Automated Nike Shoe Production: Why It's So Difficult
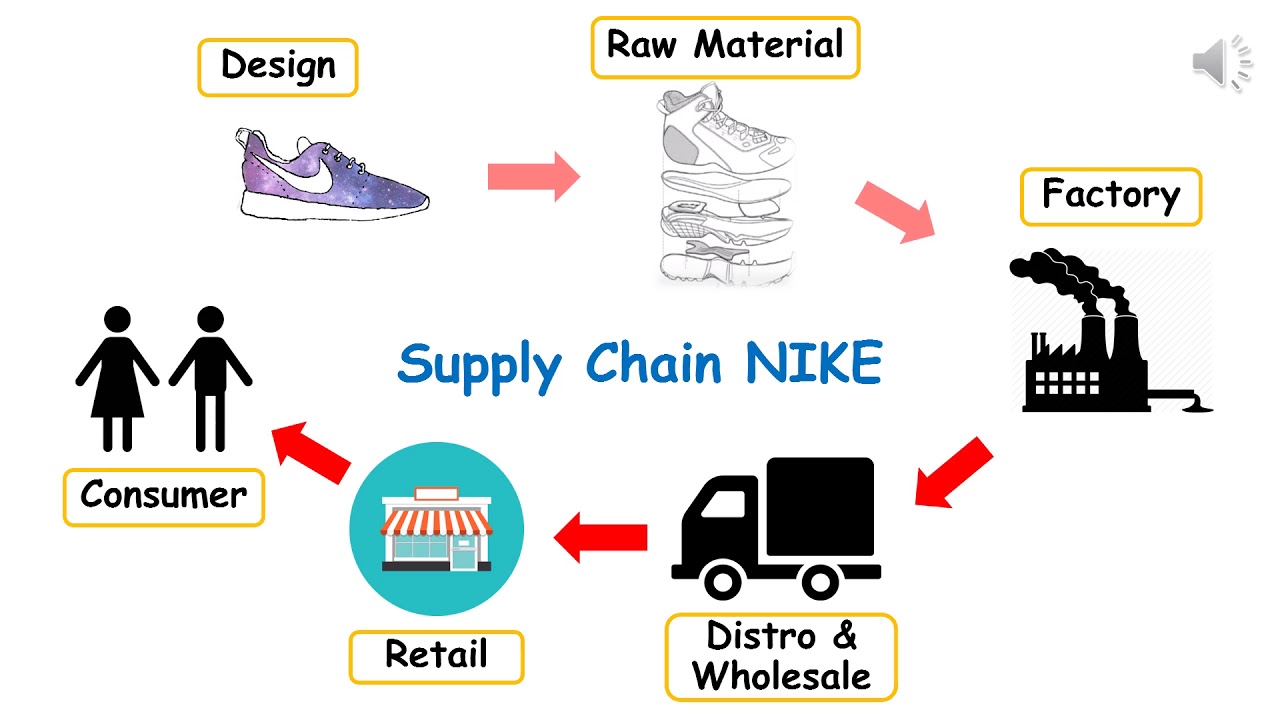
Table of Contents
The Intricacy of Shoe Design and Material Variety
Nike's success stems from its vast range of shoe designs, each employing diverse materials and construction methods. This incredible variety presents a major obstacle for automated shoe manufacturing. Automating a process designed for a single, standardized product is far easier than creating a system capable of handling the nuances of countless models.
- Adapting robots to handle different materials: From supple leather and breathable mesh to durable synthetic fabrics, each material requires unique handling techniques. Robots need sophisticated sensors to adapt to varying stiffness, thickness, and texture.
- Programming robots for complex assembly: The process of assembling a shoe involves intricate stitching, gluing, and the precise placement of numerous components. Programming robots to execute these tasks with the speed and precision of a skilled human worker is incredibly complex.
- The need for flexible automation: Nike frequently introduces new designs and limited-edition models. Automated systems must be flexible enough to adapt to these frequent changes, necessitating costly reprogramming and retooling.
