Why Stretched Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Cause For Alarm (According To BofA)
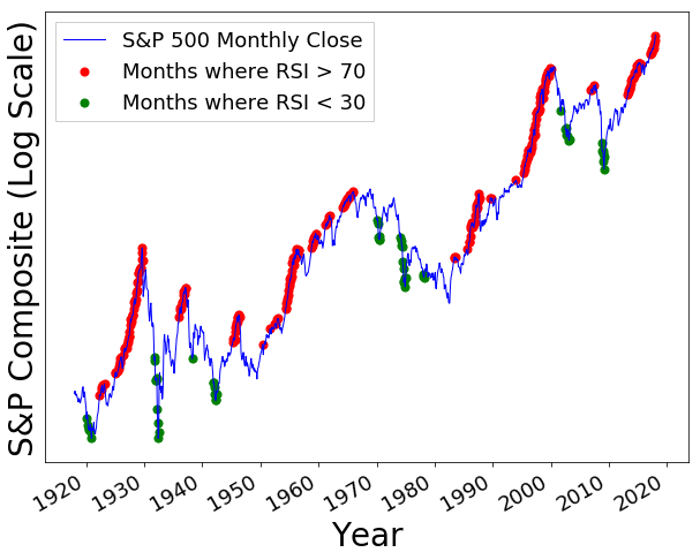
Table of Contents
BofA's Rationale: Why High Valuations Don't Necessarily Signal an Imminent Crash
BofA's assessment hinges on several key factors that, they argue, mitigate the risks associated with seemingly high valuations. These factors paint a more nuanced picture than a simple "overvalued" label suggests.
The Role of Low Interest Rates
Historically low interest rates play a crucial role in justifying higher price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios. The inverse relationship between interest rates and stock valuations is well-established.
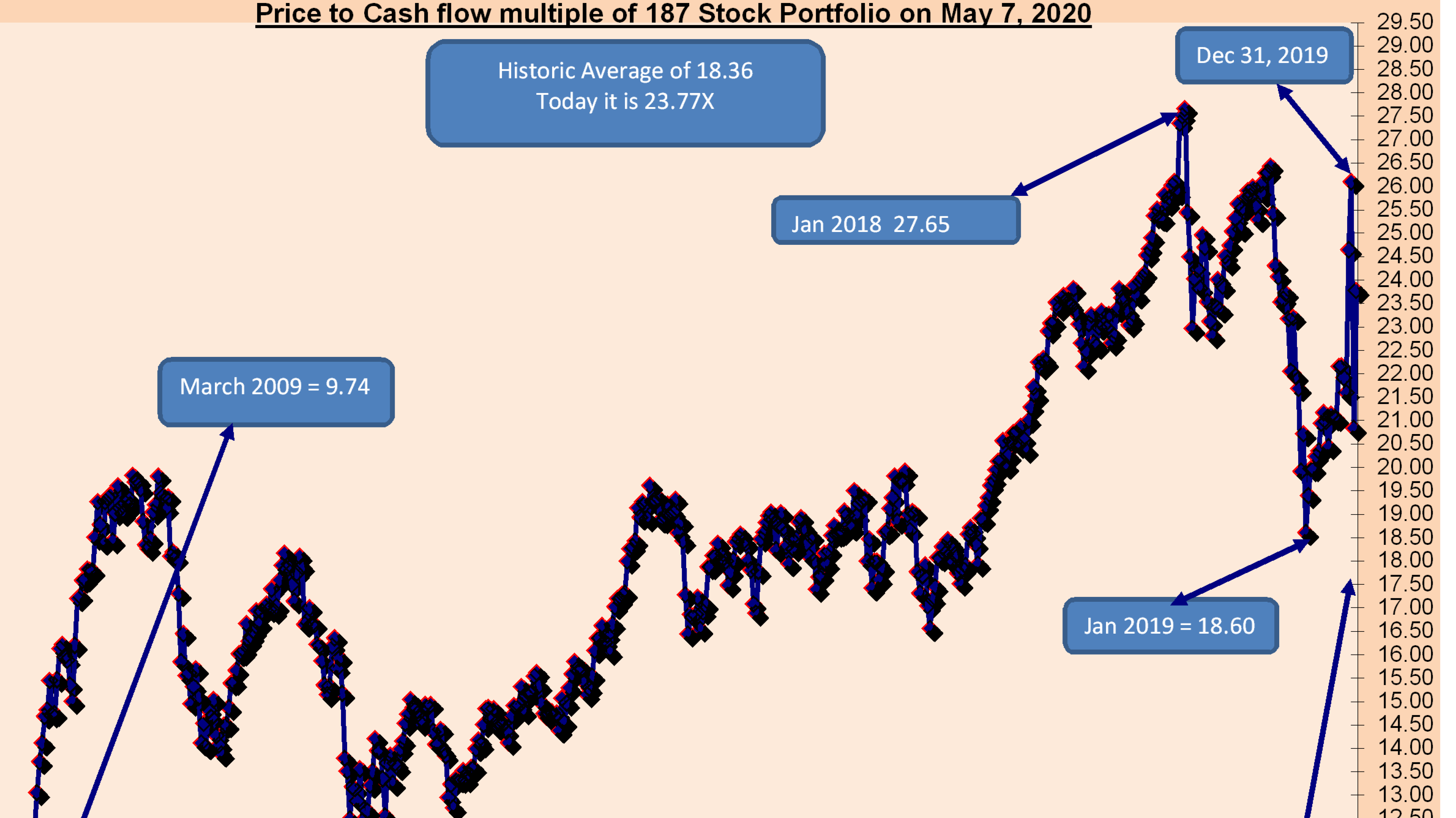
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Models: DCF models, a cornerstone of valuation analysis, heavily rely on discount rates. Lower interest rates translate to lower discount rates, making future cash flows more valuable in present terms. This directly inflates the present value of a company's future earnings, thus justifying higher stock prices. For example, a company with projected earnings of $10 per share over the next five years will have a significantly higher present value using a 2% discount rate (reflecting low interest rates) compared to a 5% discount rate (reflecting higher interest rates).
- Impact on Bond Yields: Low interest rates make bonds less attractive, driving investors towards higher-yielding assets, including equities. This increased demand for stocks further pushes up valuations.
- BofA's Data: BofA's research consistently highlights the impact of low rates on equity valuations, often citing historical data demonstrating this correlation.
Strong Corporate Earnings and Profitability
Robust earnings growth is another pillar supporting BofA's view. The current market isn't simply inflated speculation; it's fueled by solid corporate performance.
