Sino-Canadian Cooperation: A Pushback Against American "Bullying"?

Table of Contents
Economic Ties as a Foundation for Sino-Canadian Cooperation
The economic relationship between China and Canada is substantial, forming a crucial bedrock for their cooperation. Strong bilateral trade and significant investment flows characterize this partnership.
Trade and Investment
The volume of bilateral trade between China and Canada is considerable, encompassing key sectors such as:
- Natural Resources: Canada is a major exporter of raw materials like lumber, potash, and oil to China, vital for its economic growth.
- Agriculture: Canadian agricultural products, including canola and pork, represent a significant portion of exports to the Chinese market.
- Technology: While still developing, there is increasing exchange in technology sectors, with potential for future growth in areas like artificial intelligence and clean energy.
Recent data illustrates the significant growth in bilateral trade, with [insert statistics and relevant sources here]. Canadian companies like [name examples] have invested heavily in China, while Chinese companies have shown interest in Canadian resources and technology. The potential for cooperation in clean energy technologies and knowledge transfer offers exciting avenues for future growth in Sino-Canadian economic ties.
Infrastructure Development
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) presents both opportunities and challenges for Canada. Participation in BRI infrastructure projects could provide Canadian companies with access to lucrative contracts and boost economic growth.
- Potential Benefits: Access to large-scale infrastructure projects, economic stimulus, and technological exchange.
- Potential Risks: Concerns about debt sustainability, environmental impact, and alignment with Canadian values and foreign policy objectives.
Careful consideration of these factors is crucial for Canada to leverage the potential benefits of BRI participation while mitigating associated risks. The strategic alignment of Canadian participation in BRI projects with its overall foreign policy objectives requires careful planning and assessment.
Diplomatic Cooperation and Shared Global Challenges
Beyond economics, Sino-Canadian cooperation extends to addressing shared global challenges through multilateral diplomacy.
Multilateralism
Both Canada and China are active members of various international organizations, including the UN and WTO. Cooperation within these frameworks provides a platform to tackle issues like:
- Climate Change: Joint initiatives on climate action and emission reduction strategies.
- Pandemic Preparedness: Collaboration on public health initiatives, vaccine development, and disease surveillance.
- Peacekeeping Operations: Potential for joint participation in UN peacekeeping missions.
Engagement within multilateral frameworks offers a channel for both nations to coordinate efforts on shared priorities, promoting global stability and cooperation.
Navigating Geopolitical Tensions
Canada's foreign policy emphasizes navigating the complex relationship between the US and China. This requires a balanced approach that:
- Prioritizes independent foreign policy: Canada maintains its independent foreign policy, pursuing its national interests while engaging with both powers.
- Remains committed to multilateralism: Working through international institutions helps to manage the strategic competition between the US and China.
- Addresses the challenges of great power competition: Canada seeks to manage this competition while safeguarding its own national interests and global stability.
Successfully navigating this precarious geopolitical landscape requires careful diplomacy and a commitment to open communication.
Challenges and Risks in Sino-Canadian Cooperation
Despite significant potential, Sino-Canadian cooperation faces several challenges.
Human Rights Concerns
The human rights situation in China remains a significant obstacle. Canada, with its strong human rights record, must engage with China on this issue:
- Balancing human rights with diplomatic engagement: Canada must find a path that upholds its commitment to human rights while maintaining diplomatic channels for dialogue and cooperation.
- Promoting dialogue and advocacy: Canada can use its influence to advocate for human rights within the framework of its diplomatic engagement with China.
A nuanced approach that prioritizes both human rights advocacy and constructive engagement is critical for long-term success.
Economic Dependence and Vulnerability
Over-reliance on the Chinese market could create economic vulnerabilities for Canadian businesses. To mitigate this:
- Diversification of trade partners: Canada needs to diversify its export markets to reduce dependence on any single trading partner.
- Strategies for mitigating economic risks: Implementing strategies that bolster economic resilience and reduce vulnerability to external shocks.
A balanced approach that fosters diverse economic partnerships is essential for long-term economic stability.
