BOJ Governor Ueda Addresses Risks Of Long-Yield Increase
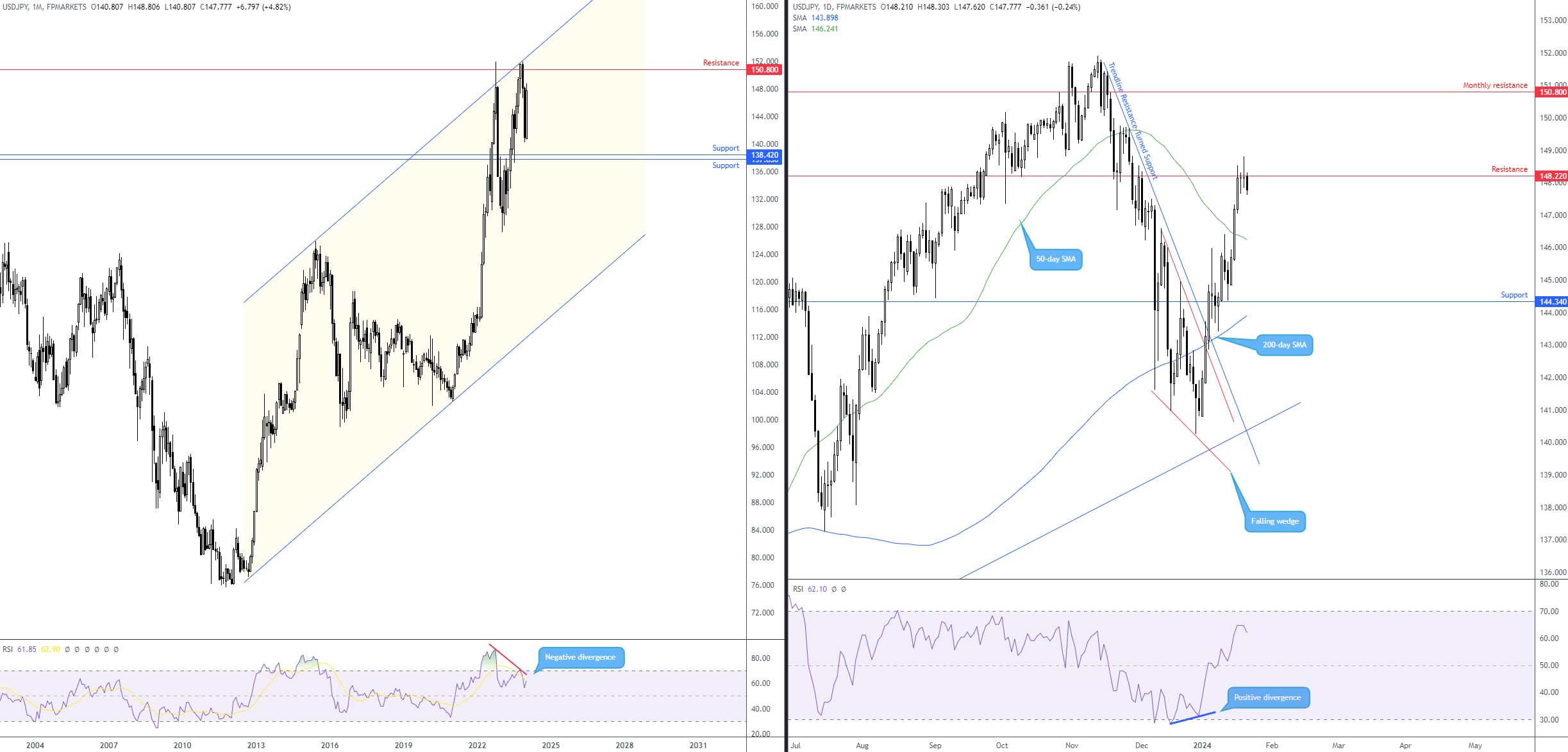
Table of Contents
Ueda's Concerns Regarding a Sustained Long-Yield Increase
Governor Ueda highlighted several potential negative consequences of a sustained increase in Japanese long-term interest rates. He expressed worry that such an increase could significantly destabilize the delicate balance of the Japanese economy. His concerns primarily revolved around the following:
-
Potential impact on economic growth: A sharp rise in long-term yields could dampen economic growth by increasing borrowing costs for businesses, leading to reduced investment and potentially hindering expansion. This is particularly relevant in Japan, given its already sluggish growth rate.
-
Increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers: Higher interest rates translate directly into increased borrowing costs for both businesses and consumers. This can curb spending and investment, impacting overall economic activity and potentially slowing down recovery from previous economic challenges. This impacts mortgage rates and corporate debt servicing.
-
Risk of destabilizing financial markets: A rapid and uncontrolled rise in long-term yields can lead to volatility in the Japanese government bond (JGB) market and broader financial markets. This instability can create uncertainty and hinder economic confidence.
-
Pressure on the Japanese yen: Rising yields can attract foreign investment into Japan, strengthening the yen. While a stronger yen can be beneficial in some aspects, it can also negatively impact Japanese exports, making them more expensive in global markets. The interplay between rising yields and currency fluctuations is a complex issue.
-
Implications for the BOJ's yield curve control policy: The rise in long-term yields directly challenges the BOJ's yield curve control (YCC) policy, which aims to keep long-term interest rates at specific targets. Maintaining this policy in the face of rising yields requires significant intervention and raises questions about its long-term effectiveness.
Analysis of the Factors Contributing to the Potential Long-Yield Increase
Several interconnected factors are contributing to the potential for a sustained long-yield increase in Japan:
-
Global inflation and rising US Treasury yields: Global inflationary pressures and the subsequent rise in US Treasury yields are exerting upward pressure on Japanese long-term interest rates. Increased global demand for safer assets can affect the JGB market.