- Economic Indicators: Positive economic indicators like strong GDP growth and robust consumer spending contribute to corporate profitability. This positive economic backdrop fuels business expansion and increased earnings, validating higher stock prices.
- Sectoral Strength: Certain sectors, such as technology and healthcare, show exceptional earnings growth, further strengthening the overall market's financial foundation. BofA's sector analysis regularly highlights these strong performers.
- Visualizing Growth: [Insert chart or graph here visualizing earnings growth data from a reputable source, ideally referencing BofA's research].
Technological Innovation and Long-Term Growth Potential
Technological advancements are a key driver of future earnings, significantly influencing market valuations. BofA emphasizes the long-term growth potential fueled by innovation.
- Disruptive Technologies: The emergence of AI, cloud computing, and other disruptive technologies is creating new markets and transforming existing ones. Companies at the forefront of these innovations often command higher valuations due to their future growth prospects.
- Growth at a Reasonable Price (GARP): BofA likely uses GARP investing strategies, focusing on companies exhibiting strong growth potential alongside relatively reasonable valuations. This approach acknowledges high valuations but prioritizes companies with sustainable growth trajectories.
- Examples: Companies like [mention specific examples of companies benefiting from technological innovation] demonstrate the potential for sustained growth even within a high-valuation environment.
Addressing Concerns about Market Bubbles
While acknowledging the possibility of overvaluation, BofA distinguishes between speculative bubbles and fundamentally driven valuations.
- Fundamental Analysis: BofA's approach emphasizes fundamental analysis, examining company financials and assessing their intrinsic value rather than relying solely on market sentiment.
