Otter Conservation In Wyoming: Reaching A Turning Point

Table of Contents
The primary threats to Wyoming's otter populations include habitat loss from development and agriculture, pollution from industrial runoff and agricultural chemicals, the impacts of climate change on water resources, entanglement in human debris, disease, and predation.
The Current State of Otter Populations in Wyoming
Understanding the current status of otter populations is crucial for effective conservation. Historically, North American River Otters (Lontra canadensis) were widespread across Wyoming, inhabiting suitable riparian habitats along rivers and streams. However, due to various factors (detailed below), their numbers have fluctuated significantly. While precise population data is still being collected through ongoing surveys and monitoring programs, certain regions show signs of thriving populations, while others reveal cause for concern. Population density maps, created using data from scat surveys and camera trapping, are essential tools in tracking these variations across the state.
- Specific otter species present in Wyoming: Primarily the North American River Otter.
- Geographic distribution within the state: Otters are found along major river systems, including the Snake, Green, and Yellowstone Rivers, and their tributaries. However, their distribution is patchy, with some areas showing higher densities than others.
- Population trends: While some areas show increasing trends, others exhibit stable or declining populations, indicating a need for targeted conservation efforts.
- Key threats affecting current populations: Habitat degradation, water pollution, and climate change are consistently cited as primary factors.
Major Threats to Otter Survival in Wyoming
Several factors contribute to the decline of otter populations in Wyoming. These threats interact in complex ways, exacerbating the challenges faced by these animals.
- Habitat loss: Development, including dam construction and agricultural expansion, leads to fragmentation and loss of crucial riparian habitats. This restricts otter movement, reduces food availability, and limits breeding opportunities. (Image: A graphic showing habitat loss due to development).
- Water pollution: Industrial runoff containing heavy metals and pesticides, as well as agricultural chemicals, contaminate water sources, impacting otter health and potentially causing reproductive problems. (Image: An illustration depicting water pollution from industrial sources).
- Climate change: Altered precipitation patterns, increased drought frequency, and changes in water temperature negatively impact water availability and quality, affecting the otters' prey base and overall survival.
- Entanglement in fishing gear and other human debris: Otters can become entangled in discarded fishing lines, nets, and other trash, leading to injuries, drowning, or starvation.
- Disease: Outbreaks of diseases can severely impact otter populations, particularly in areas with high population densities or degraded habitats.
- Predation: While natural predation occurs, habitat changes can increase the vulnerability of otters to predators like coyotes and bobcats.
Successful Conservation Strategies and Initiatives
Despite the challenges, several successful conservation strategies are underway in Wyoming. These initiatives highlight the power of collaboration between government agencies, NGOs, and local communities.
- Habitat restoration projects: Efforts are underway to restore degraded riparian habitats, including replanting native vegetation, improving water flow, and creating buffer zones to protect against pollution.
- Water quality improvement programs: Initiatives aim to reduce pollution from industrial and agricultural sources, improving the overall health of aquatic ecosystems and thus benefiting otter populations.
- Public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives: Educational outreach programs raise awareness about otter conservation and promote responsible behaviors near waterways.
- Research projects aimed at understanding otter behavior and ecology: Scientific research provides vital information for developing effective conservation strategies.
- Monitoring programs to track otter populations: Regular monitoring allows for the assessment of population trends and the effectiveness of conservation measures. These programs often employ non-invasive methods like scat analysis and camera trapping.
Future Directions for Otter Conservation in Wyoming
To ensure the long-term survival of otters in Wyoming, further actions are crucial. A multi-pronged approach is needed, combining research, policy, and public engagement.
- Strengthening existing regulations to protect otter habitats: Existing laws and regulations need to be strengthened and enforced to better protect riparian areas from development and pollution.
- Implementing stricter controls on pollution sources: Stronger regulations are required to limit pollution from industrial and agricultural sources, improving water quality and otter habitat.
- Investing in further research to understand and address emerging threats: Continued research is needed to understand the impacts of climate change and other emerging threats on otters.
- Expanding public awareness and educational programs: Increased public awareness and education can promote responsible recreational activities and support for conservation efforts.
- Promoting responsible recreational activities in otter habitats: Promoting responsible angling practices, reducing littering near water bodies, and avoiding disturbances to otter habitats are crucial.
Conclusion: The Future of Otter Conservation in Wyoming
Otter Conservation in Wyoming requires a concerted and sustained effort. This article has highlighted the current status of otter populations, the major threats they face, and the successful initiatives underway. The future of these fascinating animals depends on continued monitoring, collaborative research, strong policy implementation, and increased public engagement. We must act decisively to protect these vital components of Wyoming's ecosystems. Get involved! Support Wyoming otter conservation programs by donating to organizations like [Link to relevant organization 1], volunteering your time with [Link to relevant organization 2], or contacting your legislators to advocate for stronger environmental protections that safeguard Wyoming's otters and their habitats. Let's work together to ensure a future where these playful creatures continue to thrive in the beautiful landscapes of Wyoming. Protecting Wyoming otters is a shared responsibility, and your involvement can make a real difference.