Geopolitical Sensitivity
Closer ties with China could potentially increase tensions with the US. Canada needs to:
- Maintain transparent communication: Open and honest communication with the US is crucial to avoid misunderstandings.
- Avoid actions that could be perceived as antagonistic: Canada needs to be mindful of its actions and ensure they don't escalate tensions with the US.
Clear communication and strategic planning are critical to managing the geopolitical sensitivities inherent in this relationship.
Conclusion
Sino-Canadian cooperation presents both significant opportunities and considerable challenges. While the economic and diplomatic benefits are undeniable, navigating human rights concerns, economic vulnerabilities, and geopolitical sensitivities requires careful consideration. The argument that this cooperation serves as a pushback against perceived American pressure is plausible, but it's crucial to avoid framing it as a purely adversarial stance. This relationship must be managed strategically, prioritizing open communication and a balanced approach that values both economic growth and international principles. Further research into Sino-Canadian trade relations, Canada-China diplomacy, and managing great power competition is essential for a thorough understanding of this complex and evolving relationship. The future of global geopolitics will, in part, be shaped by the successful navigation of this vital partnership—a nuanced understanding of Sino-Canadian cooperation is paramount.

Featured Posts
-
 Buduschee Rossiysko Ukrainskogo Konflikta Rol Trampa V Mirnykh Peregovorakh
Apr 25, 2025
Buduschee Rossiysko Ukrainskogo Konflikta Rol Trampa V Mirnykh Peregovorakh
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Scouse Charm Rick Astleys Affection For Liverpools Passionate Fans
Apr 25, 2025
Scouse Charm Rick Astleys Affection For Liverpools Passionate Fans
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Nintendo Switch 2 Preorder Problems Lessons Learned From A Messy Rollout
Apr 25, 2025
Nintendo Switch 2 Preorder Problems Lessons Learned From A Messy Rollout
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Cowboys Draft Insiders Shocking List Of Potential Picks
Apr 25, 2025
Cowboys Draft Insiders Shocking List Of Potential Picks
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Renaults Abandoned Us Sports Car A Case Study Of Trump Tariff Impact
Apr 25, 2025