- Risk Assessment: BofA employs sophisticated risk assessment models to identify potential vulnerabilities within the market, distinguishing between sustainable growth and speculative bubbles.
- Alternative Valuation Metrics: Beyond P/E ratios, BofA likely utilizes other metrics such as Price-to-Sales ratios and PEG ratios (Price/Earnings to Growth) to gain a more holistic understanding of valuation.
Understanding BofA's Investment Strategy in a High-Valuation Environment
BofA's investment strategy in this environment focuses on selectivity and risk management.
Selective Stock Picking
BofA doesn't advocate for indiscriminate investment in a high-valuation market. Instead, they emphasize carefully selecting undervalued companies within specific sectors.
- Stock Picking Criteria: Their selection criteria likely involve rigorous fundamental analysis, focusing on strong balance sheets, sustainable competitive advantages, and promising growth trajectories.
- Sector Focus: BofA likely favors sectors exhibiting resilience and continued growth potential, even amidst broader market uncertainty.
- Examples: [mention specific examples of stocks or sectors favored by BofA, linking to relevant research if possible].
Diversification and Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial in a potentially volatile market. BofA's strategy emphasizes diversification and strategic risk mitigation.
- Portfolio Diversification: Diversifying across asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) helps mitigate risk by reducing exposure to any single sector or market segment.
- Asset Allocation: Strategic asset allocation, based on risk tolerance and investment goals, is key to managing volatility.
- Hedging Techniques: Employing hedging strategies can further mitigate downside risk, protecting portfolios during periods of market uncertainty.
- Long-Term Horizon: Maintaining a long-term investment horizon is essential; short-term market fluctuations should not dictate long-term investment decisions.
Navigating Stretched Stock Market Valuations with Confidence
In conclusion, while stretched stock market valuations are a legitimate concern, BofA's analysis suggests that they don't automatically signal an impending crash. Low interest rates, strong corporate earnings, technological innovation, and a strategic investment approach are factors that support their view. High valuations are not inherently bad; it's how you approach them that matters. Remember that understanding the nuances of stretched stock market valuations is key. Don't let fear drive your decisions; instead, leverage BofA's insights to develop a well-informed investment strategy tailored to your risk tolerance and financial goals. Conduct your own thorough research, consult with a qualified financial advisor, and make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the market and your own circumstances. Don't let fear of high valuations paralyze you—use this information to navigate the market effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 2000 Mlb Season Yankees Win Over Royals Detailed In Diary Entry
Apr 28, 2025
2000 Mlb Season Yankees Win Over Royals Detailed In Diary Entry
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Hollywood Production Grinds To Halt Amidst Joint Actors And Writers Strike
Apr 28, 2025
Hollywood Production Grinds To Halt Amidst Joint Actors And Writers Strike
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Addressing Investor Concerns Bof A On High Stock Market Valuations
Apr 28, 2025
Addressing Investor Concerns Bof A On High Stock Market Valuations
Apr 28, 2025 -
 5 Key Dos And Don Ts To Succeed In The Private Credit Industry
Apr 28, 2025
5 Key Dos And Don Ts To Succeed In The Private Credit Industry
Apr 28, 2025 -
 X Corporations Financial Transformation Insights From The Recent Debt Sale
Apr 28, 2025
X Corporations Financial Transformation Insights From The Recent Debt Sale
Apr 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Red Sox Roster Update Outfielders Return Impacts Lineup Casas Moves Down
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Roster Update Outfielders Return Impacts Lineup Casas Moves Down
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Boston Red Sox Adjust Lineup Casas Lowered Outfielder Back In Action
Apr 28, 2025
Boston Red Sox Adjust Lineup Casas Lowered Outfielder Back In Action
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Red Sox Lineup Changes Triston Casas Slide And Outfield Return
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Lineup Changes Triston Casas Slide And Outfield Return
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Red Sox Lineup Shakeup Casas Demoted Struggling Outfielder Returns
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Lineup Shakeup Casas Demoted Struggling Outfielder Returns
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Red Sox Outfielder Breakout Could This Player Be The Next Jarren Duran
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Outfielder Breakout Could This Player Be The Next Jarren Duran
Apr 28, 2025