Featured Posts
-
 Abn Amro Analyse Van De Stijging In Occasionverkopen En De Rol Van Autobezit
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Analyse Van De Stijging In Occasionverkopen En De Rol Van Autobezit
May 22, 2025 -
 Potential Canada Post Strike Preparing Your Business For Disruptions
May 22, 2025
Potential Canada Post Strike Preparing Your Business For Disruptions
May 22, 2025 -
 Should Investors Worry About Elevated Stock Market Valuations Bof A Weighs In
May 22, 2025
Should Investors Worry About Elevated Stock Market Valuations Bof A Weighs In
May 22, 2025 -
 G 7 Finance Ministers Prioritize Harmony Despite Us Trade Disputes
May 22, 2025
G 7 Finance Ministers Prioritize Harmony Despite Us Trade Disputes
May 22, 2025 -
 Second Reintroduced Colorado Gray Wolf Found Dead In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
Second Reintroduced Colorado Gray Wolf Found Dead In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Is Core Weave Stock A Good Investment Current Market Analysis
May 22, 2025
Is Core Weave Stock A Good Investment Current Market Analysis
May 22, 2025 -
 Core Weave Stock A Deep Dive Into Recent Developments
May 22, 2025
Core Weave Stock A Deep Dive Into Recent Developments
May 22, 2025 -
 Investment In Core Weave Crwv Understanding Last Weeks Market Activity
May 22, 2025
Investment In Core Weave Crwv Understanding Last Weeks Market Activity
May 22, 2025 -
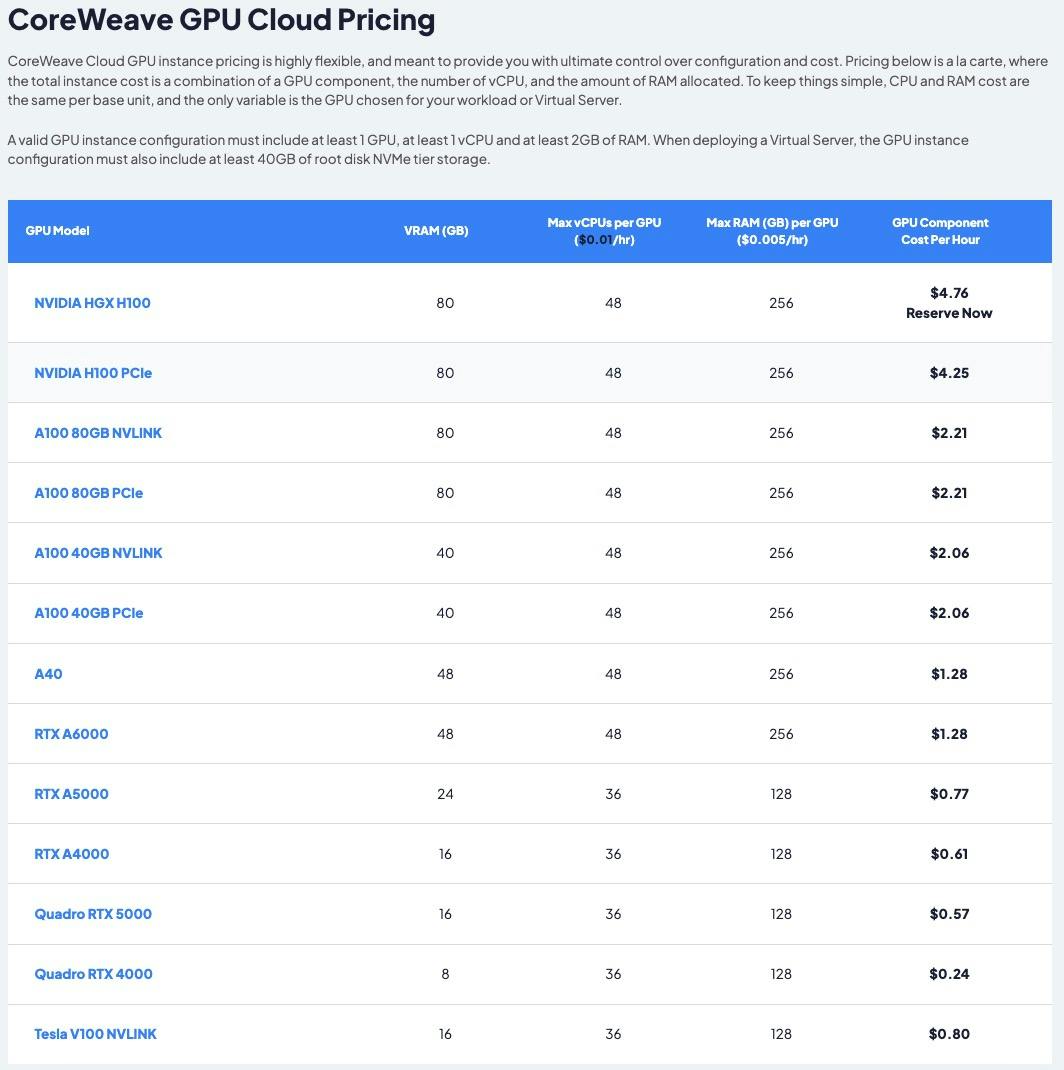 Analyzing The Current State Of Core Weave Stock
May 22, 2025
Analyzing The Current State Of Core Weave Stock
May 22, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Recent Increase In Core Weave Crwv Stock Value
May 22, 2025
Analyzing The Recent Increase In Core Weave Crwv Stock Value
May 22, 2025
