Proposed Changes To Juvenile Sentencing In France

Table of Contents
Increased Focus on Rehabilitation and Reintegration
The cornerstone of the proposed reforms is a significant shift towards rehabilitation and reintegration of young offenders. This involves a move away from punitive measures and towards a more supportive approach that prioritizes the long-term well-being of juveniles.
Expansion of Educational and Vocational Programs
The proposed changes include a substantial increase in funding for educational and vocational training within juvenile facilities. This commitment aims to equip young people with the skills and knowledge necessary to successfully reintegrate into society.
- Individualized Learning Plans: Tailored learning plans will address the specific educational needs and learning styles of each juvenile, maximizing the effectiveness of the programs.
- Integrated Mental Health Support: Recognizing the link between mental health and criminal behavior, the reforms propose integrating comprehensive mental health services and support into these programs.
- Examples of Programs: The proposed reforms envision expanding existing programs like apprenticeships in skilled trades and implementing new initiatives focused on digital literacy and entrepreneurship. Successes in similar programs in countries like Norway, which boasts significantly lower recidivism rates, will be studied and applied.
- Statistics on Recidivism: Studies consistently show a strong correlation between educational attainment and reduced recidivism. By investing in education, France aims to significantly lower the likelihood of re-offending amongst its young population.
Strengthened Aftercare Services
Rehabilitation doesn't end with release from detention. The proposed reforms significantly bolster aftercare services, providing crucial support for juveniles as they transition back into their communities.
- Mentorship Programs: Mentorship programs will pair released juveniles with positive role models who can provide guidance and support.
- Community Reintegration Initiatives: These initiatives will focus on facilitating a smooth transition back into the community, addressing issues such as housing and social reintegration.
- Housing Assistance and Job Placement: Access to stable housing and job placement services is crucial for successful reintegration and will be a central component of the aftercare support.
- Long-Term Impact on Recidivism: The goal of strengthened aftercare services is to reduce recidivism rates significantly by mitigating the challenges faced by young people upon release and providing them with ongoing support.
Emphasis on Restorative Justice Practices
Another critical aspect of the proposed changes is the increased emphasis on restorative justice practices. This approach shifts the focus from punishment to repairing the harm caused by crime and fostering reconciliation.
Increased Use of Mediation and Diversion Programs
Restorative justice aims to bring together victims, offenders, and their families to address the harm caused by the crime and facilitate healing. This involves:
- Victim-Offender Mediation: Mediation allows victims to share their experiences and offenders to take responsibility for their actions, fostering understanding and reconciliation.
- Diversion Programs: Expanding diversion programs allows juveniles to avoid formal court proceedings by participating in restorative justice initiatives. This can involve community service, restitution to victims, or participation in educational programs.
- Reduced Recidivism Through Restorative Justice: Numerous studies demonstrate that restorative justice models significantly reduce recidivism compared to traditional punitive approaches.
- Challenges to Implementation: The successful implementation of restorative justice requires sufficient resources, trained professionals, and the active participation of all stakeholders.
Community-Based Sentencing Alternatives
The proposed reforms also promote community-based sentencing alternatives as a means to keep juveniles within their communities and minimize the disruptive effects of detention.
- Community Service Orders: Community service allows juveniles to make amends for their actions while contributing to their communities.
- Community-Based Supervision: This ensures accountability while allowing juveniles to receive support within their familiar environment.
- Successful Community-Based Programs: Examples of successful community-based programs from other jurisdictions will inform the implementation of these reforms in France.
- Resource Allocation and Supervision: Challenges include allocating sufficient resources to supervise community-based sentences and ensuring effective monitoring of offenders.
Addressing Disparities in Juvenile Justice
The proposed reforms also aim to address significant disparities in the juvenile justice system.
Reducing Racial and Socioeconomic Bias
The disproportionate representation of certain racial and socioeconomic groups in the juvenile justice system is a serious concern. The proposed changes seek to:
- Address Implicit Bias: Specific measures aim to identify and mitigate implicit bias in sentencing decisions through training for judges and other judicial personnel.
- Improved Access to Legal Representation: Ensuring access to high-quality legal representation, regardless of socioeconomic status, is crucial for fair and equitable outcomes.
