Taiwan's Energy Transition: LNG Takes Center Stage After Nuclear Closure
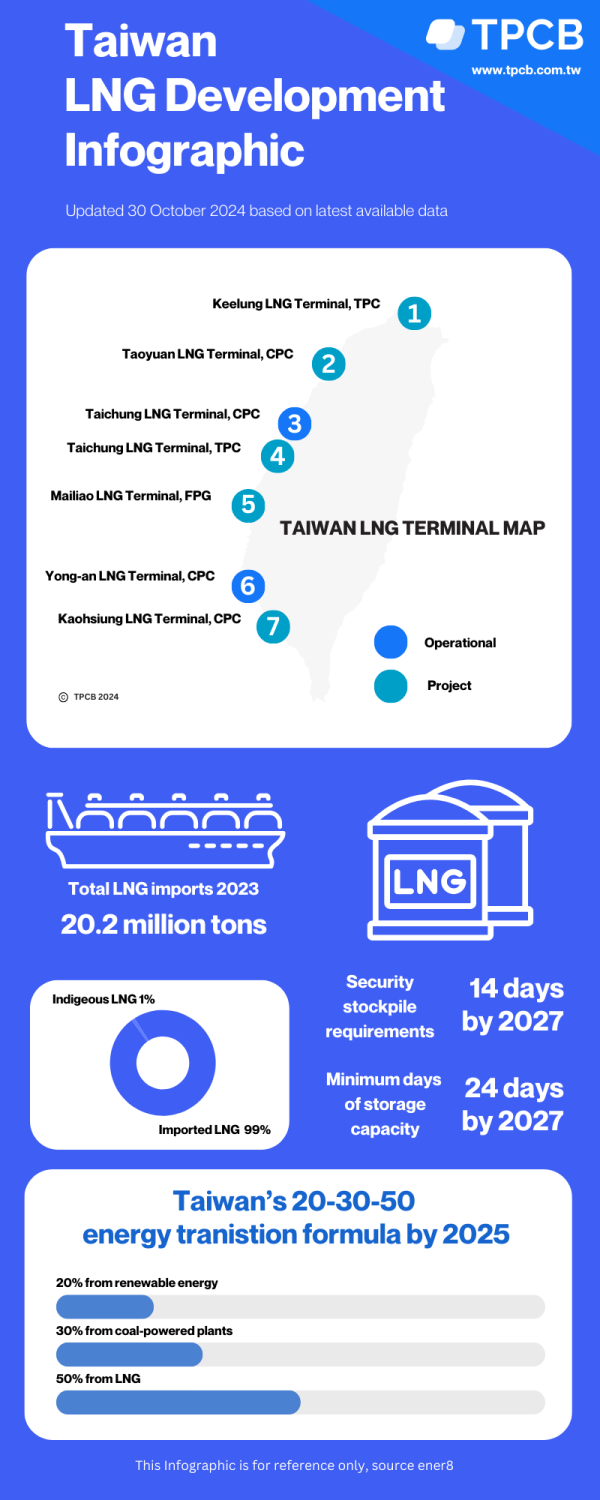
Table of Contents
The Phasedown of Nuclear Power in Taiwan
Taiwan's decision to phase out nuclear power is a multifaceted issue driven by a confluence of factors. The "nuclear phase-out" policy, stemming from a combination of public safety concerns following the Fukushima Daiichi disaster and growing anti-nuclear sentiment, has significantly altered the country's energy landscape. This policy, formalized through Taiwan's energy policy, aims to decommission all nuclear power plants by a specific timeline. This has created a substantial energy supply gap that needs to be filled.
-
Timeline of nuclear plant closures: A phased approach is underway, with specific closure dates for each of Taiwan's nuclear power plants, creating a clear roadmap for the transition. However, delays are possible.
-
Key arguments for and against nuclear power in the public discourse: Proponents highlight nuclear power's reliability and low carbon emissions, while opponents emphasize safety risks, radioactive waste disposal, and the long-term costs associated with decommissioning.
-
Impact on energy supply and demand: The closure of nuclear plants has inevitably increased reliance on other energy sources, particularly LNG, to meet the nation's electricity demand. This increased demand has implications for energy security and pricing.
LNG: Filling the Energy Gap
In the wake of the nuclear phase-out, LNG has emerged as a crucial bridging fuel, filling the immediate energy gap. Taiwan's increased reliance on "LNG imports" necessitates substantial investment in energy infrastructure. The nation is rapidly expanding its LNG import capacity and building new "natural gas pipelines" and terminals. However, this reliance on LNG as a transition fuel isn't without its drawbacks.
-
Growth in LNG import capacity: New LNG terminals and storage facilities are being constructed to accommodate the rising demand for imported liquefied natural gas.
-
Investment in new LNG terminals and pipelines: This large-scale infrastructure development is essential for the efficient import and distribution of LNG across the island.
-
Price volatility and energy security implications: Fluctuations in global LNG prices pose a significant challenge, impacting energy costs and potentially threatening energy security if Taiwan becomes overly reliant on a single supplier.
Challenges in Taiwan's LNG-Centric Transition
While LNG offers a solution to the immediate energy needs, a heavy reliance on it presents challenges to "Taiwan's Energy Transition." The primary concerns revolve around "energy security," "geopolitical risks," and the environmental impact.
