diversions, resulting in significant financial losses for airlines and passengers.
-
Impact on Airlines and Airports: Airlines incur costs associated with fuel consumption, passenger compensation, and operational disruptions. Airports experience reduced throughput and revenue.
-
Investigations and Legal Settlements: Investigations into system failures and subsequent legal settlements can impose significant financial burdens.
-
Examples (Illustrative, requiring factual data):
- Estimated cost of delays and cancellations due to a specific ATC failure event.
- Economic impact on a region due to airport closure following a system failure.
Operational Disruptions
ATC system failures cause widespread operational disruptions, affecting a range of sectors:
-
Air Travel Schedules: Disruptions cascade through air travel schedules, impacting passenger itineraries and creating significant inconvenience.
-
Air Cargo and Logistics: Delays and cancellations have a direct impact on air cargo operations, affecting supply chains and businesses relying on timely delivery.
-
Cascading Effects: Disruptions can have cascading effects on other connected industries, including tourism, hospitality, and manufacturing.
-
Examples:
- Major airport closures causing widespread flight cancellations.
- Delays in transporting perishable goods due to air cargo disruptions.
Prevention Strategies for Air Traffic Control System Failures
Mitigating the risks associated with air traffic control system failures requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing technological advancements, human factors mitigation, and robust regulatory measures.
Technological Advancements
Investing in advanced technologies can significantly enhance the reliability and resilience of ATC systems:
-
AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning can improve system monitoring, predict potential failures, and automate tasks, enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
-
Redundancy Systems: Implementing redundant systems and fail-safe mechanisms ensures continued operation even if a component fails.
-
Cybersecurity Measures: Robust cybersecurity measures are crucial to protect ATC systems from cyberattacks that could compromise their functionality.
-
Examples:
- Implementation of advanced radar systems with improved accuracy and reliability.
- Use of data analytics to identify potential system vulnerabilities.
Human Factors Mitigation
Addressing human factors is crucial for enhancing ATC system safety:
-
Comprehensive Training: Improved training programs that focus on stress management, workload management, and effective communication are vital.
-
Effective Communication Protocols: Clear, concise, and standardized communication protocols minimize the risk of misunderstandings and errors.
-
Fatigue Countermeasures: Strategies to mitigate controller fatigue, such as optimized shift patterns and rest periods, are essential.
-
Examples:
- Simulator-based training to prepare controllers for various emergency situations.
- Implementation of crew resource management (CRM) techniques to enhance teamwork and communication.
Regulatory and Policy Measures
Robust regulatory and policy frameworks are essential for ensuring ATC safety:
-
Safety Regulations and Oversight: Strict safety regulations and independent oversight mechanisms are necessary to ensure compliance and identify potential risks.
-
International Collaboration: International collaboration and information sharing are critical for addressing global challenges related to air traffic control safety.
-
Independent Audits and Safety Investigations: Regular audits and thorough investigations of incidents are crucial for identifying weaknesses and improving system safety.
-
Examples:
- Mandatory reporting of incidents and near-misses.
- Regular inspections and audits of ATC facilities and equipment.
Conclusion
Air traffic control system failures pose significant safety, economic, and operational risks. The causes are complex, stemming from technological limitations, human error, and environmental factors. The consequences can be catastrophic, leading to accidents, delays, and economic losses. However, proactive measures can significantly mitigate these risks. Continuous improvement in air traffic control system reliability is paramount, requiring a concerted effort to implement technological advancements, enhance human factors mitigation strategies, and strengthen regulatory frameworks. Investing in advanced technologies, improving controller training, and strengthening international collaboration are crucial steps towards preventing future air traffic control system failures. Learn more about ATC safety initiatives and advocate for increased investment in technological upgrades and safety training to ensure the continued safety and efficiency of our skies.

Featured Posts
-
 Prica S Reddita Postaje Film Sa Sydney Sweeney
May 22, 2025
Prica S Reddita Postaje Film Sa Sydney Sweeney
May 22, 2025 -
 Home Depot Stock Impact Of Tariffs On Q Quarter Earnings
May 22, 2025
Home Depot Stock Impact Of Tariffs On Q Quarter Earnings
May 22, 2025 -
 V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Details A 1 050 Price Increase Proposed By Broadcom
May 22, 2025
V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Details A 1 050 Price Increase Proposed By Broadcom
May 22, 2025 -
 Vybz Kartel Electrifies Brooklyn With Sold Out Concerts
May 22, 2025
Vybz Kartel Electrifies Brooklyn With Sold Out Concerts
May 22, 2025 -
 House Bill Restores Game And Fishs Otter Management Role
May 22, 2025
House Bill Restores Game And Fishs Otter Management Role
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
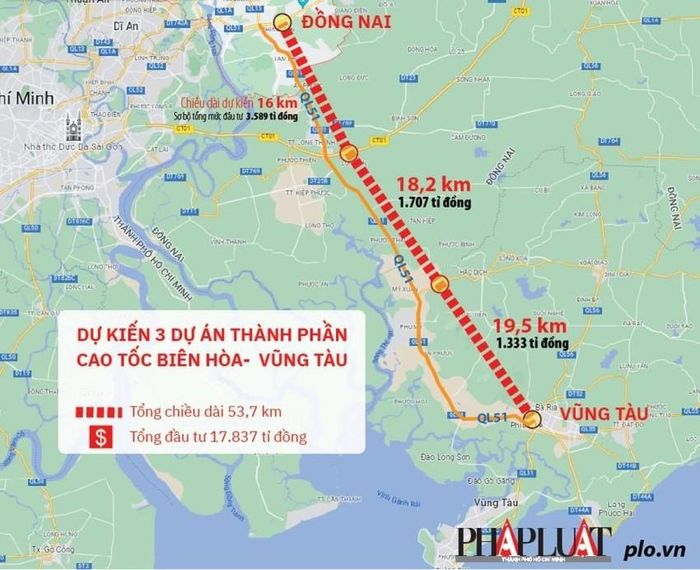 Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Thong Xe Du Kien 2 9
May 22, 2025
Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Thong Xe Du Kien 2 9
May 22, 2025 -
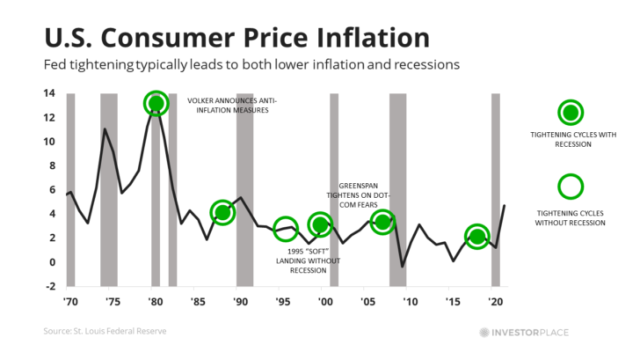 The Future Of Core Weave Stock Predictions And Projections
May 22, 2025
The Future Of Core Weave Stock Predictions And Projections
May 22, 2025 -
 Whats Driving Core Weave Stocks Current Price
May 22, 2025
Whats Driving Core Weave Stocks Current Price
May 22, 2025 -
 Core Weave Stock Performance Factors Influencing Its Trajectory
May 22, 2025
Core Weave Stock Performance Factors Influencing Its Trajectory
May 22, 2025 -
 Deconstructing Core Weaves Crwv Impressive Stock Performance Last Week
May 22, 2025
Deconstructing Core Weaves Crwv Impressive Stock Performance Last Week
May 22, 2025