Renaults Abandoned Us Sports Car A Case Study Of Trump Tariff Impact
Apr 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
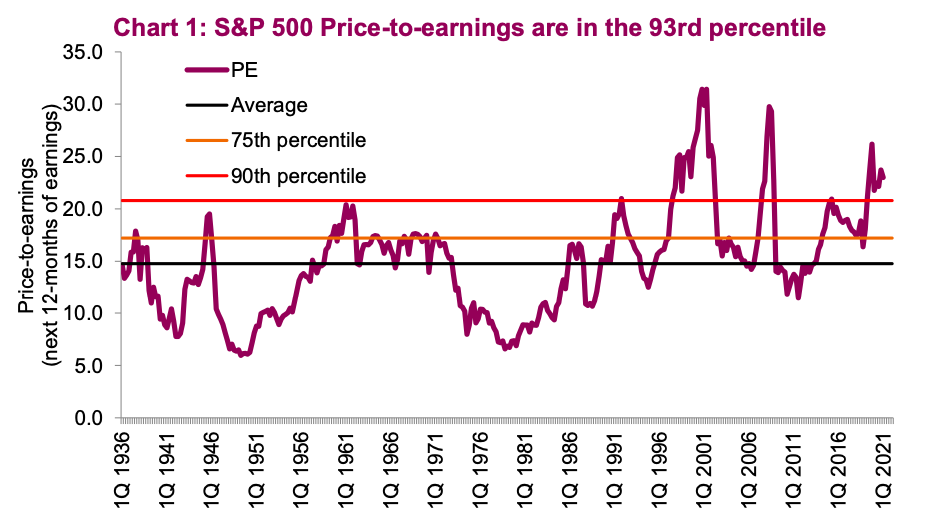 Addressing Investor Concerns Bof As View On High Stock Market Valuations
Apr 26, 2025
Addressing Investor Concerns Bof As View On High Stock Market Valuations
Apr 26, 2025 -
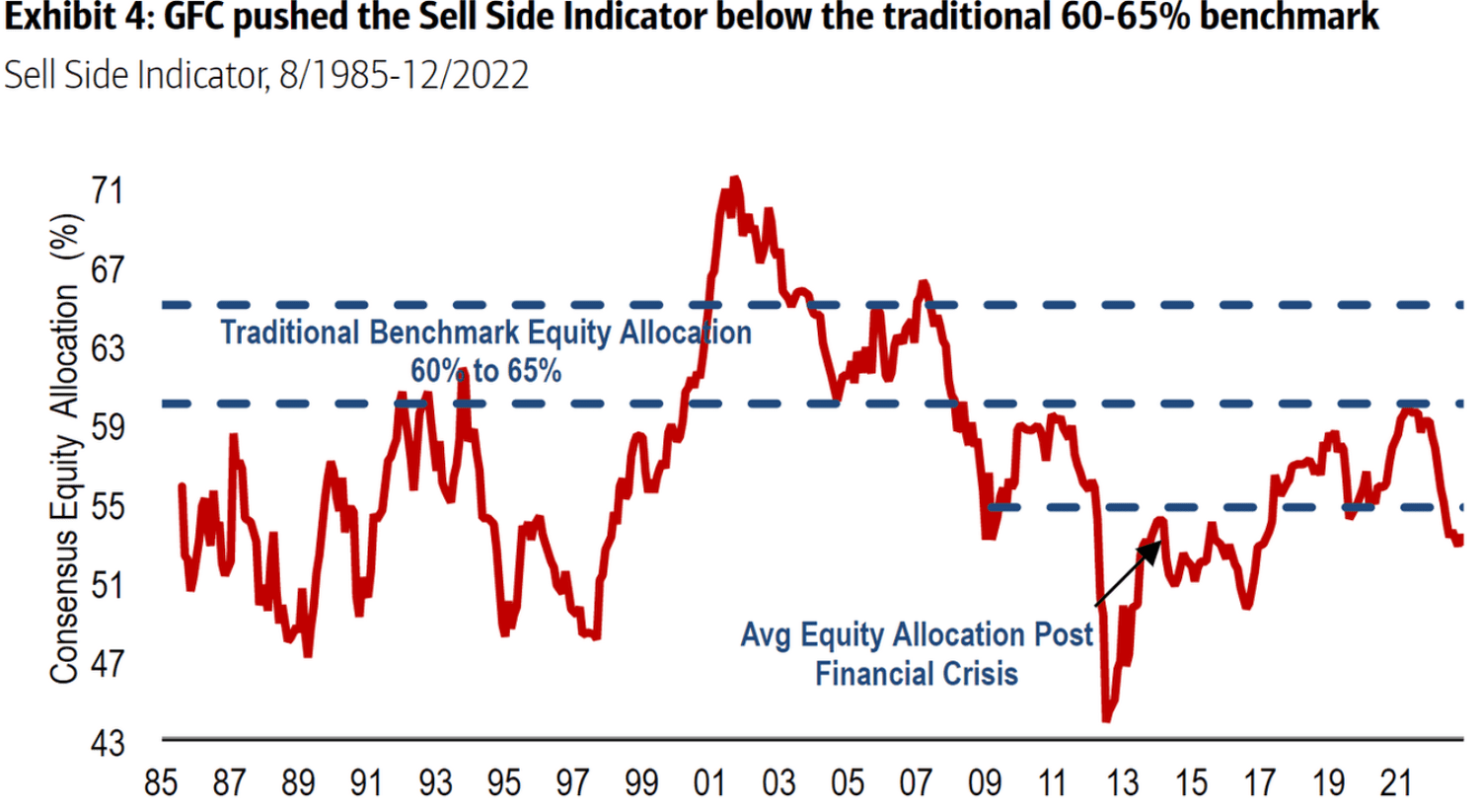 Bof A On Stock Market Valuations A Rationale For Investor Confidence
Apr 26, 2025
Bof A On Stock Market Valuations A Rationale For Investor Confidence
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Why Current Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Reason To Panic According To Bof A
Apr 26, 2025
Why Current Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Reason To Panic According To Bof A
Apr 26, 2025 -
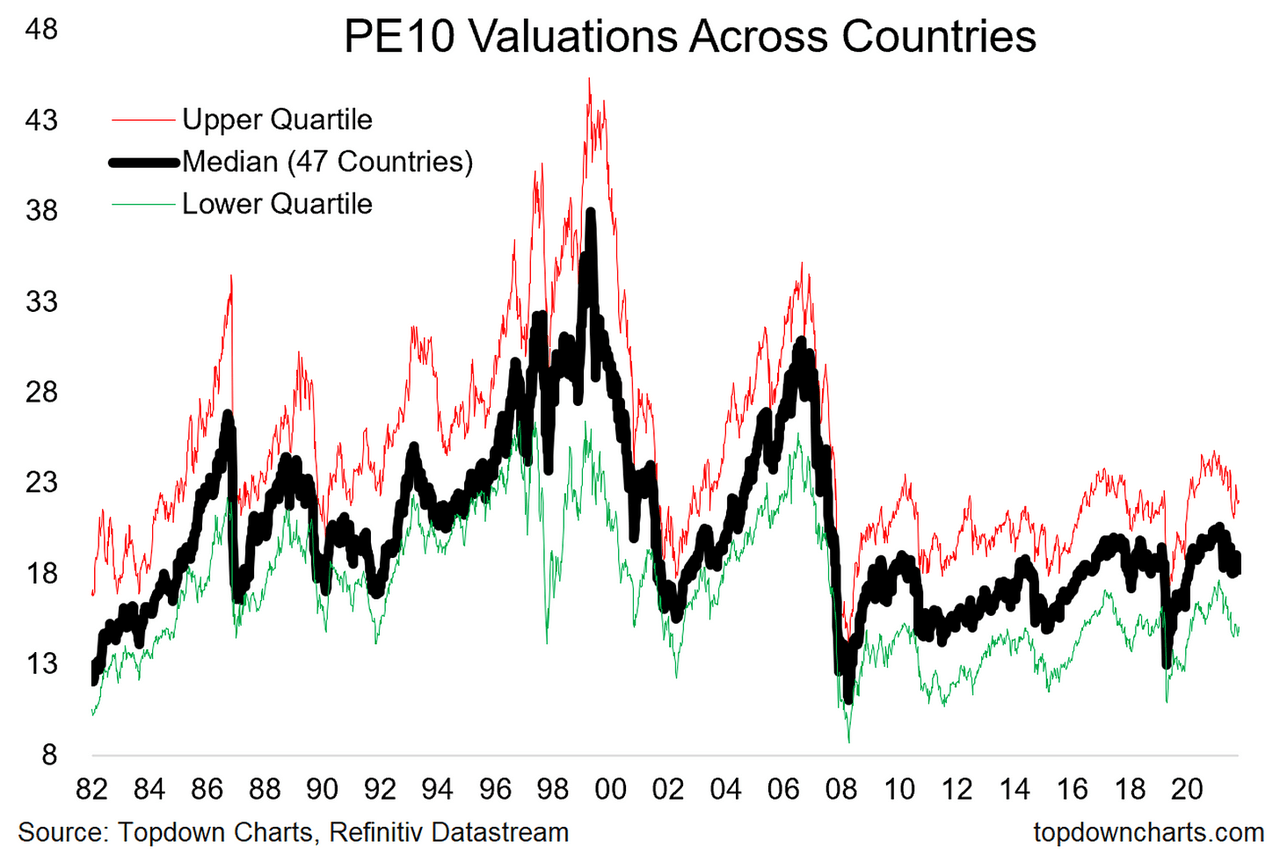 Understanding Stock Market Valuations Bof As Argument For Calm
Apr 26, 2025
Understanding Stock Market Valuations Bof As Argument For Calm
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Bof A Reassures Investors Why High Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Threat
Apr 26, 2025
Bof A Reassures Investors Why High Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Threat
Apr 26, 2025