-
Changes in investor sentiment towards Japanese government bonds (JGBs): Investor sentiment plays a crucial role. A shift in confidence towards JGBs, possibly due to changing economic forecasts or perceptions of risk, can influence demand and consequently, yields.
-
Potential for a shift in the BOJ's monetary policy stance: Speculation about a potential shift in the BOJ's monetary policy, away from its ultra-loose stance, is a significant factor influencing investor expectations and long-term yields.
-
Speculation about future interest rate hikes: Market speculation about the possibility of future interest rate hikes by the BOJ contributes to expectations of rising yields, influencing current market behavior.
-
Impact of the strengthening US dollar: A strong US dollar can put downward pressure on the Japanese yen, potentially leading to increased demand for higher-yielding assets, including Japanese government bonds, indirectly influencing their yields.
The BOJ's Response and Potential Policy Adjustments
The BOJ's response to the rising long-term yields will be crucial in determining the future trajectory of the Japanese economy. Currently, the BOJ continues to maintain its yield curve control (YCC) policy. However, potential future adjustments could include:
-
Continued yield curve control (YCC)? The continued use of YCC will depend heavily on how long the current pressures persist and the overall economic outlook.
-
Potential adjustments to the YCC target range: Adjusting the target range for long-term yields could be a significant policy move, signaling a potential shift in monetary policy stance.
-
Increased bond purchases to suppress yields: The BOJ could increase its bond purchases to directly suppress the rise in long-term yields, but this approach could face challenges if market forces exert continued upward pressure.
-
Communication strategies to manage market expectations: Clear communication and guidance to manage market expectations are crucial in mitigating uncertainty and preventing excessive volatility.
-
Forward guidance on future monetary policy: Providing forward guidance on future policy decisions could help shape market expectations and reduce uncertainty.
Market Reactions and Investor Sentiment
The market's reaction to Governor Ueda's statements and the overall investor sentiment have been closely watched. Following the announcement:
-
Movements in the JGB market following the announcement: The JGB market experienced increased volatility, reflecting uncertainty about the future direction of interest rates and BOJ policy.
-
Changes in the yen's exchange rate: The yen's exchange rate showed fluctuations in response to the changing expectations regarding interest rates and monetary policy.
-
Shifts in investor confidence in the Japanese economy: Investor confidence in the Japanese economy has shown some degree of sensitivity to the developments concerning long-term yields and potential policy shifts.
-
Impact on Japanese stock markets: Japanese stock markets have also shown some sensitivity to the developments surrounding long-term interest rates and BOJ policy, although the relationship is complex and influenced by other factors.
Conclusion
Governor Ueda's concerns regarding a sustained long-yield increase are valid and highlight significant risks to the Japanese economy. The factors contributing to this potential increase, from global inflation to changing investor sentiment and the potential adjustments to the BOJ's YCC policy, create a complex and dynamic situation. Understanding the interplay between these factors is crucial for navigating the current uncertainty. The impact of rising Japanese long-term interest rates on economic growth, inflation, the yen's exchange rate, and global financial markets requires careful monitoring. The BOJ's response and potential policy adjustments will play a critical role in determining the ultimate impact of this trend.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving situation surrounding the long-yield increase and the BOJ's monetary policy decisions. Regularly check reputable financial news sources for updates on Japanese long-term interest rates (JGB yields) and their potential impact on the Japanese economy and global markets. Understanding the risks associated with a sustained long-yield increase is crucial for informed investment decisions and sound economic analysis.

Featured Posts
-
 Jacqie Rivera And More Discovering The Next Generation Of Latin Music
May 29, 2025
Jacqie Rivera And More Discovering The Next Generation Of Latin Music
May 29, 2025 -
 The Rising Stars Latin Women Dominating The Music Scene In 2025
May 29, 2025
The Rising Stars Latin Women Dominating The Music Scene In 2025
May 29, 2025 -
 Addressing Toxicity Ubisofts Plan For A Safer Assassins Creed Shadows Of London
May 29, 2025
Addressing Toxicity Ubisofts Plan For A Safer Assassins Creed Shadows Of London
May 29, 2025 -
 Analisis Del Partido Real Madrid 3 2 Celta Vigo Tres Preguntas Y Respuestas
May 29, 2025
Analisis Del Partido Real Madrid 3 2 Celta Vigo Tres Preguntas Y Respuestas
May 29, 2025 -
 Hudsons Bay Announces Mass Layoffs And Store Closures
May 29, 2025
Hudsons Bay Announces Mass Layoffs And Store Closures
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Receta Facil De Lasana De Calabacin Paso A Paso Pablo Ojeda Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025
Receta Facil De Lasana De Calabacin Paso A Paso Pablo Ojeda Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025 -
 La Mejor Receta De Lasana De Calabacin Segun Pablo Ojeda Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025
La Mejor Receta De Lasana De Calabacin Segun Pablo Ojeda Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025 -
 Major Search Operation For Missing Child In River Thames
May 31, 2025
Major Search Operation For Missing Child In River Thames
May 31, 2025 -
 Couts De La Foire Au Jambon 2025 Une Situation Financiere Preoccupante A Bayonne
May 31, 2025
Couts De La Foire Au Jambon 2025 Une Situation Financiere Preoccupante A Bayonne
May 31, 2025 -
 Receta De Lasana De Calabacin De Pablo Ojeda Facil Y Deliciosa Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025
Receta De Lasana De Calabacin De Pablo Ojeda Facil Y Deliciosa Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025