-
Vulnerability to global LNG price spikes: Price volatility in the global LNG market creates uncertainty and potential economic strain for Taiwan.
-
Dependence on specific supplier nations: Over-reliance on a limited number of LNG suppliers exposes Taiwan to geopolitical risks and potential supply disruptions.
-
Environmental impact of LNG combustion (greenhouse gas emissions): Although cleaner than coal, LNG combustion still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, hindering Taiwan's long-term sustainability goals.
The Role of Renewable Energy Sources
To mitigate the risks associated with LNG dependence, Taiwan must aggressively pursue the development of "renewable energy" sources. The government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment, aiming to diversify the "energy mix" and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Government targets for renewable energy deployment: Ambitious targets have been set for solar power, wind energy, and hydropower generation, aiming for a significant increase in renewable energy's contribution to the national energy supply.
-
Successes and challenges of renewable energy integration into the grid: Integrating intermittent renewable sources into the existing grid requires substantial upgrades and smart grid technologies.
-
Investment in renewable energy infrastructure: Large investments are required in renewable energy infrastructure, including solar farms, wind farms, and energy storage solutions.
Conclusion: Securing Taiwan's Energy Future Through Strategic Transition
Taiwan's "energy transition" is a complex undertaking. While LNG plays a crucial bridging role in filling the energy gap left by the nuclear phase-out, the long-term success of this transition depends critically on the rapid development and integration of renewable energy sources. Addressing the challenges of "LNG price volatility," securing diverse energy supplies, and minimizing the environmental impact are essential. The path forward requires continued investment in renewable energy infrastructure, smart grid technologies, and a robust energy policy that balances energy security, economic stability, and environmental sustainability. We encourage further research and discussion on the specific aspects of Taiwan's energy transition – from refining LNG infrastructure development strategies to accelerating renewable energy investment – to ensure a sustainable and secure energy future for Taiwan.

Featured Posts
-
 Abn Amro Analyse Van De Aex Prestatie Na Kwartaalcijfers
May 21, 2025
Abn Amro Analyse Van De Aex Prestatie Na Kwartaalcijfers
May 21, 2025 -
 Groeiend Autobezit Stimuleert Occasionmarkt Abn Amro Cijfers
May 21, 2025
Groeiend Autobezit Stimuleert Occasionmarkt Abn Amro Cijfers
May 21, 2025 -
 Peppa Pigs Parents Throw Gender Reveal Party A New Baby Arrives
May 21, 2025
Peppa Pigs Parents Throw Gender Reveal Party A New Baby Arrives
May 21, 2025 -
 Will The Trans Australia Run World Record Be Broken
May 21, 2025
Will The Trans Australia Run World Record Be Broken
May 21, 2025 -
 Gender Reveal Mummy Pig Chooses A London Landmark
May 21, 2025
Gender Reveal Mummy Pig Chooses A London Landmark
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Explaining The Significant Drop In 2025
May 21, 2025
D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Explaining The Significant Drop In 2025
May 21, 2025 -
 The 2025 Plunge Of D Wave Quantum Qbts Causes And Implications
May 21, 2025
The 2025 Plunge Of D Wave Quantum Qbts Causes And Implications
May 21, 2025 -
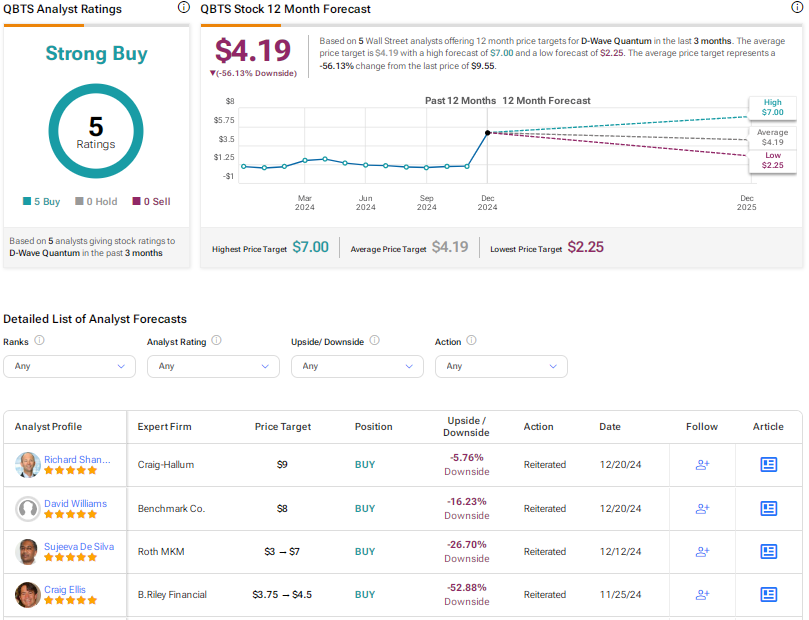 2025 D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Performance Factors Contributing To The Fall
May 21, 2025
2025 D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Performance Factors Contributing To The Fall
May 21, 2025 -
 D Wave Quantum Inc Qbts Analyzing The 2025 Stock Market Performance
May 21, 2025
D Wave Quantum Inc Qbts Analyzing The 2025 Stock Market Performance
May 21, 2025 -
 Understanding The D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Drop In 2025
May 21, 2025
Understanding The D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Drop In 2025
May 21, 2025