- Statistics on Disparities: Data illustrating existing racial and socioeconomic disparities will be used to track the effectiveness of reforms aimed at reducing these imbalances.
- Reforms to Sentencing Guidelines: Reforms to sentencing guidelines aim to eliminate discriminatory practices and promote fairer outcomes.
Protecting Vulnerable Youth
The reforms prioritize the specific needs of vulnerable youth, including victims of abuse and children with disabilities.
- Specialized Programs: Specialized programs will be created to cater to the unique needs and challenges faced by these vulnerable young people.
- Trauma-Informed Care: A core element will be implementing trauma-informed care in juvenile justice settings, recognizing the impact of trauma on behavior and well-being.
- Success Stories of Specialized Programs: Research on successful specialized programs from other countries will inform the development of effective interventions in France.
- Types of Vulnerabilities: The reforms will address the specific needs of victims of domestic violence, sexual assault, and other forms of abuse, as well as children with mental health issues or disabilities.
Conclusion: The Future of Juvenile Sentencing in France: A Call for Reform
The Proposed Changes to Juvenile Sentencing in France represent a significant shift towards a more humane and effective approach to juvenile justice. By prioritizing rehabilitation, embracing restorative justice principles, and actively addressing systemic disparities, these reforms aim to reduce recidivism, promote social justice, and ultimately create a safer and more equitable society for all. We urge readers to engage with this important discussion by learning more about these proposed changes and contacting relevant organizations and policymakers to express their support and participate in shaping the future of juvenile justice in France. The success of these proposed changes to juvenile sentencing hinges on the active involvement of all stakeholders.

Featured Posts
-
 The National Rallys Sunday Demonstration A Lower Than Anticipated Turnout For Le Pen
May 25, 2025
The National Rallys Sunday Demonstration A Lower Than Anticipated Turnout For Le Pen
May 25, 2025 -
 Avrupa Borsalarinda Karisik Seans Guenuen Oezeti
May 25, 2025
Avrupa Borsalarinda Karisik Seans Guenuen Oezeti
May 25, 2025 -
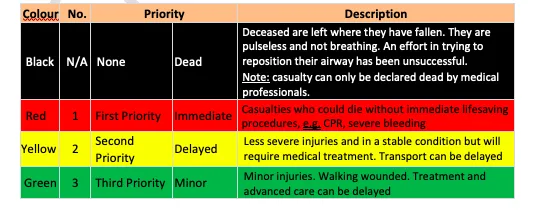 M56 Motorway Incident Car Rollover Casualty Receives Treatment
May 25, 2025
M56 Motorway Incident Car Rollover Casualty Receives Treatment
May 25, 2025 -
 Emergency Services Respond To Princess Road After Pedestrian Vehicle Collision
May 25, 2025
Emergency Services Respond To Princess Road After Pedestrian Vehicle Collision
May 25, 2025 -
 Evrovidenie 2014 Konchita Vurst Put K Uspekhu I Ambitsioznye Plany
May 25, 2025
Evrovidenie 2014 Konchita Vurst Put K Uspekhu I Ambitsioznye Plany
May 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 7 Fall In Amsterdam Stock Market Trade War Uncertainty Deepens
May 25, 2025
7 Fall In Amsterdam Stock Market Trade War Uncertainty Deepens
May 25, 2025 -
 Philips 2025 Annual General Meeting Key Updates And Agenda
May 25, 2025
Philips 2025 Annual General Meeting Key Updates And Agenda
May 25, 2025 -
 Royal Philips 2025 Annual General Meeting Of Shareholders Update
May 25, 2025
Royal Philips 2025 Annual General Meeting Of Shareholders Update
May 25, 2025 -
 Trade War Fears Trigger 7 Plunge In Amsterdam Stock Market
May 25, 2025
Trade War Fears Trigger 7 Plunge In Amsterdam Stock Market
May 25, 2025 -
 Amsterdam Stock Market Plunges 7 Drop Amidst Trade War Fears
May 25, 2025
Amsterdam Stock Market Plunges 7 Drop Amidst Trade War Fears
May 25, 2025