The variability in material properties requires sophisticated sensing and adaptive control systems, currently unavailable at scale for cost-effective implementation. This significantly increases the cost and complexity of automated Nike shoe production.
The Dexterity and Precision Demands of Shoe Assembly
Many shoemaking processes demand a high degree of dexterity and precision that even the most advanced robotics struggle to replicate. While robots excel at repetitive, high-force tasks, the subtle manipulations required in shoe assembly remain a significant challenge.
- Limitations of robot grippers: Current robot grippers often lack the dexterity to handle delicate materials and perform intricate stitching patterns with the necessary accuracy and finesse.
- Maintaining quality control: Achieving the same level of quality control and consistency as human workers is crucial. Inconsistencies in automated assembly could lead to defects and product recalls, outweighing any potential cost savings.
- Advanced AI requirements: To enable robots to adapt to variations in materials and assembly processes, highly advanced artificial intelligence is required—a technology still under development.
The nuances of shoe assembly require a level of dexterity and adaptability currently beyond the capabilities of existing robotic systems. This gap highlights the need for significant advancements in robotic manipulation and AI before widespread automation can be realistically achieved.
The High Cost of Implementing and Maintaining Automated Systems
The initial investment in robotic systems, programming, and integration for automated Nike shoe production is substantial, posing a high barrier to entry, especially for smaller manufacturers.
- High upfront costs: Advanced robotics, specialized end-effectors (the tools attached to robot arms), and sophisticated vision systems represent a significant capital expenditure.
- Software development and maintenance: The cost of developing, implementing, and maintaining the software that controls these complex systems is substantial and ongoing.
- Skilled technician requirements: Specialized technicians are needed to operate and maintain the automated equipment, adding to the overall operational costs.
The return on investment (ROI) for automating shoe production remains a key concern. The high upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses must be carefully weighed against the potential cost savings, particularly for companies producing niche shoe models with limited production runs.
The Labor Factor and Job Displacement Concerns
Automating shoe production raises significant concerns about job displacement in manufacturing sectors that currently rely heavily on manual labor. This has considerable social and economic implications that demand careful consideration.
- Reskilling and upskilling initiatives: To mitigate job losses, substantial investment in reskilling and upskilling initiatives is crucial to prepare workers for roles in automated environments.
- Ethical considerations: The potential for job displacement in developing countries where shoe manufacturing is a significant source of employment necessitates ethical considerations and careful planning for a just transition.
Conclusion
While the prospect of fully automated Nike shoe production is undeniably appealing, significant technological, economic, and social challenges remain. The intricate nature of shoe design, the dexterity required for assembly, and the substantial costs associated with automation are major hurdles. Overcoming these obstacles requires further breakthroughs in robotics, AI, and materials science. However, continued innovation in automated Nike shoe production holds the promise of greater efficiency, consistency, and potentially lower costs in the long term. Therefore, sustained research and development are crucial to unlocking the full potential of automated footwear manufacturing and addressing the challenges it presents.

Featured Posts
-
 Bof A On Stock Market Valuations A Reason For Investor Confidence
Apr 22, 2025
Bof A On Stock Market Valuations A Reason For Investor Confidence
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Higher Stock Prices Higher Risks What Investors Should Know
Apr 22, 2025
Higher Stock Prices Higher Risks What Investors Should Know
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Fsu Security Flaw And The Heightened Student Anxiety A Case Study In Rapid Response And Lingering Fear
Apr 22, 2025
Fsu Security Flaw And The Heightened Student Anxiety A Case Study In Rapid Response And Lingering Fear
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Supreme Court Hearing On Obamacare Trumps Unexpected Role And Rfk Jr S Political Future
Apr 22, 2025
Supreme Court Hearing On Obamacare Trumps Unexpected Role And Rfk Jr S Political Future
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Ai Driven Podcast Creation Analyzing And Transforming Repetitive Scatological Data
Apr 22, 2025
Ai Driven Podcast Creation Analyzing And Transforming Repetitive Scatological Data
Apr 22, 2025
